‘Can you tell the story of your research in a single image?’ That’s the challenge we set BU’s academics and postgraduates earlier this year, and the overwhelming response saw researchers from all across the university downing tools to take up their cameras and think of unusual ways to illustrate their research.
The resulting images demonstrate not just the creativity of our academics and postgraduates, but also the fascinating range of research taking place at BU.
Researchers from all across the university, working in areas as diverse as dementia, archaeology, kayaking and 3D printing submitted images to the competition.
Thousands of BU students, staff and members of the public voted for their favourite images, and we can now reveal the winners.
Winner – Sarah Hambidge, ‘Care Farming: Providing Brighter Futures for Young and Old’

Down on a farm, tucked away in the beautiful Dorset countryside, the therapeutic use of farming practices is being used to provide health, social and educational care services for a wide range of people. The farm offers the opportunity for people who are the hardest to reach, to utilise a rural environment to enhance their well-being and to achieve their potential. The farm has achieved many great success stories of people who have turned their lives around, been given confidence in their own value and become equipped with the learning they need to successfully engage in wider society. The challenge they now face is to show this model of care is successful to enable their work to continue and grow.
Historically, much of the awareness and research regarding mental health issues has focused predominantly on females, whilst males with mental health concerns have faced an element of negativity from society, despite being at higher risk of depression and loneliness, alcohol dependency, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and suicide. My study aims to explore the benefits of the care farm model as an alternative social care intervention on improving physical / mental health outcomes and the quality of life of young males with behavioural, emotional and social difficulties as well as older men with dementia, and the benefits of intergenerational interaction between the two groups.
Runner up – Rosa Spencer-Tansley, ‘What causes mental illness?’

1 in 4 of us will experience mental health problems in our lifetime. The pathophysiology of mental illness involves a interplay of genetic and environmental factors and it is only the last few years that the aetiological picture has started to show. As a result uncertainty and oversimplified ideas regarding the causes of mental illness exist. This can exacerbate stigma and increase the emotional burden of mental illness amongst families. A major function of Psychiatric Genetic Counselling is to help affected individuals and families. This can help them successfully adapt to the condition as well as address and reduce feelings of shame, guilt, blame and stigma, thus having both informative and therapeutic values.
I will explore understanding amongst the UK about the causes of mental illness in order to evaluate the application of Psychiatric Genetic Counselling to the UK. This photograph captures 100 BU students’ answers to the question: “What causes mental illness?”
Runner up – Jordan Thomas, Stephanie Farrant, Robert Moore and Sulaf Assi, ‘On-spot Identification of Counterfeit Products Using Handheld Instruments’
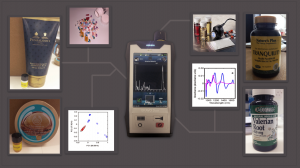
The last decade has witnessed a change in the use of medicine products beyond diseases’ treatments to improve an individual’s life. Lifestyle products include medicines, cosmetic and herbal products which improve physical appearance and physical/mental performance. Counterfeit lifestyle products could be encountered anywhere across the wholesale supply chain.
The effects resulting from a counterfeit lifestyle product could range from ineffectiveness (at their best) to toxic/lethal effects (at their worst). As these products can be encountered anywhere, it is important to develop rapid, non-destructive and mobile technology for their identification. Handheld instruments techniques offer these advantages. Therefore, this project underlies developing methods for the rapid and non-destructive identification of counterfeit lifestyle products using handheld spectroscopic techniques.
In particular, the project involves building libraries which contain signatures of lifestyle products and materials commonly present in these products.
 Congratulations to your winners of the 2017 Research Photography Competition!
Congratulations to your winners of the 2017 Research Photography Competition! Only one week left to submit your entry for The Research Photography Competition!
Only one week left to submit your entry for The Research Photography Competition!










 No access to BRIAN 5-6th February
No access to BRIAN 5-6th February Missing Persons Indicator Project Recruitment
Missing Persons Indicator Project Recruitment Celebrating our Research: Postgraduate Research Showcase 2026
Celebrating our Research: Postgraduate Research Showcase 2026 Nursing Research REF Impact in Nepal
Nursing Research REF Impact in Nepal ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease