
Author provided
Matthew Robert Bennett, Bournemouth University and Sally Christine Reynolds, Bournemouth University
Every parent knows the feeling. Your child is crying and wants to go home, you pick them up to comfort them and move faster, your arms tired with a long walk ahead – but you cannot stop now. Now add to this a slick mud surface and a range of hungry predators around you.
That is the story the longest trackway of fossil footprints in the world tells us. Our new discovery, published in Quaternary Science Reviews, comes from White Sands National Park in New Mexico, US, and was made by an international team working in collaboration with staff from the National Park Service.
The footprints were spotted in a dried-up lakebed known as a playa, which contains literally hundreds of thousands of footprints dating from the end of the last ice age (about 11,550 years ago) to sometime before about 13,000 years ago.
Unlike many other known footprint trackways, this one is remarkable for its length – over at least 1.5km – and straightness. This individual did not deviate from their course. But what is even more remarkable is that they followed their own trackway home again a few hours later.

M Bennett, Bournemouth University., Author provided
Each track tells a story: a slip here, a stretch there to avoid a puddle. The ground was wet and slick with mud and they were walking at speed, which would have been exhausting. We estimate that they were walking at over 1.7 metres per second – a comfortable walking speed is about 1.2 to 1.5 metres per second on a flat dry surface. The tracks are quite small and were most likely made by a woman, or possibly an adolescent male.
Mysterious journey
At several places on the outward journey there are a series of small child tracks, made as the carrier set a child down perhaps to adjust them from hip to hip, or for a moment of rest. Judging by the size of the child tracks, they were made by a toddler maybe around two years old or slightly younger. The child was carried outward, but not on the return.
We can see the evidence of the carry in the shape of the tracks. They are broader due to the load, more varied in morphology often with a characteristic “banana shape” – something that is caused by outward rotation of the foot.
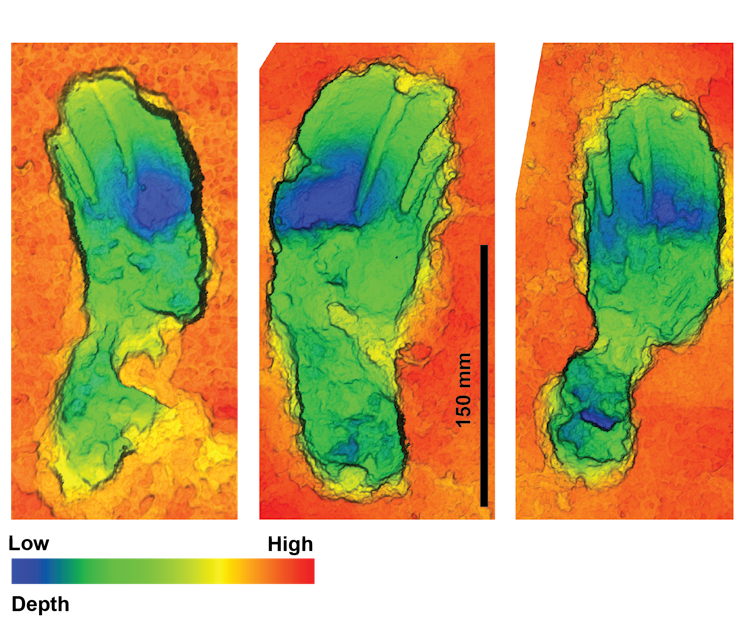
Bournemouth University., Author provided
The tracks of the homeward journey are less varied in shape and have a narrower form. We might even go as far as to tentatively suggest that the surface had probably dried a little between the two journeys.
Dangerous predators
The playa was home to many extinct ice age animals, perhaps hunted to extinction by humans, perhaps not. Tracks of these animals helped determine the age of the trackway.
We found the tracks of mammoths, giant sloths, sabre-toothed cats, dire wolves, bison and camels. We have produced footprint evidence in the past of how these animals may have been hunted. What’s more, research yet to be published tells of children playing in puddles formed in giant sloth tracks, jumping between mammoth tracks and of hunting and butchery.
Between the outward and return journeys, a sloth and a mammoth crossed the outward trackway. The footprints of the return journey in turn cross those animal tracks.
The sloth tracks show awareness of the human passage. As the animal approached the trackway, it appears to have reared-up on its hind legs to catch the scent – pausing by turning and trampling the human tracks before dropping to all fours and making off. It was aware of the danger.
In contrast, the mammoth tracks, at one site made by a large bull, cross the human trackway without deviation, most likely not having noticed the humans.
The trackway tells a remarkable story. What was this individual doing alone and with a child out on the playa, moving with haste? Clearly it speaks to social organisation, they knew their destination and were assured of a friendly reception. Was the child sick? Or was it being returned to its mother? Did a rainstorm quickly come in catching a mother and child off guard? We have no way of knowing and it is easy to give way to speculation for which we have little evidence.
What we can say is that the woman is likely to have been uncomfortable on that hostile landscape, but was prepared to make the journey anyway. So next time you are rushing around in the supermarket with a tired child in your arms, remember that even prehistoric parents shared these emotions.
Matthew Robert Bennett, Professor of Environmental and Geographical Sciences, Bournemouth University and Sally Christine Reynolds, Principal Academic in Hominin Palaeoecology, Bournemouth University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.


 The South West Partnership for Environmental and Economic Prosperity (
The South West Partnership for Environmental and Economic Prosperity (




 The
The 
 From 8th September, the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) are launching a weekly zoom for early career researchers working in the broad field of Paleo sciences.
From 8th September, the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) are launching a weekly zoom for early career researchers working in the broad field of Paleo sciences.




























 FHSS academics teaching in Nepal
FHSS academics teaching in Nepal New weight change BU paper
New weight change BU paper One week to go! | The 16th Annual Postgraduate Research Conference
One week to go! | The 16th Annual Postgraduate Research Conference Geography and Environmental Studies academics – would you like to get more involved in preparing our next REF submission?
Geography and Environmental Studies academics – would you like to get more involved in preparing our next REF submission? Congratulations to three former BU staff
Congratulations to three former BU staff MSCA Staff Exchanges 2024 Call – internal deadline
MSCA Staff Exchanges 2024 Call – internal deadline Applications are now open for 2025 ESRC Postdoctoral Fellowships!
Applications are now open for 2025 ESRC Postdoctoral Fellowships! Horizon Europe – ERC CoG and MSCA SE webinars
Horizon Europe – ERC CoG and MSCA SE webinars MaGMap: Mass Grave Mapping
MaGMap: Mass Grave Mapping ERC grants – series of webinars
ERC grants – series of webinars