Roman Gerodimos, Bournemouth University
As polls closed in Greece on July 7, with pollsters predicting a convincing victory for the centre-right New Democracy and a defeat for the left-wing Syriza government of Alexis Tsipras, an unusual sense of calm prevailed across the country. Rarely has a Greek election night been so quiet.
New Democracy’s incoming prime minister, Kyriakos Mitsotakis, went out of his way to unite and manage expectations. His supporters were just relieved to have ousted Tsipras. Tsipras himself looked relieved, having managed to reverse his party’s losses at the recent European Parliament elections, to win a respectable 31.5% of the vote, which will allow him to remain as a strong second pole in the system. With 39.9% of the vote, New Democracy will have 158 seats in the Greek parliament, an outright majority.
Smaller parties all put on a happy face for their own internal reasons, with the exception of the neo-Nazi Golden Dawn, which failed to pass the 3% threshold to elect MPs. It looked as if Greece had finally attained what it had been desperately seeking for one long decade: a sense of normalcy.
Exactly ten years ago, in the summer of 2009, the first signs that Greece was in economic trouble started to become apparent. As the markets’ confidence in Greek bonds collapsed, the government turned to the European Union and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Within weeks it had entered a vortex of excruciating negotiations, conditional bailouts and tough austerity measures that went on and on. To an extent these are still going on and, in different forms, are expected to go on for much of the 21st century.
It’s hard to overstate the impact of the crisis and austerity on Greek society. Beyond the obvious effects – unemployment reaching 25%, hundreds of thousands of mostly young and well-educated people leaving the country to seek employment abroad, pensions and public services facing severe cuts – the political system was rattled. One of the two main pillars of the post-1974 system, the centre-left PASOK, collapsed. Far right parties such as Golden Dawn and the xenophobic, homophobic Independent Greeks – entered parliament.
The crisis has been the single biggest challenge to Greece’s survival since World War II. Its root causes, the way Greeks were stereotyped in the world’s media, and the way lenders and successive Greek governments designed and implemented austerity measures, all became sources of collective shame and humiliation. This in turn polarised a political culture that has been historically prone to bouts of instability and violence.
Rise of violence
Tsipras weaponised and normalised this populist narrative of victimhood, pitting the “innocent people” against “the corrupt elites”, including Greece’s EU partners and lenders. As I have shown in my research, this narrative was also used by far-left radical groups to justify revenge and aggression.
Political violence tripled between 2008 and 2018. Far-left violence was 3.5 times bigger in scale than far-right violence, which itself soared. Low-level incidents are a daily occurrence with thousands of them having taken place during the decade of the crisis, especially before Syriza got into power. Radicalisation and extremism have been particularly prominent among young people. While many are politically apathetic, those who do engage tend to do so in radical ways. Golden Dawn drew most of its supporters from the 18-25 age group, while Syriza has consistently topped the polls in that group.
The January and September 2015 victories of Syriza, which governed in alliance with the Independent Greeks, acted as pressure valves that allowed Greek society to vent a lot of its anger and frustration. That radicalism, which was such a prominent element of Greek political culture during the first period of the crisis, gradually ran out of steam.
From January to June 2015, Yanis Varoufakis, the flamboyant poster boy of the “Caviar left”, led catastrophic and slightly surreal negotiations with EU and IMF lenders. These ended up costing Greece billions of euros, triggered a bank run and capital controls, caused it to default on its debts to the IMF and brought it within hours of exiting the Eurozone. Eventually, Tsipras did a U-turn and, in late 2015 began implementing all of the lenders’ requests, effectively showing that there really was no alternative to austerity.
Mitsotakis’s moment
Since being elected leader of New Democracy in 2016, Mitsotakis worked hard to renew his party. In the space of three years, he managed to turn an out of touch, old-school, conservative party into a modern, liberal, social media savvy electoral machine. While banking on his image as a well-educated and professionally successful technocrat who will cut taxes and facilitate foreign direct investment, he also placed strategic emphasis on the youth vote.
He voted in favour of civil partnerships for same-sex couples and spent time meeting with drug addicts in rough parts of Athens. He also carried out a radical renewal of New Democracy’s parliamentary candidates and party workers, promoting many people in their 20s, 30s and 40s. In doing so, he managed to build up support in the crucial 18-24 demographic, reaching 27%-30% in the recent elections, and so ending Syriza’s monopoly on the youth vote.
Whether Greece has really entered a new era of normalcy will become apparent fairly soon. One of the first moves Mitsotakis pledged to take is to scrap the so-called “asylum” law, which forbids police from entering university premises. As a result of the law, urban university campuses have become hotspots of crime, vandalism, drug-dealing and anarchist propaganda and public opinion has recently shifted in favour of taking action. However, far-left groups still carry street credit in universities and in the urban pocket of Exarchia in downtown Athens, where law-and-order has completely collapsed.
On election day in Greece, the only incident that broke the peaceful hum of post-election dinner parties took place there: a previously unknown anarchist group stole and burnt a ballot box, threatened electoral clerks and threw tear gas. What happens at Exarchia over the next few months – whether and how the government decides to enforce the law and how young people and wider society react – will be the best indicator of whether Greece has truly turned the page.
Roman Gerodimos, Associate Professor of Global Current Affairs, Bournemouth University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
 BU2025 sets out ambitious plans and targets for research at BU. In support of these, an exciting new opportunity has been developed.
BU2025 sets out ambitious plans and targets for research at BU. In support of these, an exciting new opportunity has been developed.


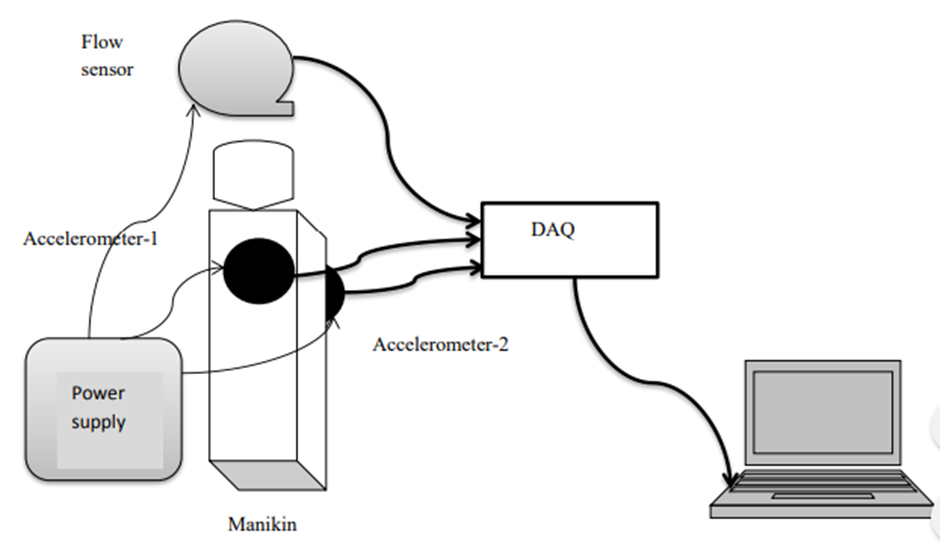
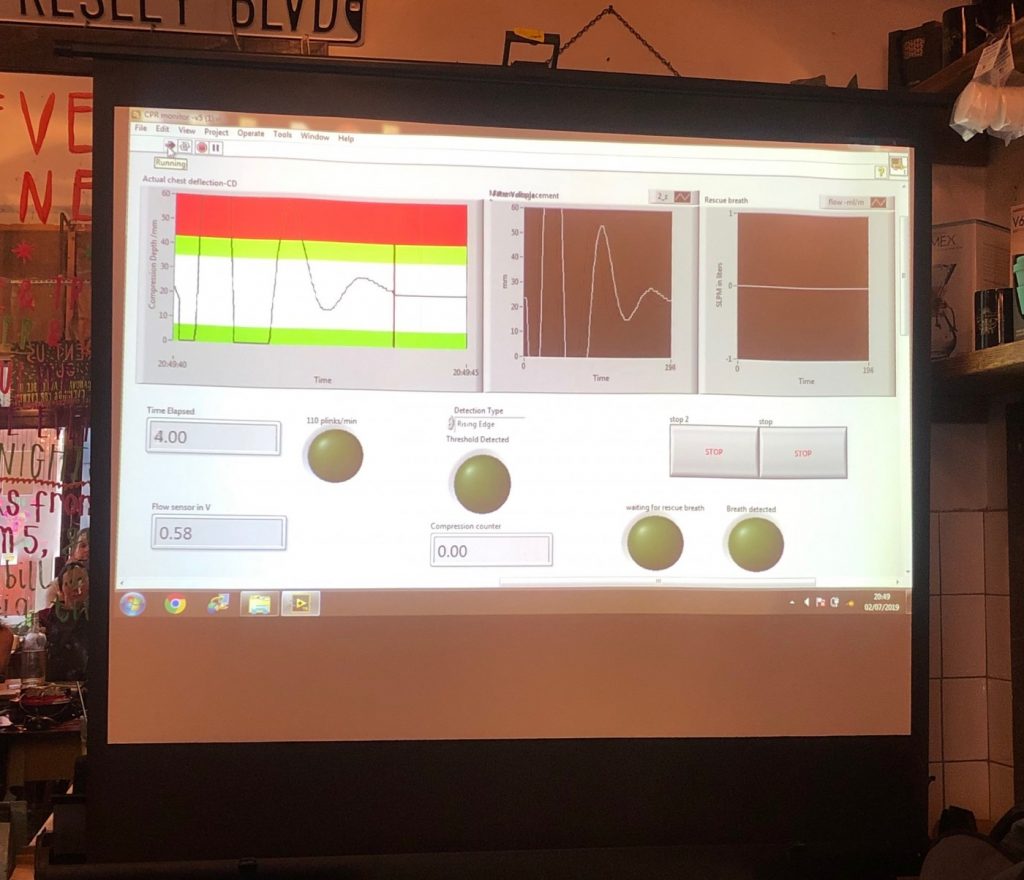






 At Bournemouth University we collaborate with global institutions and organisations through our education, research and practice.
At Bournemouth University we collaborate with global institutions and organisations through our education, research and practice. The Ageing and Dementia Research Centre’s Amanda Adams and Dina Blagden attended the Annual Alzheimer’s Society Conference at the Oval in London last May 2019, and joined Health Education England (HEE) (Jan Zietara: Head of Programme Delivery – South Health Education England, and Chris O’Connor: Consultant Admiral Nurse/HEE Dementia Fellow Health Education England) on the stand. They spoke to a range of people about the
The Ageing and Dementia Research Centre’s Amanda Adams and Dina Blagden attended the Annual Alzheimer’s Society Conference at the Oval in London last May 2019, and joined Health Education England (HEE) (Jan Zietara: Head of Programme Delivery – South Health Education England, and Chris O’Connor: Consultant Admiral Nurse/HEE Dementia Fellow Health Education England) on the stand. They spoke to a range of people about the 

















 Upcoming opportunities for PGRs – collaborate externally
Upcoming opportunities for PGRs – collaborate externally BU involved in new MRF dissemination grant
BU involved in new MRF dissemination grant New COVID-19 publication
New COVID-19 publication MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024 Horizon Europe News – December 2023
Horizon Europe News – December 2023