 On World Refugee Day 2025, Friday 20 June, the new Maternal and Infant Health Equity Research Centre (MIHERC) website was launched. MIHERC is a hub for research, collaboration and action on maternal and infant health equity. MIHERC) is a collaborative effort between Sheffield Hallam University, Bournemouth University and City of Doncaster Council working to reduce health inequalities for mothers and babies. This year’s World Refugee Day’s theme, hashtagSolidarity, reflects MIHERC’s mission to stand with all mothers and babies – especially those facing health and social inequalities or barriers to care.
On World Refugee Day 2025, Friday 20 June, the new Maternal and Infant Health Equity Research Centre (MIHERC) website was launched. MIHERC is a hub for research, collaboration and action on maternal and infant health equity. MIHERC) is a collaborative effort between Sheffield Hallam University, Bournemouth University and City of Doncaster Council working to reduce health inequalities for mothers and babies. This year’s World Refugee Day’s theme, hashtagSolidarity, reflects MIHERC’s mission to stand with all mothers and babies – especially those facing health and social inequalities or barriers to care.
Category / NHS
Centre for Wellbeing & Long-term Health, Rehabilitation & Prevention workstream Networking and Development Event – Wed 25th June!

Centre for Wellbeing & Long-term Health, Rehabilitation & Prevention workstream Networking and Development Event – Wed 25th June! In BG-212.
Does your research broadly fit the category of “rehabilitation and prevention”? Then join us for this first event of the Rehabilitation & Prevention workstream of the Centre for Wellbeing and Long-term Health!
Whatever the focus of your research is or your professional background, whether it be at population or individual level, public health or rehabilitation of a particular condition in a particular demographic of people, whether you are a PGR or a senior academic, we would like this to be your research home. Come and share the highlights of what you do in a 5-minute Lightning talk, and hear from the highlights of others.
We want this to be a stimulating event and you might just find your next collaborator(s). Dr Jonny Branney and Dr Katie Collins, the workstream leads, will be taking notes with a view to creating a quick reference guide of what the workstream members are working on to make it easier for you to find the expertise you need for your next project. We want the workstream to be a place to talk about the sort of research enquiry that gets you out of bed in the morning, that puts the joy into your working life. A place to share and celebrate in your project successes, and to get a welcome lift when your latest research bid or journal submissions are rejected. A place to learn from those more experienced, from those with alternative expertise, identify a mentor or a coach, and for others to learn from you and benefit from your coaching and mentorship. A place to test out your ideas and get feedback from critical friends. A place to identify collaborators for your next research project. Is your research broadly “rehabilitation and prevention”? Then this is your place. Register here!!
Lightning Talks
Attendees are required to prepare a 5 minute lightning talk – 5 PowerPoint slides maximum to summarise your background as a researcher, what you’ve done, are doing, and plan to do. Nice and concise so we quickly get to know what everyone is about. There will be a timer!
Rough Itinerary
12:30pm Lunch – provided
1pm Welcome from workstream leads
1.05pm 5-minute Lightning talks
2.50pm – 3pm Closing remarks from workstream leads
See you there! Room BG-212.
For further information on this event please contact theme leads, Dr Jonny Branney (jbranney@bournemouth.ac.uk) or Dr Katey Collins (kcollins@bournemouth.ac.uk).
CMWH academics promoting women’s health in Dorset
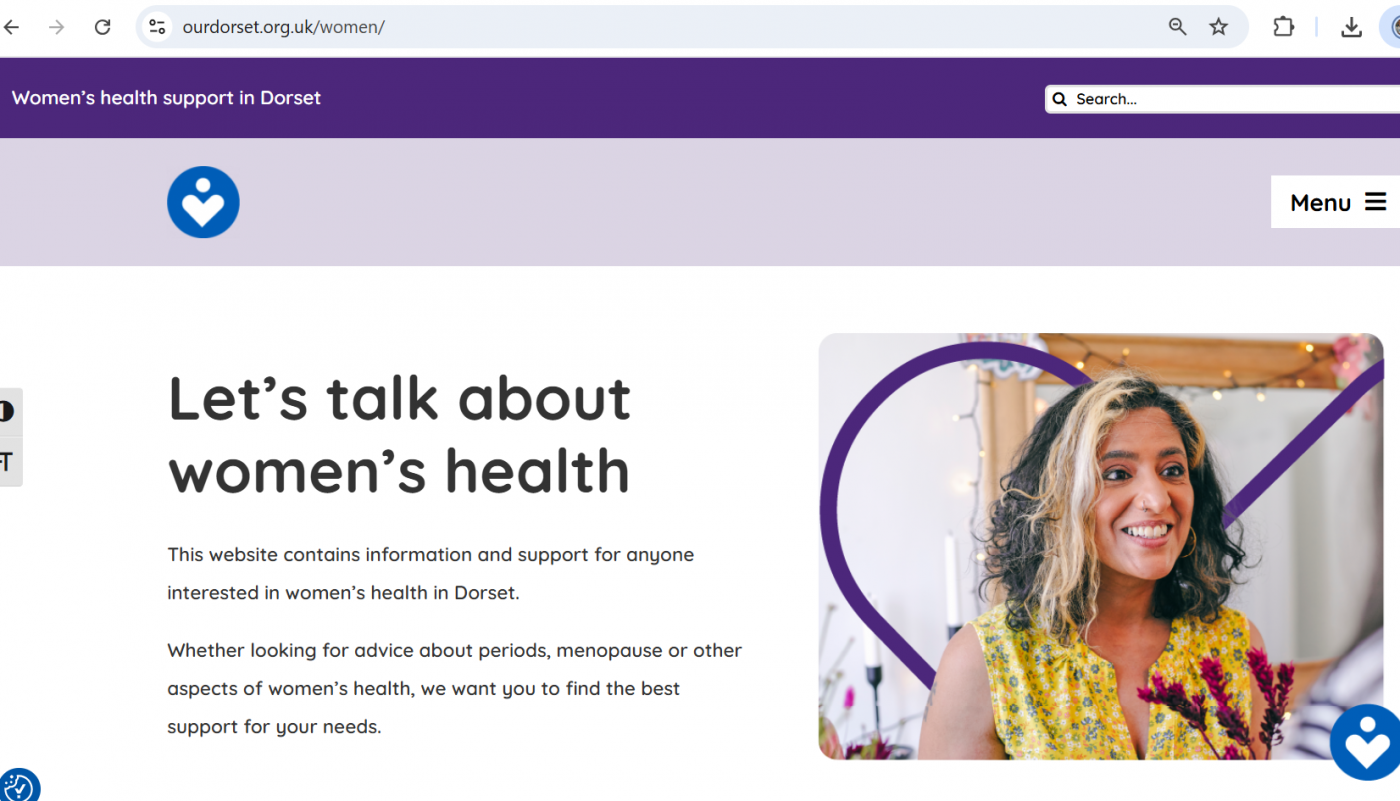 Women’s Health is now firmly on the Dorset map [i.e. online]. The new website, produced by Dorset Women CIC in conjunction with the NHS in Dorset, Bournemouth University, clinicians and the public, raises awareness of local community services. The website also provides resources to empower people with an interest in women’s health to make informed decisions about women’s mental and physical well-being. This is expected to improve access and quality of care – a priority identified by women – and ease pressures on the NHS.
Women’s Health is now firmly on the Dorset map [i.e. online]. The new website, produced by Dorset Women CIC in conjunction with the NHS in Dorset, Bournemouth University, clinicians and the public, raises awareness of local community services. The website also provides resources to empower people with an interest in women’s health to make informed decisions about women’s mental and physical well-being. This is expected to improve access and quality of care – a priority identified by women – and ease pressures on the NHS.
 Prof. Vanora Hundley and Carol Clark from the Centre for Midwifery and Women’s Health and colleagues from the Centre for Wellbeing and Long-Term Health have been central to the development of the website. There is an opportunity to hear about how we have been involved on Thursday 24th April 2025, where Bournemouth University’s academics Linda Agyemang and Sarah Hillier will present.
Prof. Vanora Hundley and Carol Clark from the Centre for Midwifery and Women’s Health and colleagues from the Centre for Wellbeing and Long-Term Health have been central to the development of the website. There is an opportunity to hear about how we have been involved on Thursday 24th April 2025, where Bournemouth University’s academics Linda Agyemang and Sarah Hillier will present.
If your are interested, you can registered to attend the event here.
First paper by PhD student

 The systematic review, co-authored with Heidi Singleton, Steven Ersser, Debbie Holley, Ian Pearson, and Abdulrahman Shadeed, rigorously analyzed studies from 1992 to 2024, assessing the role of nurses in diagnosing, treating, and supporting skin cancer patients. The findings demonstrate that nurse-led models can complement or even substitute traditional physician-led care, offering high diagnostic accuracy, improved access to care, and enhanced patient education.
The systematic review, co-authored with Heidi Singleton, Steven Ersser, Debbie Holley, Ian Pearson, and Abdulrahman Shadeed, rigorously analyzed studies from 1992 to 2024, assessing the role of nurses in diagnosing, treating, and supporting skin cancer patients. The findings demonstrate that nurse-led models can complement or even substitute traditional physician-led care, offering high diagnostic accuracy, improved access to care, and enhanced patient education. The study also emphasizes the need for further research and standardized national guidelines to scale and integrate nurse-led models effectively into healthcare systems.
The study also emphasizes the need for further research and standardized national guidelines to scale and integrate nurse-led models effectively into healthcare systems.- Kattach, L., Singleton, H., Ersser, S., Holley, D., Pearson, I. & Shadeed, A. (2025), Nurse-Led Models of Service Delivery for Skin Cancer Detection: A Systematic Review. Journal of Advanced Nursing.[online first] https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.16854
Consider starting M.Res. at Bournemouth University
 The National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) INSIGHT programme is a unique opportunity designed to inspire and equip the next generation of health and social care researchers. As part of its commitment to fostering a world-class research workforce, the NIHR INSIGHT programme offers a transformative experience with numerous benefits:
The National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) INSIGHT programme is a unique opportunity designed to inspire and equip the next generation of health and social care researchers. As part of its commitment to fostering a world-class research workforce, the NIHR INSIGHT programme offers a transformative experience with numerous benefits:
- Exposure to Research Opportunities: Gain invaluable insight into health and social care research.
- Hands-On Experience: Engage directly with researchers and practitioners, acquiring real-world skills.
- Mentorship: Receive guidance from experienced professionals, helping to shape your research career and development.
Cancer Awareness Event at BU
 The Dorset Indian Association in collaboration with the NHS Wessex Cancer Alliance and Bournemouth University ran a very successful Cancer Awareness Event at Bournemouth University today Saturday, 25th January 2025. At the event a range of experts from University Hospitals Dorset NHS Foundation Trust spoke about the risks and prevention and early detection of various cancers, including bowel, lung, breast, skin, head and neck and other cancers. The presentations also included early detection and aspects of mental health in cancer patients. BU’s Professor Steve Ersser, for example, spoke about a currently on-going interdisciplinary health education project in the cancer field.
The Dorset Indian Association in collaboration with the NHS Wessex Cancer Alliance and Bournemouth University ran a very successful Cancer Awareness Event at Bournemouth University today Saturday, 25th January 2025. At the event a range of experts from University Hospitals Dorset NHS Foundation Trust spoke about the risks and prevention and early detection of various cancers, including bowel, lung, breast, skin, head and neck and other cancers. The presentations also included early detection and aspects of mental health in cancer patients. BU’s Professor Steve Ersser, for example, spoke about a currently on-going interdisciplinary health education project in the cancer field.
There were separate opportunities for the audience to get on breast screening and health checks, provided by the Dorset Breast Screening Unit, LiveWell Dorset and staff based in BU’s Faculty of Health and Social Science.
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Faculty of Health & Social Sciences
New BU midwifery publication by Joanne Rack
 This week the international scientific journal Midwifery published Ms. Joanne Rack’s second paper from her PhD research. This latest paper ‘The Pregnant Pause: Engaging and Involving Public Contributors in Maternal Health Research‘ [1] appeared online two days ago. This paper focuses on Joanne’s PPI (Patient Public Involvement) in prepartion for her PhD research. The public contributors of PPI groups can include an extensive range of people, including patients, family members or carers, people from allied organisations, service users, and members of the general public who have an interest in research for other reasons. Participants bring their unique perspectives and experiences that can help to shape and inform the research process. This type of involvement ensures that maternal health research is grounded in the needs and preferences of those it aims to serve and grows a sense of ownership and investment among those who use the services but also those who provide them. Joanne stresses that PPI is an essential element for all maternal health endeavours.
This week the international scientific journal Midwifery published Ms. Joanne Rack’s second paper from her PhD research. This latest paper ‘The Pregnant Pause: Engaging and Involving Public Contributors in Maternal Health Research‘ [1] appeared online two days ago. This paper focuses on Joanne’s PPI (Patient Public Involvement) in prepartion for her PhD research. The public contributors of PPI groups can include an extensive range of people, including patients, family members or carers, people from allied organisations, service users, and members of the general public who have an interest in research for other reasons. Participants bring their unique perspectives and experiences that can help to shape and inform the research process. This type of involvement ensures that maternal health research is grounded in the needs and preferences of those it aims to serve and grows a sense of ownership and investment among those who use the services but also those who provide them. Joanne stresses that PPI is an essential element for all maternal health endeavours.
Joanne is doing a Clinical Doctorate in the Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH) specialising in personalised care for women of advanced maternal age. This PhD study is matched-funded by University Hospitals Dorset (UHD) NHS Foundation Trust and Bournemouth University.  Her PhD is supervised and supported by Profs. Vanora Hundley, Ann Luce and Edwin van Teijlingen at BU and Dr. Latha Vinayakarao in Poole Maternity Hospital. The first PhD paper with Joanne as lead author was her research protocol ‘Understanding perceptions and communication of risk in advanced maternal age: a scoping review (protocol) on women’s engagement with health care services’ published int he summer of 2024 [2].
Her PhD is supervised and supported by Profs. Vanora Hundley, Ann Luce and Edwin van Teijlingen at BU and Dr. Latha Vinayakarao in Poole Maternity Hospital. The first PhD paper with Joanne as lead author was her research protocol ‘Understanding perceptions and communication of risk in advanced maternal age: a scoping review (protocol) on women’s engagement with health care services’ published int he summer of 2024 [2].
References:
- Rack, J., Hundley, V., van Teijlingen, E., Luce, A. (2025)The Pregnant Pause: Engaging and Involving Public Contributors in Maternal Health Research, Midwifery (online first)
- Rack, J., Hundley, V., van Teijlingen, E., Luce, A., Vinayakarao. L. (2024) Understanding perceptions and communication of risk in advanced maternal age: a scoping review (protocol) on women’s engagement with health care services, MIDIRS Midwifery Digest, 34(3): 201-204.
Meeting at BU to address maternal inequalities
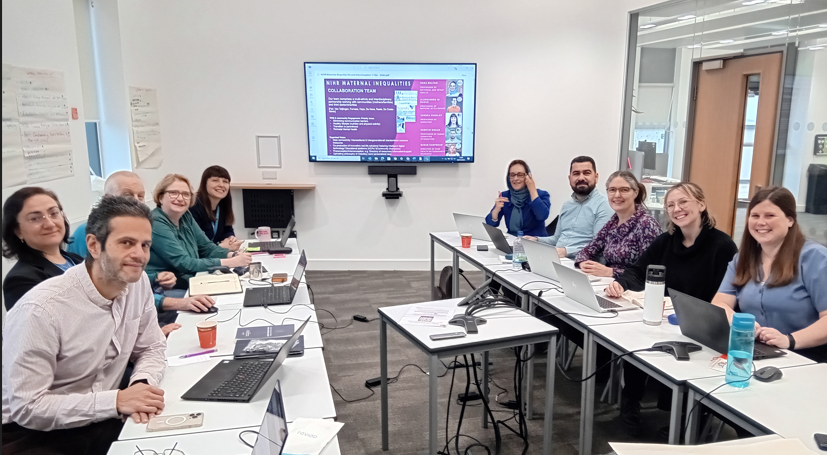 Today and yesterday (January 7-8) academics involved in MIHERC (Maternal and Infant Health Equity Research Centre), the successful interdisciplinary collaboration to address challenges in maternity care, met in Bournemouth. MIHERC is led by Sheffield Hallam University, along with Bournemouth University, South Yorkshire Digital Health Hub (SYDHH) and the Health Determinant Research Collaboration, Doncaster. In addition, a range of local and national partners are recognised. MIHERC is one of the nine groups of UK universities making up the new NIHR Challenge Maternity Disparities Consortium. This NIHR Consortium aims of tackling inequalities in maternity outcomes, focusing on inequalities before, during and after pregnancy.
Today and yesterday (January 7-8) academics involved in MIHERC (Maternal and Infant Health Equity Research Centre), the successful interdisciplinary collaboration to address challenges in maternity care, met in Bournemouth. MIHERC is led by Sheffield Hallam University, along with Bournemouth University, South Yorkshire Digital Health Hub (SYDHH) and the Health Determinant Research Collaboration, Doncaster. In addition, a range of local and national partners are recognised. MIHERC is one of the nine groups of UK universities making up the new NIHR Challenge Maternity Disparities Consortium. This NIHR Consortium aims of tackling inequalities in maternity outcomes, focusing on inequalities before, during and after pregnancy.
 Our second planning meeting highlighted our collective strengths including our expertise in community engagement and PPIE (Public & Patient Involvement & Engagement); intelligent digital solutions in maternity service delivery; research into under-served communities; and capacity building of both communities and maternity staff. The first planning meeting was held late last year at Sheffield Hallam University.
Our second planning meeting highlighted our collective strengths including our expertise in community engagement and PPIE (Public & Patient Involvement & Engagement); intelligent digital solutions in maternity service delivery; research into under-served communities; and capacity building of both communities and maternity staff. The first planning meeting was held late last year at Sheffield Hallam University.
MIHERC is the only midwifery-led collaboration with a strong community engagement and digital inclusive research. MIHERC will work with various NHS Trusts as well as charities such as the Active Pregnancy Foundation, Active Dorset, and Maternal Mental Health Alliance.
BU academics’ paper read 170,000 times!
This week ResearchGate notified us that our methods paper ‘The Importance of Pilot Studies‘ [1], published 22 years ago in The Nursing Standard,  has now been read 170,000 times! Prof. Vanora Hundley and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen wrote this more elementary paper after publishing an in-depth academic paper on a pilot study into assessing maternity care in Scotland [2]. The latter paper described their learning from a pilot study which we conducted prior to a cross-national study of births in Scotland.
has now been read 170,000 times! Prof. Vanora Hundley and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen wrote this more elementary paper after publishing an in-depth academic paper on a pilot study into assessing maternity care in Scotland [2]. The latter paper described their learning from a pilot study which we conducted prior to a cross-national study of births in Scotland.
The methods paper in the Nursing Standard is also their most highly cited paper. Today Google Scholar lists it with 2,035 citations, interestingly this is not the case on SCOPUS as The Nursing Standard is not listed on SCOPUS. Researchers seem to be quoting this paper in their research methods section when they have done pilot or feasibility study for a larger-scale study.

References:
- van Teijlingen E, Hundley, V. (2002) The importance of pilot studies, The Nursing Standard 16(40): 33-36. Web: nursing-standard.co.uk/archives/vol16-40/pdfs/vol16w40p3336.pdf
- van Teijlingen E, Rennie, AM., Hundley, V, Graham, W. (2001) The importance of conducting & reporting pilot studies: example of Scottish Births Survey, Journal of Advanced Nursing, 34: 289-95.
Race Equity Month: Disparities in maternity care
Race Equity Month – Can the UK finally tackle health disparities in maternity care?
Last week Prof. Hora Sultani, who leads the joint bid submitted by Sheffield Hallam University (SHU) and Bournemouth University (BU) in reply to the ‘NIHR Challenge: Maternity Inequalities funding call’, wrote an article on the website of the Council of Deans for Health. This piece with the title ‘Race Equity Month – Can the UK finally tackle health disparities in maternity care?‘ can be freely accessed (click here!). One of Prof. Soltani’s key arguments is that it is vital that national policy makers and service providers collaborate with researchers and communities to co-design and provide practical solutions for such important maternity challenges in UK society.
Prof. Soltani was writing on behalf of the UK Network of Professors in Midwifery and Maternal and Newborn Health, an organisation to which both Profs Hundley and van Teijlingen belong.
Pregnancy & COVID-19 in UK: New study published
This morning the editor of the Frontiers in Psychiatry emailed us that the paper reporting the findings of the baseline data of a large-scale epidemiological study into pregnancy during COVID-19 in the UK has been published [1]. The interdisciplinary research team includes researchers from University Hospitals Dorset NHS Foundation Trust (Dr. Latha Vinayakarao & Prof. Minesh Khashu) and Bournemouth University (Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen). 
This longitudinal study explores how the SARS-CoV-2 [COVID-19] pandemic affected the mental health of pregnant people in the UK. In mid-to-late 2020, we recruited 3666 individuals in the UK for the EPPOCH pregnancy cohort (Maternal mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic: Effect of the Pandemic on Pregnancy Outcomes and Childhood Health). Participants were assessed for depression, anxiety, anger and pregnancy-related anxiety using validated scales. Additionally, physical activity, social support, individualized support and personal coping ability of the respondents were assessed as potential resilience factors.
 Participants reported high levels of depression (57.05%), anxiety (58.04%) and anger (58.05%). Higher levels of social and individualized support and personal coping ability were associated with lower mental health challenges. Additionally, pregnant individuals in the UK experienced higher depression during the pandemic than that reported in Canada. Finally, qualitative analysis revealed that restrictions for partners and support persons during medical appointments as well as poor public health communication led to increased mental health adversities and hindered ability to make medical decisions.
Participants reported high levels of depression (57.05%), anxiety (58.04%) and anger (58.05%). Higher levels of social and individualized support and personal coping ability were associated with lower mental health challenges. Additionally, pregnant individuals in the UK experienced higher depression during the pandemic than that reported in Canada. Finally, qualitative analysis revealed that restrictions for partners and support persons during medical appointments as well as poor public health communication led to increased mental health adversities and hindered ability to make medical decisions.
The study highlights the increased mental health challenges among pregnant individuals in the UK during pandemic. These results highlight the need for reassessing the mental health support measures available to pregnant people in the UK, both during times of crisis and in general.

Reference:
- Datye, S., Smiljanic, M., Shetti, R.H., MacRae-Miller, A., van Teijlingen, E., Vinayakarao, L., Peters, E.M.J., Lebel, C.A., Tomfohr-Madsen, L., Giesbrecht, G., Khashu, M., Conrad, M.L. (2024) Prenatal maternal mental health and resilience in the United Kingdom during the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic: A cross-national comparison, Frontiers in Psychiatry, 15 https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1411761
New midwifery publication
 Congratulations to Ph.D. student Joanne Rack on the publication today of her paper ‘Understanding perceptions and communication of risk in advanced maternal age: a scoping review (protocol) on women’s engagement with health care services’ [1]. Joanne is currently doing a Clinical Doctorate in the Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH) focusing on personalised care for women of advanced maternal age. Her doctoral study is matched-funded by University Hospitals Dorset NHS Foundation Trust and Bournemouth University [BU].
Congratulations to Ph.D. student Joanne Rack on the publication today of her paper ‘Understanding perceptions and communication of risk in advanced maternal age: a scoping review (protocol) on women’s engagement with health care services’ [1]. Joanne is currently doing a Clinical Doctorate in the Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH) focusing on personalised care for women of advanced maternal age. Her doctoral study is matched-funded by University Hospitals Dorset NHS Foundation Trust and Bournemouth University [BU].  Her PhD is supervised and supported by Profs. Vanora Hundley, Ann Luce and Edwin van Teijlingen at BU and Dr. Latha Vinayakarao in Poole Maternity Hospital.
Her PhD is supervised and supported by Profs. Vanora Hundley, Ann Luce and Edwin van Teijlingen at BU and Dr. Latha Vinayakarao in Poole Maternity Hospital.
Well done!
Reference:
- Rack, J., Hundley, V., van Teijlingen, E., Luce, A., Vinayakarao. L. (2024) Understanding perceptions and communication of risk in advanced maternal age: a scoping review (protocol) on women’s engagement with health care services, MIDIRS Midwifery Digest, 34(3): 201-204.
Everyday Law & Ethics Public Lecture Series: Your rights to the right diagnosis in Dorset
Join our public lecture and debate on Wednesday 17 July, 5:30-7pm to find out how to advocate for your rights to medical treatment

People living in Dorset currently face some of the worst levels of contact with health services in the UK, with GP waiting times in the county the second longest in England.
Join our public lecture and debate, led by Bournemouth University legal experts Dr Samuel Walker and Dr Matthew Watkins to explore your legal and ethical rights to timely care and treatment. Discover practical steps you can take to speed up diagnosis and treatment for you and your family, and discuss the recent introduction of ‘Martha’s Rule’, which enables you to seek a second opinion on the NHS.
After the lecture (30 minutes approx.), you will be invited to move into small groups to discuss your own experiences and suggest ways to improve local access and provision to healthcare services
Find out more
Interdisciplinary Computational and Clinical Approaches at the Edge of Brain Research
We cordially invite you to the 3rd Symposium of the BU Interdisciplinary Neuroscience Research Centre on Wednesday, the 12th of June 2024, from 9:30-13:00 at the Inspire Lecture Theatre, Fusion Building (1st floor).
The symposium is entitled: “Interdisciplinary Computational and Clinical Approaches at the Edge of Brain Research”.
This third symposium revolves around contrasting computational and translational methodologies from a cross-disciplinary standpoint, leveraging synergies between BU and our collaborators in other universities and at the NHS. It is an opportunity for informal discussions on grant proposals and to explore shared interests with our external guests.
The schedule is as follows:
9:00-9:15. Welcome and Coffee.
9:30. Keynote talk: Prof. Dr Miguel Maravall (School of Life Sciences, Sussex Neuroscience Centre of Excellence, Sussex University): “What is the function of sensory cortex in a world full of actions? From sensory maps to task-directed responses”. The speaker will be on the screen.
10.20-10:40. Coffee and Discussions.
10:40-11:40. Session I. Integrating Cognitive and Computational Neuroscience.
- Michal Gnacek (Emteq Labs, Brighton and Centre for Digital Entertainment, BU): “Affect Recognition in Virtual Reality using Physiological Signals and Machine Learning”. The speaker will be on the screen.
- Dr Matteo Toscani (Department of Psychology, BU): “Unsupervised learning of haptic material properties”.
- Dr Géza Gergely Ambrus (Department of Psychology, BU): “Investigating Face Perception Using Cross-Experiment Multivariate Pattern Analysis of Neural Time-Series Data”.
11.40 -12.00. Coffee and Discussions.
12.00-13:00. Session II. Interdisciplinary Clinical Approaches and Closing Remarks.
- Prof. Dr Jonathan Cole (University Hospital Dorset, NHS): “Perception and action; Observations from congenital and acquired deafferentation”.
- Prof. Dr Caroline Edmonds (Department of Psychological Sciences, University of East London): ”Real-life implications arise from co-occurring memory impairments in children with neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy”.
- Prof Dr Birgit Gurr (Community Brain Injury and Adult Neuropsychology Services Dorset at Dorset HealthCare University, NHS) and Dr Ellen Seiss (Department of Psychology, BU). “An initial evaluation of the Dynamic Information Processing Programme”.
If you have any queries, please do not hesitate to contact Ellen Seiss, eseiss@bournemouth.ac.uk or Emili Balaguer-Ballester, eb-ballester@bournemouth.ac.uk. Feel free to forward this information to any colleague or student who may be interested.
Thank you very much, and we are looking forward to seeing you there.
Kind regards,
Ellen and Emili, on behalf of all of us.

2nd HSS PGR Conference – submission deadline 19th April

Last chance to submit…
The Conference Committee welcome all PGRs in HSS to submit an abstract to present at the 2nd annual department conference, which will be held on Tuesday 4th June.
HE policy update no 8 25th March 2024
Some more optimistic takes on what might be in the party manifestos for HE: the sort of commitments being asked for seem somewhat optimistic: later in this update I look at some detailed proposals on maintenance finance, a call to scrap the REF (which might have more take-up in the manifestos), the KEF via a HE- BCI survey (might someone suggest scrapping the KEP?), apprenticeship results are out and numbers on international education. Amongst all that I also look at a speech from Susan Lapworth.
Manifesto for HE
You’ve seen the UUK one, here is the one from MillionPlus. (Policy update from February: The UUK manifesto sets out a wish list for the sector. It all looks very expensive and so while ambitious, unlikely to be replicated in anyone’s actual manifesto. We can expect to see more of these over the next few months. Research Professional have the story here.)
Scrap REF and save money
Iain Mansfield says that Labour should ‘scrap REF and save half a billion’, Research Professional reports. Not because there is any problem with a metric for research: just a strong feeling that it shouldn’t include a metric for environment and culture. RP add: Speaking at Research Professional News live last week, Labour’s shadow science minister, Chi Onwurah, said she was “concerned about some of the bureaucracy associated with the REF” and stopped short of committing to retaining it in its current form. I don’t think that means stopping the culture and environment part, but it is hard to know. These debates will run for a while.
HE-BCI review
The HE-BCI survey is used in the Knowledge Exchange Framework. Just how much difference the KEF makes to anything and how interested anyone except the sector really is in it, is still, for me, an open question that I have asked since KEF was just a glint in Jo Johnson’s eye (the third leg of the HE stool etc…). Of course if they started using KEF to allocate HEIF it would matter a lot more, but the KEF data doesn’t really lend itself to that. As a reminder, it uses a different comparison group (clusters) to everything else, three of its “perspectives” are self-assessed and all it tells you is whether engagement with the perspective is deemed to be low, medium or high. In a highly technical presentation format.
But as the (only real) metrics behind the (incomprehensible) KEF wheels (just take a look here and see what you learn), HE-BCI data does have some influence. And HESA did a survey on some bits of it which closed in January. There will be another consultation at some point.
The regulator speaks
It is always interesting to hear or read a speech by the head of the OfS, so here is one.
After a friendly introduction telling the Association of Colleges what good work their members do, it is straight in on quality:
- Although, of course, not every college higher education student is in that position, the college sector should collectively be very proud that so many who are get the guidance and support they need in further education settings.
- But, sadly, we know that in too many parts of the system, students’ interests are not always being well-served
- …[Students] have serious questions about:
- the amount of teaching they receive,
- the frequency and usefulness of feedback provided to them, and
- the level of support, both academic and pastoral, they can access.
Talking about the ongoing quality assessments, there are some changes coming:
- Updating some of the language we use. So we might talk more about assessments or compliance assessments, rather than investigations.
- We think there’s scope for additional training for assessment teams, for example, focusing on welfare to ensure staff are appropriately supported during visits and the wider process.
- And we know the sector would like us to publish more information about how institutions are selected for assessment and how the process unfolds from there
A defensive approach to the big effort on freedom of speech? You decide
- Defining more clearly and coherently the student interest will also support another area where our regulation is developing: freedom of speech and academic freedom.
- As that work has progressed, we have sometimes been told, including by some students, that students do not consider this a priority. But we know that the National Student Survey found that one in seven students in England felt unable to freely express their views.
- … the collective act of debate and dissection of ideas, old and new, is what allows us to be confident that what and how students are learning represents the best knowledge we currently have. If students don’t recognise this, we need to understand why. Is it an artefact of who speaks loudest in our current systems? Or that cost-of-living worries and the associated challenges have reduced the scope for considering these broader issues? Or that students today have a fundamentally different conception of what freedom of speech and academic freedom ought to entail?
And some new areas of focus:
- For example, although access to accommodation appears in our Equality of Opportunity Risk Register, we’ve been cautious about stepping into that arena in regulatory terms. But it is clear that students are increasingly concerned about the cost, quality and uneven availability of accommodation for their studies. It’s the most frequently mentioned issue in discussions with students in my visits to institutions.
- Likewise, while we’ve taken steps to encourage stronger working links between those we regulate and the organisations that provide health services to students, particularly to support their mental health, we’re not the regulator of those services, and much of the most critical care can’t be provided by universities and colleges directly…. we are open to the view that, as a regulator framed and formed in relation to the interests of students, it may fall to us to take action, or to seek to better co-ordinate the activity of others, or to just talk about them because they matter to students.
And there is a new strategy consultation coming for the OfS.
Apprenticeships
Achievements rate update: a update published by the DfE. The Minister for Skills, Apprenticeships and Higher Education, Robert Halfon has written an open letter to the apprenticeship sector celebrating the latest achievement rates and setting out some developments.
While the government are very keen to encourage more apprenticeships, there is a stern approach to providers here: not dissimilar to the rhetoric on HE, there will be student number controls linked to quality as defined by outcomes. While “training not being as good as hoped” is a factor in the list above, as is “poor organisation” of the programme, that is in the context of all the other reasons linked to employers and jobs. However, the government can’t do much about those, and is not in the business of discouraging employers from participating. But this will put more pressure on providers who are already finding apprenticeships bureaucratic and hard and expensive to deliver.
It’s not putting them off just yet, though. This update from the OfS on the second wave of funding for apprenticeships highlights how many providers are really going for it. Degree apprenticeships funding competition: Funding allocated to wave 2 projects (officeforstudents.org.uk)
Anyway, the ideas for future development in the Minister’s letter are:
- Apprenticeship Standards. IfATE will be looking closely at apprenticeship standards that are not producing good outcomes for employers or the economy – especially where they are underused or too many learners are dropping out without completing – and speed up action to either improve them or remove them where it is clear the apprenticeship standard is not working.
- Quality of Training. We know that the quality of training is a major factor in whether apprentices complete. Through the apprenticeship accountability framework, we have assessed provider performance against a range of measures to give an overall picture of their quality of delivery. ….. In future performance assessments, we will not hesitate to robustly challenge providers showing insufficient improvement. We will deploy appropriate support, where providers demonstrate a capacity to improve in a timely manner, and we will continue to consider factors outside of providers’ control, where these can be evidenced. However, we will also use contractual measures including potential limitations on growth, stopping delivery of standards with low apprenticeship achievement rates and removal from the market where this is necessary to protect apprentices and employers and ensure they have access to high quality training. Concurrently we will also seek to enrich the market by making it easier to enter for providers that can deliver to our priorities – for example to increase participation from SMEs and young people.
- Employer improvement. We now want to give employers better access to information and data to help manage their own apprenticeship programme and benchmark against others to help drive up improvements across the programme. We will test options for the information we could use to support this and work with Top 100 employers to identify how to make the information available. This will be in addition to the support offered to employers through resources, best practice sharing, and events to support self-improvement.
- End-Point Assessment. We continually review the assessment process for apprenticeships to make sure it is proportionate, supports achievement and is fit for the future. Working with IfATE, the providers engaged with the Expert Provider pilot and the FE Funding Simplification pilot, we will identify further options to improve the assessment model, making it more efficient for the whole sector…
- Expert Provider Pilot and SME engagement. … As a result of the pilot we are developing a new, simple one step approval for SMEs engaging with apprenticeships for the first time. This new flexibility is being developed with colleges and training providers and will be available later this year. …
Student finance
Oh dear, another negative story about student debt that will discourage potential applicants (and as always, their parents). This time it is the BBC who revealed that the UK’s highest student debt was £231k. Quite how they managed to rack up that much is unclear: by doing lots of courses, it seems (although surely there are limits on that – apparently there are exceptions to those rules). The highest level of interest accumulated was around £54,050. The student interviewed is a doctor: the length of medical programmes means that, along with vets and dentists, doctors tend to accumulate the highest student loans.
The Sutton Trust have published a report on reforming student maintenance ahead of the general election.
There are suggestions about how to address the challenges.
- The analysis covers three potential systems, all of which would increase the amount of maintenance students would have available to them day to day, rising from the current level of £9,978 to £11,400. This is the level that recent Sutton Trust research has found is the median spending on essentials for students living away from home outside of London for 9 months of the year,… This would also set maintenance support at a similar level to what they would receive if paid the National Living Wage while studying, a method the Diamond Review in Wales used to set maintenance levels.
Scenarios include
- Scenario 1 – Increasing overall maintenance levels, with equal loans for all students and maintenance grants making up the difference.
- Scenario 2 – Increasing overall maintenance levels, with variable loans and with maintenance grants focused on the poorest students.
- Scenario 3 – Increasing overall maintenance levels by means-tested loans only.
The value of international education
The government has issued 2021 data on UK revenue from education related exports and transnational education activity.
David Kernohan from Wonkhe has some analysis, always worth checking out for the nuances, including:
- 2021 was a long time ago
- It’s also notable that all these figures are based on exports only – there is no adjustment at all for costs incurred in delivering a service overseas.
- pathway provider income (programmes that help to prepare overseas students for study at a UK university) is estimated based on a survey of six large providers (CEG, INTO, Kaplan, Navitas, Oxford International, Study Group) conducted by one of the participants (Kaplan)
Research Professional also has an article.
Appreciative Inquiry Resource
 Today we received a copy of the book Appreciating Health and Care in the post. This book has a sub-title ‘A practical appreciative inquiry resource for the health and social care sector’ and refers to the work led by Bournemouth University’s Dr. Rachel Arnold. Appreciative Inquiry values people’s expertise and vision and can motivate people to see the world differently and instigate positive change. Rachel been the lead author on several publications around Appreciative Inquiry [1-3].
Today we received a copy of the book Appreciating Health and Care in the post. This book has a sub-title ‘A practical appreciative inquiry resource for the health and social care sector’ and refers to the work led by Bournemouth University’s Dr. Rachel Arnold. Appreciative Inquiry values people’s expertise and vision and can motivate people to see the world differently and instigate positive change. Rachel been the lead author on several publications around Appreciative Inquiry [1-3].

Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH)
References:
- Arnold, R. (2024) Learning to use Appreciative Inquiry, i2Insights, 16th January.
- Arnold, R., Way, S., Mahato, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2024) “I might have cried in the changing room, but I still went to work”. Maternity staff managing roles, responsibilities, and emotions of work and home during COVID-19: an Appreciative Inquiry, Women & Birth 37: 128-136.
- Arnold, R., Gordon, C., Way, S., Mahato, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2022) Why use Appreciative Inquiry? Lessons learned during COVID-19 in a UK maternity service, European Journal of Midwifery 6 (May): 1-7.
Team-based Learning for supported self-management of low back pain?
Plus two upcoming TBL workshops next week – sign up!
TBL for supported self-management of low back pain
A team based in the Department of Nursing Science led by Dr Jonny Branney have began a research project to investigate the potential role of Team-based Learning (TBL – for more on TBL, please read on) in enhancing the supported self-management of patients with low back pain. The team will be working with Joe Barry, musculoskeletal physiotherapist, NHS Somerset, to implement this new approach in a 5-week course for patients with persistent back pain. The project began with a patient-public involvement (PPI) online consultation in February 2024, funded by NIHR RDS South West, where 10 expert patients gave their views on what was planned – and the plans have been modified and improved accordingly. The TBL pain classes will be implemented in April-May 2024. The team are eagerly awaiting the outcome of a bid for a TBLC Research Grant which would fund a researcher to interview the patients who attend the first class to learn from their experiences with a view to learning how best to scale up the innovation.
Connected to this research there are two TBL workshops running next week – if this has piqued your interest then please read on and we hope you can join us next week!
Team-Based Learning (TBL) is an evidence based flipped classroom teaching and learning strategy. With TBL, students are required to engage with pre-class materials before working through a test in class as an individual and then in a team of 5-6 students. This process helps to prepare the student teams to then engage with application exercises, where they apply their knowledge in making decisions to manage real-world scenarios relevant to their discipline. Think TBL might be a good fit for your teaching and learning approach? Fancy trying something different? Come and join us!
Facilitators: Dr Jonny Branney, Principal Academic in Nursing and Clinical Sciences; Certified Consultant-Trainer in TBL
and Ryan Muldoon, Lecturer in Adult Nursing
Venue: BRANKSOME – Talbot Campus
Date: Wednesday 6th March 2024
Workshop 1: Fundamental Principles and Practices of TBL (10am – 12pm)
Learning outcomes:
- Describe the essential elements of TBL
- Explain clearly and concisely how and why TBL works
- Evaluate the benefits of using TBL
Workshop 2: Evaluating Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) for Readiness Assurance Tests (RATs) and Application Activities (1pm – 3pm)
Learning outcomes:
- Compare and contrast MCQs for RATs, exams and applications
- Link MCQs to session learning outcomes
- Identify common errors and barriers to writing effective MCQ questions
Want to know more? Have a look here: www.teambasedlearning.org
Hope to see you there!













 Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week
Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian
Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian NIHR-funded research launches website
NIHR-funded research launches website MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
Explore our work, meet our partners, and find out how you can collaborate with us by clicking here! MIHERC is led by Sheffield Hallam University, with Bournemouth University as a key partner and the important funding coming from NIHR (National Institute for Health and Care Research) Maternity Challenge Initiative. The BU key academics are: Huseyin Dogan, Vanora Hundley, Edwin van Teijlingen, and Deniz Çetinkaya. Please share with all who may be interested.