Tuition fees – here to stay?
Sir Keir Starmer has announced that Labour are reviewing what to do about tuition fees if they win the general election next year (widely expected in autumn 2024, latest it can be is January 2025) giving a clear indication in an interview on BBC Radio 4 that the previous policy of abolishing fees will not survive because of costs concern. The narrative was all about replacing it with something fairer – does that mean a graduate tax is the most likely outcome (which is, arguably what we already nearly have). He also acknowledged that the current system is not working for universities, although a blanket freedom to raise fees, or even an increased cap, might not be what he meant. They will be doing a review ahead of publishing their manifesto – so more news to follow.
Nurse Review: RDI organisational landscape report
The Government published Sir Paul Nurse’s final report on his Research, development and innovation (RDI) organisational landscape: an independent review. It’s a 163 page behemoth that was commissioned in 2021 to identify strengths and weaknesses, and to make recommendations for improvement of the RDI landscape, with a primary focus on researchers and RDI funded by the public purse. It also comments on how the various RDI organisations interact with and support industry, commerce, and society more generally.
It speaks of a patchwork of funders and sometimes short-term public policy priorities and initiatives. These are part of the significant problems that the Nurse Review identifies and Sir Paul calls for the governance to step away from further piecemeal changes and urges Government to consider the Review as a whole rather than a pick and mix assortment to be selected from. Government has a very important long-term role to play in bringing this about. It will require increased investment, reduced policy volatility, a clear focus on optimising and implementing change, good data collection, and a long-lasting, consistent, systematic approach to policy development and safeguarding of the RDI landscape.
Concerns include
- underinvestment in R&D (confirmation of R&D spend figures due late 2023).
- ensuring the pursuit of research is the pursuit of truth. Recommendations aim to strengthen: high research quality; agility and flexibility in approach; permeability between sectors, disciplines and organisations; transparency and navigability for those seeking to engage with R&D; a skilled workforce; inspirational leadership; a good research culture embracing ethical behaviour; strong international collaboration; and financial sustainability.
- political interest can have the unintended consequence of driving policy volatility and short-term policymaking, and recent years have seen an increasing turnover of new initiatives, schemes and programmes which are not always properly integrated with one another. This undermines development of RDI, particularly within the application part of the research spectrum, which can have a negative effect on private investment.
- The UK RDI landscape is hard to navigate – defects in permeability and inter-sectoral collaboration may be contributing to the UK’s present weak productivity.
- the financial sustainability of public research funding – The future success of UK RDI is explicitly contingent upon the Government’s commitment to grow investment in RDI. There is a pressing need for more complete ‘end-to-end’ funding of research activities beyond Independent Review of the Research, Development and Innovation Organisational Landscape 8 direct research costs, including adequate support for administrative services, sophisticated technical cores and facilities, and for ‘well-found’ laboratories
- university research has been sustained partly through increasing reliance on cross-subsidy from commercial sources – The excellent UK universities should receive increased support for the outstanding research they can deliver, to ensure that they are competitive with universities in other countries
- Excessive bureaucracy – Checks and balances on organisations using public research funding are important, but the operations of research funders and RPOs are hindered by excessive bureaucracy, with too much emphasis on audit-oriented reviewing and reporting rather than the quality of the research being produced…Much of this bureaucracy has its origin in Government controls and rules, particularly from the Treasury…These ways of working, combined with deficiencies in ‘end-to-end’ research funding have led to long-standing inefficiencies, wasting both money and researchers’ time. The problem of excessive bureaucracy has also been independently verified by the 2021 Review of Research Bureaucracy, led by Professor Adam Tickell, and the 2022 Review of UK Research and Innovation (UKRI), led by Sir David Grant.
The report concludes:
The financial sustainability of the public research funding for universities needs to be urgently addressed. ‘End-to-end’ research support has four components: direct research costs; administrative services; technical facilities; and laboratory facilities. The present funding arrangements do not provide adequate support for all these components, and need to be overhauled to ensure that they do so. Proper ‘end-to end’ funding is required in universities to fully support research activities with mechanisms that do not have perverse incentives or outcomes, and that better consider the quality and not just the quantity of research delivered. There needs to be a detailed review of response-mode and competitive grants, full Economic Costing (fEC) and Quality-related Research Funding (QR), and where necessary, these funding mechanisms should be reformed or replaced. The present underpinning of UK university research by other commercial income sources, notably fees paid by international students, is valuable, but care is needed as such sources are not always reliable and sustainable.
Government response
Michelle Donelan wrote to Sir Paul to warmly welcome the report:
- the importance of this Review cannot be understated. You have eloquently demonstrated the potential that science, innovation and technology have to change our world and improve all of our lives. To maximise these benefits you make a strong case for the vital role of effective leadership and co-ordination. I strongly agree, and this is why the Prime Minister has recently established a new department in the Department for Science, Innovation and Technology. I am delighted to have the privilege of leading the department to deliver on the UK’s mission to become the most innovative economy in the world and a Science and Technology Superpower. I am confident that this Review will play a foundational role in shaping and delivering that vision. I look forward to working with you to ensure the UK can be at the forefront of critical and emerging fields of science and technology.
- My department will swiftly respond with a package of measures that take account of your advice and I hope to publish that shortly. I am confident that the report’s recommendations offer important ways to further support the world-leading research organisations based in the UK, future-proofing the existing system and helping to support important societal goals around net zero and improving the nation’s health.
The Government also confirm here that they will respond to the [Nurse] Review’s recommendations in the coming months.
Recommendations – full list
- Government should take account of the true cost of ‘end-to-end’ research activity to generate a sustainable RDI endeavour.Government, working with UKRI and the UK higher education funding bodies, should review and when necessary reform competitive and response-mode grant funding, QR (and Devolved Administration equivalents), and full economic costings (fEC), and replace them with improved mechanisms. Overall objectives should be to optimise research delivery, remove perverse incentives and outcomes, and ensure the longer-term sustainability of the research system.
- Universities should develop plans to optimise their operationsin support of research, to empower researchers and reduce their administrative loads, and to improve the quality of support services, core technical facilities, and well-found laboratory buildings and infrastructures. Government, working with UKRI, the UK higher education funding bodies and the wider sector, should consider more transparent mechanisms to provide assurance and accountability on QR funding.
- Government departments should clarify the missions of their individual public sector research establishments (PRSEs), allow them greater freedom of action, and ensure their effectiveness.Departments should improve internal awareness of PSREs’ capabilities, and use PSREs to inform RDI strategy and policy making, working within and across departments. Permeability and agility would be further improved by increasing the visibility, interactions and partnerships between PSREs, and between PSREs and the rest of the RDI landscape, including commercial organisations. Funding streams for PSREs need to be protected and reformed to ensure long-term sustainability. Constraints, which appear to have their origins in the Treasury, over funding, pay and other conditions of working should be reduced. The reforms of funding proposed for the universities should also be applied to PSREs. PSREs should be stringently reviewed, and those that have outlived their purpose or are not working effectively should be reformed, reduced or closed, and any savings generated recycled into Government R&D budgets.
- Institutes and units need sustained financial support, including un-hypothecated funding, to ensure ‘end-to-end’ research support.The funding arrangements of recently established institutes and units, particularly the ‘hub and spoke’ models, must be reviewed to make sure that they are fit for purpose. The reforms of funding proposed for the universities should also take account of the needs of institutes and units. Institutes and units need a well-defined mission and purpose, and should be given the autonomy and funding necessary to achieve their objectives, which may be time limited. There need to be clear and agreed mechanisms by which institutes and units can be adapted, reduced or closed when necessary.
- Institutes and units must have high quality administrative as well as scientific leadership.They generally benefit from being co-located with other research performing organisations (RPOs), but if their overall administration is the responsibility of another co-located or funding organisation, rigorous contractual arrangements must be in place to ensure independence of operation and quality of service.
- New research institutes and units should be considered when strategic RDI priorities best supported by focused research missions are identifiedby Government, UKRI and other funders. Possible examples include enhanced activities in climate change and its mitigation, antimicrobial resistance, synthetic biology, and artificial intelligence. Themes should be identified through mapping and reviewing, taking account of emerging technologies, scientific areas, and Government priorities. Pre-existing institutes and units could be merged and expanded to create new institutes, and consideration should be given to co-location and co-funding with other RPOs. Establishment of new institutes and units should follow the principles outlined in the Review.
- Government and the charitable sector should work togetherto ensure that ‘end-to-end’ funding is provided for research supported by philanthropy.
- Support for research undertaken by galleries, libraries, archives, museums, and the heritage and cultural sectors should be increased, and support for long-neglected collections-based research put in place.
- Coherence between translational research organisations, including those embedded within other RPOs, and the rest of the landscape should be increased.Government is advised to optimise translational research organisations by increasing their number, widening access and promoting the benefits of translational research capability, including regionally. Government should explore routes by which RPOs across the RDI landscape, including PSREs, can contribute to translational activities.
- Government should use its convening power to create a favourable environment for business to invest in RDI, tackling causes identified by this Review as holding back further business investment, and where expedient, providing financial support. Examples of such support are funding which leverages private investment or promotes collaboration between industry and the rest of the RDI landscape.
- To understand the benefits of RDI for commercial activities and the economy, a culture change promoting openness, mutual respect, closer interaction, collaboration, and permeability of ideas, technologies and people has to occurin both business and academia. Government has a role in conveying the benefits of RDI investment to businesses, shareholders and academia, embracing practices from countries with high business RDI investment rates. Mechanisms to deliver this should be explored and implemented.
- Government should take particular responsibility for driving RDI that provides societal benefit as well as economic growth.Examples are health care delivery, equitable regional economic growth throughout the UK, and the delivery of net zero. Where appropriate, public-private partnerships should be encouraged.
- Government and RPOs should partner with local communities to support RDI relevant to their needs, to bring about more equitable regional economic growth based on local expertise and demands and driven by community benefit as well as academic criteria. Universities and other RPOs should support their local community and economy by enhancing their role as an information nexus and by helping local industries link to research capabilities wherever they are in the UK.
- There is an urgent problem with the current mechanisms for clinician scientists to effectively develop and undertake their research careers.The Government, taking into account devolved competencies, must rectify this to both improve the ability of the NHS to deliver more effective health care and to help the UK economy.
- Government must work with UKRI and the wider RDI community toconsider more stable and properly costed funding structures, aimed at ensuring the quality of the existing landscape and its sustainability.
- Government must increase its long-term commitment to invest more in RDI.In addition to reviewing incentives in public funding for university research, Government should review the balance of funding across the landscape, and explore how planned increases in RDI public funding can provide more un-hypothecated core funding for RPOs to allow them to deliver their mission more effectively, to promote collaboration and interaction across RDI sectors, and to empower local RPO leadership and researchers.
- Government should ensure that international collaboration is protected and encouraged, and should resolve problems damaging the UK RDI landscape’s international links. This is particularly relevant to our close scientific collaborators in the EU, and it is essential that the UK associates with Horizon Europe. Government should take action, including consultation with devolved administrations, if its broader policy objectives on areas such as immigration, ODA and education are hindering wider objectives for long-term RDI policy. The UK should consider opportunities to hostnew intergovernmental multinationally funded institutes and international research infrastructures.
- DSIT should define the overall architecture and governance for cross-Government RDI policy, setting out accountabilities from Cabinet and below. This should include the National Science and Technology Council (NSTC), as well as other key RDI spending departments, UKRI and other funders, to ensure roles are complementary, and to improve alignment on policies.
- From Cabinet level downwards, all interested parties in Government must take responsibility for the high level and effective safeguarding of the future success of the UK RDI landscape.This oversight should include an authoritative working group set up by DSIT, operating across Government, the RPOs and the funding organisations, which will take long-term responsibility for implementation of the recommendations of this Review.
- Government should establish a research vision and strategy including long-term programmatic, infrastructure and technological initiatives, which is especially relevant at the applied end of the research spectrum. This will give RPOs, investors and global companies the confidence to invest, operate and interact with the UK RDI landscape.
- Government needs to develop effective mapping of UK RDI, covering the missions, financial investment in different sectors, research capabilities, and locations of RPOs, and also monitor international RDI activities to identify successful features and models. DSIT, working with UKRI and other interests across Government, could carry out this function. An agreed shared picture of the RDI landscape should be produced, together with a commitment to regularly update it.
- Government should increase efforts to link the different elements of the UK RDI landscape together with the commercial, industrial and societal components that benefit from research.To spread the benefits of research through communities across the UK, partnerships, collaborations and interactions must be built so that all components are mutually aware, and permeable with respect to ideas, information, technologies and people.
- Government must replace frequent, repetitive, and multi-layered reporting and audit by Government departments and UKRI with a culture of confidence and earned trust, as also referenced by the Independent Review of Research Bureaucracy. Reporting and reviewing of RPOs should focus on the quality and appropriateness of the research being carried out. The framework by which ARIA will operate should be applied to other components of the RDI landscape.
- Public sector controls which reduce the agility and performance of RPOs need to be reformed.Salaries must be internationally competitive. Where Government-imposed pay limitations are damaging the mission of an RPO, they must be revised, and the decision-making mechanisms made more flexible.
- Government should ensure that there is a well-trained RDI workforce available at all levels, and long-term educational planning to ensure a future pipeline of researchers and technicians.Career pathways for those roles that underpin effective research delivery, including technicians and project and programme managers, should be strengthened so the importance of these roles is better recognised. Training and career structures for early career researchers, including PhD students, post-doctoral researchers and starting faculty, need to be reviewed and reformed. Career path diversity and permeability between different RPOs should be encouraged.
Blogs:
Parliamentary News
Ministerial Change: Michelle Donelan has temporarily stepped away from her role as Secretary of State for Science, Innovation and Technology for her maternity leave. On leaving Donelan tweeted a series of items to highlight the achievements she and colleagues have accomplished whilst she has been in role. It’s a quick reminder on the latest Government policies within science and tech.
Donelan’s SoS role is being covered by Chloe Smith (former work and pensions secretary). Chloe is the daughter of a teacher (mum) and furniture designer (dad). She is a graduate of York University and has held school governance roles. Chloe worked as a Business Consultant for Deloitte UK. She sees herself as a progressive Conservative and is a member of the Tory Reform Group (more on the Left of the Party), voted to Remain in the EU and has announced she will not seek re-election as a MP at the next general election.
Free Speech – imminent: The Free Speech Bill will return to the Commons following the latest Lords amendments on Tuesday 2 May. At a Westminster event last Wednesday a Parliamentarian indicated that this could be it and the Bill may well soon become an Act. There is still widespread concern about the Bill within the sector, primarily because it is unclear how the different provisions within the Bill, such as academic freedom, will play out in practice. The Westminster event highlighted that even Parliamentary Members, expert sector and legal bodies, and University representatives do not interpret aspects of the Bill in the same way. The Bill adds to a complex legislative background where many other Acts influence the ‘ins’ and ‘outs’ should the Free Speech Bill be enacted in its current form. The first few cases brought under the legislation will be crucial in determining how the potential Act will change behaviour in the sector.
As a recap the final stages (ping pong) of the Bill centred on the argument over the inclusion of the statutory tort allowing those who think their free speech rights have been infringed to bring a legal claim for damages against a university or a students’ union. The Lords removed it, the Commons added it back in. Currently a compromise has been reached with the tort as a watered down backstop – included in the Bill as a means of last recourse after complaints processes have been exhausted.
Education Committee: Mohammad Yasin has joined the Education Select Committee. Mohammad is a Labour MP who has demonstrated a keen interest in securing better funding for education, social services and healthcare provision. Chair of the Commons Education Committee Robin Walker has announced his decision to stand down from Parliament at the next General Election. New Chairs of select committees are elected after each general election so this isn’t big news. We simply know there won’t be any continuity between the Chairs and therefore the focus of the business will likely change to a greater degree as a new Chair with new priorities will be selected.
DSIT is being beefed up with three additional ministers:
- Julia Lopez Minister of State for Data and Digital Infrastructure, she also retains her role in DCMS (media, tourism and creative industries). Her responsibilities include Digital infrastructure/ telecoms; data, including Data Protection and Digital Information Bill; data security; Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO); Ofcom. However, she is about to go on maternity leave, so her role will be covered by John Whittingdale. Whittingdale was a DCMS Minister during 2021.
- Viscount Camrose (Jonathan Berry) appointed as Parliamentary Under-Secretary of State for AI and Intellectual Property and Government Spokesperson in the Lords. This is his first ministerial position. He has sat in the Lords since his by-election win in March 2022.
- Stuart Andrew MP appointed Parliamentary Under-Secretary of State for Sport, Gambling and Civil Society; Minister for Equalities covering: sport; gambling and lotteries; civil society and youth; ceremonials, including Coronation; major events, including Eurovision and City of Culture.
Select Committees will reform (from 26 April) to model the new Government departmental structure:
- The International Trade Committee will be dissolved – its scrutiny function will transfer to the BEIS Committee.
- The Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS) Committee will become the Business and Trade Committee, and will scrutinise the work of DBT.
- The Science and Technology Committee (not currently a departmental select committee) will now be renamed the Science, Innovation and Technology Committee, and will now scrutinise the work of DSI (i.e. now be a departmental select committee).
- The Digital, Culture, Media and Sport Committee will become the Culture, Media and Sport Committee, and will scrutinise the work of DCMS. Which makes one wonder why DCMS is retaining its former name. Incidentally if you’re interested in the forthcoming policy priorities check out their newly published ARI.
- A new Energy Security and Net Zero Committee will be established as the Trade Committee is being abolished the SNP will Chair this new committee.
Financial health of HE sector: Wonkhe report on the House of Lords debate on financial pressures in higher education. Lord Knight of Weymouth opening proceedings with the observation that “it appears that the university business model is teetering.” For the government, Baroness Barran argued that “we know that the finances of HE providers are sound when we look at this at a sector level,” though recognised the uneven impact of cost pressures. She drew attention to OfS’ forthcoming report on the financial health of the sector, due next month. You can read the report on Hansard.
Lifelong Learning (HE Fee Limits) Bill
It’s a busy time for HE in Westminster because the Lifelong Learning Bill will proceed through the final legislative Commons stages shortly. We wrote about this Bill extensively in this policy update in March and this is the one that is intended to fundamentally change how the HE sector delivers or packages their provision.
Upon completion the Bill will move to the House of Lords for their scrutiny. Two key amendments have been tabled for the final Commons stages. One seeks to prevent variable fees being changed based on course or subject. The second proposes that one credit equates to 10 learning hours.
For a catch up on the Bill this Library briefing is useful. The briefing also sets out a timeline for the next steps for implementation:
- The roll-out of the LLE will include:
- From 2025, full courses formerly funded by the higher education student finance system and full courses formerly funded through Advanced Learner Loans that can demonstrate learner demand and employer endorsement.
- From 2025, modules of some “job-specific” technical qualifications at levels 4 and 5, including Higher Technical Qualifications.
- From 2027, modular student finance will be extended to levels 4 to 6where the Government “can be confident of positive student outcomes”.
- In autumn 2023, the Government will publish details on the courses eligible for additional entitlement under the LLE, and the principles for calculating the residual entitlement for returning eligible learners.
- In December 2023, the Government will review qualifications currently funded by Advanced Learner Loans (ALLs) to determine which ones should be included within the scope of the LLE.
- By “late 2023”, the Government will provide an update on Sharia-compliant student finance.
- The Office for Students (OfS) will consult “in due course” on the development and introduction of a new third registration category for providers offering LLE-funded course and modules.
Source
The sector reaction to the Bill has been cautiously positive. The Library reports:
- The planned removal of ELQ restrictions and the expansion of maintenance support for living costs to level 4 and 5 subjects was welcomed by many across the education and employment sectors as an important way to ensure learners could access funding to retrain, develop their careers, and fill skills gaps in the economy.
- The Chief Executive of the Association of Colleges (AoC), David Hughes, welcomed the LLE as a potential “game changer”. However, he argued modular learning needs to become more mainstream, and the LLE alone would not change the behaviours and priorities of the vast majority of learners focussed on achieving a traditional undergraduate degree above all else.
- The decision to cap eligibility for the LLE at age 60 has also been described as an “ageist strategy”, while the general secretary of the University and College Union (UCU), Jo Grady, has said more funding was neededso learners could stay in their studies and not leave because of financial reasons, and to ensure providers can adapt courses for modular learning.
For more on the full ‘ins’ and ‘outs’ at each stage of parliamentary consideration of the Bill see this separate briefing.
Wonkhe Blog: Including postgraduate study in the LLE could be expensive, but leaving it out carries risk. Mark Bennett weighs up the potential options and outcomes.
Research
The Department for Science, Innovation and Technology (DSIT) published making Innovation Matter: How the UK can benefit from spreading and using innovative ideas. It aims to bring together insights and analyse innovation enablers and barriers. Here are the most relevant key points:
- Innovation diffusion and adoption (IDA) takes place within a fragmented, complex and poorly intra-connected ecosystem. There are many different stakeholders, organisations and structures influencing IDA. Funding, praise, status and incentives are often centred around having and owning an idea as opposed to its successful application at scale.
- A lack of incentive is compounded by the different skillsets required to support an idea through the early majority stage of innovation. Academic know-how must be combined with entrepreneurial vision, appetite for risk, investment, marketing, sales, logistics and customer service. Taken together otherwise successful innovations fail to make it beyond early adoption because stakeholders are not properly incentivised to go to market and/or do not have the skills to do so.
- Government and Business have already acted to address this issue with a wide range of institutions, accelerators, funds and initiatives to support innovation. Whatever the merits of existing and planned initiatives it is clear from both international experience and domestic data that more can be done, particularly around identifying priorities and challenges, setting out roadmaps with clear direction, using its buying power as anchor customers, and creating the right funding and regulatory environment to enable innovation to thrive.
Opportunities to better understand and improve IDA include:
- Inspire stakeholders and communities to address key innovation challengesin an open and inclusive way, giving them freedom to experiment, with Government taking more of the lead by setting concrete direction.
- Invest in skills(both innovation skills and specialist skills such as in STEM, business, research and professional expertise) and drive collaboration at all levels, including leadership and skills development.
- Broaden the diversityof participation and perspectives and build trust.
- Develop a more joined-up ‘supply chain’ approach, with cross-sector fertilisation of ideas and technologies, and place-based specialisms, creating ‘hubs’.
- Increase funding for diffusion and adoption activitiessuch as improving public sector procurement with multi-year grants for innovations that ensure emphasis on IDA.
- Target supportfor IDA activities, including better metrics.
Science and Technology Framework (and friends)
Recent weeks have seen the publication of a melting pot of various Government strategies, funding initiatives and policy declarations. We try to bring them all together (relatively) simply under the banner of the new Science and Technology Framework.
Published a couple weeks ago the Government’s Science and Technology Framework for the UK sets out the vision for the UK to be a science superpower by 2030. It seeks to identify critical technologies, invest in R&D, develop talent, build international relationships, and do better in communicating the UK’s R&D strengths. The new measures sitting alongside the framework are backed by £500 million of funding.
The Framework is owned by DSIT but will be a coordinated cross-government approach. Here are the 10 key actions:
- identifying, pursuing and achieving strategic advantage in the technologies that are most critical to achieving UK objectives
- showcasing the UK’s science and technology strengths and ambitions at home and abroad to attract talent, investment and boost our global influence
- boosting private and public investment in research and development for economic growth and better productivity
- building on the UK’s already enviable talent and skills base
- financing innovative science and technology start-ups and companies
- capitalising on the UK government’s buying power to boost innovation and growth through public sector procurement
- shaping the global science and tech landscape through strategic international engagement, diplomacy and partnerships
- ensuring researchers have access to the best physical and digital infrastructure for R&D that attracts talent, investment and discoveries
- leveraging post-Brexit freedoms to create world-leading pro-innovation regulation and influence global technical standards
- creating a pro-innovation culture throughout the UK’s public sector to improve the way our public services run
Here’s the funding and policy breakdown:
- £250 million in 3 transformational technologies (AI, quantum technologies and engineering biology) to support industry to tackle the biggest global challenges
- (e.g. climate change and health care). Also part of the framework are semiconductors and future telecoms. More detail on these priorities can be found within the related International Technology Strategy.
- The Nurse Independent Review of the Research, Development and Innovation Organisational Landscapeand implementing the recommendations to make the most of the UK’s research organisations, ensuring they are effective, sustainable and responsive to global challenges.
- Testing different models of funding science, to support a range of innovative institutional models, such as Focused Research Organisations (known as FROs), working with industry and philanthropic partners to open up new funding for UK research. For example, this could include working with a range of partners to increase investment in the world leading UK Biobank, to support the continued revolution in genetic science
- £50 million co-investment in science from the private sector to drive the discoveries of the future.
- £117 million of existing funding to create new PhDs for AI researchers and £8 million to find the next generation of AI leaders around the world to do their research in the UK.
- £50 million uplift to World Class Labs funding to help research institutes and universities to improve facilities so UK researchers have access to the best labs and equipment they need to keep producing world-class science, opening up entirely new avenues for economic growth and job creation.
- £10 million uplift to the UK Innovation and Science Seed Fund, totalling £50 million, to boost the UK’s next tech and science start-ups.
- Set up an Exascale supercomputer facility – the most powerful compute capability which could solve problems as complex as nuclear fusion – as well as a programme to provide dedicated compute capacity for important AI research, as part of the response to the Future of Compute Review.
- £9 million to support the establishment of a quantum computing research centre by PsiQuantum in Daresbury in the North-West.
- Also within this overall policy context is the UKRI’s International Science Partnerships Fund which will support close working with international partners to address global challenges, build knowledge and develop the technologies of tomorrow. More info here; the four themes: resilient planet; transformative technologies; healthy people, animals and plants; tomorrow’s talent. Also the Japan-UK research collaboration in neuroscience, neurodegenerative diseases and dementia; clean energy and climate change with Australia, Canada and the US; and partnership with South Korea for digital health, clean energy, advanced manufacturing and materials, future mobility and smart cities.
- Horizon Europe doesn’t get a mention in the framework – and the Opposition asks why in this parliamentary question.
- Here is Donelan’s Written Ministerial Statement providing a Science and Technology update. It covers the framework and wider policy matters.
- Finally, Sir Patrick Vallance’s Pro-innovation Regulation of Technologies Review: life sciences – while currently at interim findings stage the Government committed to supporting all of Patrick’s recommendations in the March 2023 budget, including providing clarity on the Intellectual Property rules. If you need a refresher browse through our write up in this policy update.
Not particularly insightful, but nonetheless entertaining, was the Opposition’s response to the publication of the Science and Technology Framework. Chi Onwurah, Shadow Minister for Science, Research and Innovation, highlighted the turnover of nine science ministers in the last five years and stated the country deserved a science framework “with a longer shelf-life than a lettuce”.
Horizon
Always in the news but no real movement is the latest on Horizon association. The Windsor Framework resuscitated hope in what had become a Horizon dead duck. The rhetoric from the research associated Government departments continues to indicate progress and the assumption that association is still on the table and desired by both sides.
Here’s the short version of all the recent noise:
- The Government announced another extension (until 30 June 2023) to the financial guarantee to the UK’s Horizon Europe scheme so that eligible and successful bids for calls closing by the deadline will continue to be guaranteed funding. (The particulars are on the UKRI website.) It’s a short extension so speculation (and hope) abounds about what might happen afterwards – June isn’t far off on the horizon.
- Greg Clark (Chair of Science and Tech Committee, and ex-BEIS long standing Secretary of State) is feeling impatient and spoke out urging the Government to accelerate negotiations leading to Horizon Europe association (after the Committee received a dreary letter from DSIT SoS Michelle Donelan following the clawback of £1.65 billion of research funds to the central Government pot in February).
- Following the funding clawback Clark challenged Donelan during the Science and Technology Framework announcements. He called on Donelan to confirm when fresh negotiations for Horizon association would begin and how long until the Government throws in the towel and falls back on Plan B. Finally, he questioned what mechanisms were in place to ensure that, in areas such as batteries, that there was a united and coherent approach across Government, so investors know what the policy is and who to get deal with. Donelan responded to confirm the same level of funding would be available to researchers if Horizon association isn’t achieved: …funding remains available to finalise association with EU programmes. In the event that we do not associate, UK researchers and businesses will receive at least as much as they would have through Horizon over the spending review period. (Hansard.)
- Wonkhe tell us that (then) Scottish Minister for HE & FE Jamie Hepburn made some good point in his letterto Michelle Donelan urging for Horizon Europe association to be secured. He expresses concern that the UK government “appears to be working on the assumption that if we succeed in associating to the Horizon Europe programme, participation will be costed from the point of re-entry,” arguing that this has never been guaranteed. A good point!
- For completeness here are the transitional measures the Government put in place during July 2022 to stop UK research falling into the lack of Horizon abyss.
- Finally, Horizon featured in the first ever DSIT oral questions. Discouraging, but not unexpected, was confirmation that the government’s position was unchanged, and discussions are ongoing.
Parliamentary Questions:
Quick Research News
- UKRI has publishedits EDI strategy, setting out four strategic objectives to achieve its aim of fostering a research and innovation system “by everyone, for everyone”. (Wonkhe)
- (Not) Levelling up: The R&D funding ecosystem just isn’t designed to level up the country. James Coe investigates where R&D funding is spent and what that means for levelling up. (Wonkhe Blog.)
- Recognition: Wonkhe report that Science Europe, which represents research organisations around Europe including UKRI, has released recommendations on recognition systems in research and case studies of good practice. It has also become a signatory of the San Francisco Declaration on Research Assessment (DORA).
- India cooperation: Wonkhe report that the UK signed a memorandum of understanding with India at yesterday’s UK-India Science Innovation Council meeting in Parliament. The agreement is intended to “remove red tape” to enable more efficient and effective joint research projects into major issues such as climate change, decarbonisation, pandemic preparedness, and artificial intelligence – among other programmes. Science Minister George Freeman believes this move will create skilled jobs and drive economic growth. India was also named as a partner for the UK’s International Science Partnerships Fund which will see £5 million UK funding – to be matched by India – for research into Farmed Animal Diseases and Health, and £3.3 million UK funding – also to be matched by India – towards a technology and skills partnership programme.
- AI: The Government has announced the creation of a new Foundation Model Taskforce which will be responsible for accelerating the UK’s capability in a rapidly emerging type of artificial intelligence (AI). The Taskforce will be backed by £100m in funding, and modelled on the success of the COVID-19 Vaccines Taskforce – its main aim will be to develop the safe and reliable use of these AI systems across the economy to ensure the UK is globally competitive in this technology. Foundation models – including large language models such as ChatGPT and Google Bard – are a category of AI trained on huge volumes of data such as text, images, video or audio to gain broad and sophisticated capabilities across many tasks. The Government say that, in areas such as healthcare, this technology has potential to speed up diagnoses, drug discovery and development, and that in education it could transform teachers’ day-to-day work by freeing up more time. The Taskforce, announced as part of the Integrated Review Refresh last month, will bring together government and industry experts and report directly to the Prime Minister and Technology Secretary. The Taskforce’s expert Chair is yet to be appointed (announcement due summer 2023).
- Horizon Europe related parliamentary questions: UK funding share; the costs of Pioneer (the alternative programme); where the Pioneer funding is coming from; the negotiating position for UK contributions to Horizon Europe. On this last question Minister George Freeman stated: The Government are discussing association to Horizon Europe with the EU and hope our negotiations will be successful. That is our preference. We will not be providing a running commentary on these discussions. Association would need to be on the basis of a good deal for the UK’s researchers, businesses and taxpayers. If we are not able to secure association on fair and appropriate terms, we will implement Pioneer – our bold, ambitious alternative.
- George Freeman’s (Minister for Science, Research, and Innovation) responsibilities have been confirmed. They include:
- international science and research
- domestic science and research ecosystem, including university research and public sector research establishments (PSREs)
- Horizon Europe
- R&D People and Culture Strategy
- Innovation Strategy
- space sector
- life sciences
- quantum
- engineering biology
- place and levelling up
- regulation of innovation, including the Regulatory Horizon Council
- Research Professional has a quick read on the links between universities, place and inward investment (particularly in light of the Budget’s Investment Zones announcements).
- REF: The Research Excellence Framework (REF) encourages “higher quantity and lower quality” of academic output, according to a study from a group of researchers led by Queen Mary, University of London’s Moqi Groen-Xu. The research found that papers published in the run-up to REF deadlines generally received fewer citations and were more likely to be retracted than those published after REF assessments. The authors call for better support for long-term exploratory research. (Wonkhe.)
- The House of Commons Science and Technology Committee has published a report on diversity in science, technology, engineering and maths (STEM). In the report Dods tell us that MPs highlight the underrepresentation of people from Black Caribbean backgrounds, and others, across all STEM subjects throughout education and work. A low uptake of physics and computer science in girls at school as well as persistent issues with women’s career progression in STEM also stand out. MPs say it is “sadly notable” that many of the conclusions from a predecessor Committee’s 2014 report on women in science could still apply today. The Committee recommends a series of changes to education policy, following the Prime Minister’s commitment to grow STEM pupil numbers. MPs call on the new Department for Science, Innovation and Technology to make improving diversity and inclusion in STEM part of its mission, and to set out how it intends to achieve this.
- Michelle Donelan introduced the Data Protection and Digital Information Bill
- AI & Data Science Scholarships: The OfS confirmed £8.1 million new funding from DSIT and the Office for Artificial Intelligence for universities to deliver AI and data science scholarships to underrepresented groups. The funding runs from April 2023 for one year, with a possible additional one year extension. The programme has run before and the interim report found the scholarships attracted a diverse student profile. However, the in the previous iteration more scholarships were awarded to international students as the scheme progressed and recently UK students received less than half of scholarships. On outcomes most students quickly secured jobs that specialise in or use data and/or AI. DSIT also published an AI regulation white paper. Secretary of State, Michelle Donelan, made a ministerial statement here.
Parliamentary Questions:
Students
Sharia Compliant Finance
Previously DLUHC appointed an Independent Faith Engagement Adviser to review how the Government should engage with faith groups in England. The Adviser, Colin Bloom, recently published the review report. The report includes a recommendation for Sharia compliant finance and places a firm timescale on the Government:
- Government should accelerate proposals to introduce Sharia-compliant student loanson equalities grounds. Faith-sensitive student finance should be made available from the beginning of academic year 2024-25.
Sharia compliant finance feels like one of the slowest progress policy priorities within HE. The Government first proposed a student finance product consistent with Muslim beliefs regarding interest-bearing loans in 2013. The Higher Education Research Act, passed in 2017, allows the Government to introduce such a product in England, but it has yet to do so. The issue has been raised in Parliament a number of times, with the delay described as “shameful” by Lord Sharkey.
Following the Lifelong Learning Entitlement (LLE) Consultation the Government announced Sharia compliant finance would not be ready as part of the LLE launch in 2025 but that the Government remained committed to delivering such a product “as soon as possible after 2025”. A parliamentary Library briefing on the topic informs that findings from the Muslim Census study suggest over 12,000 students per year are affected (deterred from taking out loans which acts as a barrier to entering HE or causes financial hardship).
It remains to be seen whether Bloom’s timescale will be met by the Government – it seems unlikely given the Government have already ruled out including Sharia compliant finance within LLE in 2025.
On other student finance matters Wonkhe have a new blog – As the state reduces its support for students in real terms, Jim Dickinson considers the role of institutional student finance measures in addressing the cost of living crisis.
Spiking
The Labour party intend to make spiking a specific offence if they are elected to government. It would form part of several measures aiming to tackle violence against women and girls (VAWG) and broaden the Labour party’s “tough on crime” credentials. Dods report that the Home Affairs Committee previously recommended the creation of a new standalone offence, however the Government’s response to the inquiry’s findings suggested this wasn’t necessary as there were already measures and guidance in place to improve reporting, data collection and police response to incidents. The Committee’s inquiry focused heavily on night-time venues, and heard from many in the university sector about the prevalence and nature of spiking on campuses. UUK also published a practice note for HEIs to support their response to spiking.
Student Accommodation
Wonkhe – Over half of students living in the private rented sector have experienced damp or mould on walls or ceilings, and half say their accommodation is poorly insulated, according to a new report from SOS-UK in partnership with Universities UK. Homes Fit for Study 2023. Universities UK has published a note on how universities can support students facing fuel poverty. ITV news has some experiences from students up on YouTube.
Duty of Care
The petition to Parliament for universities to have a legal duty of care for students (started by the families of student’s who took their own lives) has reached a significant threshold and the matter will be debated on Monday 5 June. Previously the Government responded to this petition:
- Higher Education providers do have a general duty of care to deliver educational and pastoral services to the standard of an ordinarily competent institution and, in carrying out these services, they are expected to act reasonably to protect the health, safety and welfare of their students. This can be summed up as providers owing a duty of care to not cause harm to their students through the university’s own actions.
- Over the last decade, higher education providers have devoted considerable resources to their student support services, and a good deal of support is now widely provided to students who struggle with their mental health. However, tragically suicides do still occur in higher education, and investigations into the circumstances of such deaths have sometimes shown the support offered by the university was not all it might have been. We have encouraged universities to learn from such cases and redouble their prevention efforts.
We’ll bring you the outcome of the debate after it takes place.
Cost of living
The APPG for Students published their Report of the Inquiry into the impact of the cost-of-living crisis on students. They conclude that most students are facing significant financial pressures, with some groups particularly hard hit, risking academic outcomes and participation in the extra-curricular activities that are so valuable for future careers. We are concerned that this is unfair on a generation of students already affected by the pandemic, and risks widening inequality.
… Alongside reports of students cutting back on meals and other essentials, as many other people, we were struck by evidence of the additional hours many students were working to cover their costs and the development of a ‘grab and go’ approach to their qualifications, as they can no longer invest time and energy in participating in all the other aspects of student life that prepare them for employment, having an impact not just on the tertiary education sector, but on a generation of working adults.
The inadequacies of relying on current hardship measures are acknowledged:
…we must not only provide students with the necessary immediate financial assistance – through increased hardship funding and restoring maintenance loan entitlements – but also to address issues in the student funding system which have seen student support incrementally reduced in real terms over several years and reduced resilience as inflation has risen sharply over the last two years. We have noted the increase in university support and believe that there is more that could be done to ensure all students are helped but recognise that current services are designed to help small numbers of students in emergencies, and not hardship experienced by a large proportion of the student body.
The APPG calls on the Government to provide a financial solution:
… We recognise the demands and pressures across every area of government spending but feel that our recommendations for both an immediate spending commitment to support students who have been placed in significant financial hardship, as well as longer-term changes are needed for both current and prospective students.
The OfS published an insight brief – Studying during rises in the cost of living. They conclude: Universities, colleges and students’ unions have worked innovatively and at speed to help alleviate these pressures, with additional help from government for their hardship funds. These responses have been diverse, and the support available has varied from university to university. The mitigating activities…may not all be sustainable over a long period. It’s worth a scan through to read the box sections covering actions by universities (financial needs, warm spaces, food needs).
- Part time work dramas: 30% of students are unsuccessful in finding part-time work because of their scheduled classes.
- 72% report that their timetable stopped them securing more hours at work.
- 76% found it challenging to attend scheduled teaching on time – due to classes scheduled at inconvenient times of the day, not having enough time to get from one class to another, not being able to find the lecture room or seminar location.
- Asked why they had a job, 52% of student said it was to fund their basic lifestyle (pay for rent, utilities, food, etc.), 49% blamed the rising cost of living, 33% wanted to fund a comfortable lifestyle (pay for night outs, clothes, holidays, etc) – given the percentages don’t tall presumably students could select multiple categories for the reason to work.
- 53% of students have a part time job alongside their studies. 32% do not have a job but would like one and 5% full time.
Source – FE News
Cost of living blogs:
Students: Quick links
Wonkhe content:
Parliamentary Questions
Admissions
Wonkhe report on the House of Commons Education Committee’s latest report – The future of post-16 qualifications which calls on the government to pause the withdrawal of funding for existing level 3 technical qualifications (such as BTECs) until evidence is available that T Levels are more effective at meeting student and employer needs and promoting social mobility. The report notes that universities are often requiring applicants to offer A levels alongside T levels (the latter being nominally equivalent to three A levels), and calls on DfE to work with universities to avoid “unreasonable” entry requirements. The report is covered on BBC News.
Wonkhe: Fewer significantly disadvantaged and economically precarious students are entering higher education in England – and they are less likely to complete their degree and progress to skilled employment or further study than their peers, new data from the Office for Students (OfS) shows. CEED, one of its new and updated key performance measures, shows that 53.6 per cent of the most significantly disadvantaged students progress to further study or skilled jobs, compared with 68.4 per cent of students who are neither “significantly disadvantaged” nor “economically precarious”. 49,600 students categorised as significantly disadvantaged entered in 2021/22, a decrease from 51,100 in the previous year. KPM 8, which measures the proportion of subjects taught and the number of higher education providers (relative to population) in each English region, shows that the North East has the lowest level of subject diversity in the country for full time students, and KPM 7 on Degree attainment by ethnicity shows that students receiving first class degrees in 2021-22 was 15 percentage points lower than the proportion for all students.
Access & Participation
Advance HE has published the Disabled Student Commitment which was developed by the OfS funded independent strategy group the Disabled Students’ Commission. The Commitment draws on three years of consultation with disabled students and sets out a framework of 43 recommendations for HEIs, Government, funders, agencies, regulators and professional, statutory and regulatory bodies. It highlights expectations for information sharing and consent and offers guidance on key touchpoints of the HE journey, outlining the commitments that HEIs and others should make to give disabled students confidence their needs and expectations will be met.
Professor Geoff Layer, chair of the Disabled Students’ Commission, said: We have developed this Commitment because disabled students have told us they want communication, consistency, certainty and choice. The Commitment is a call to the sector and sector bodies to make the step-change required to create a more inclusive environment. We need to create a sense of belonging in which students are able to focus on what they went into higher education for, and not spend untold hours fighting their way through the system.
Professor Layer said the Commission was asking providers to work in partnership with their disabled students on a statement of commitment which should be updated annually and published on their website, alongside a logo of the Disabled Student Commitment so that disabled students and applicants have confidence in the system, allowing them to get on with their education.
New data dashboard and risks plan for A&P
OfS published new data on HE access and participation. The completion rates data highlight:
- 6% of students from the most deprived backgrounds completed their course (92% from the most advantaged group)
- 5% of students eligible for free school meals completed their course (91% non-free school meals)
- 7% of black students completed their course (88.5% of white students)
There is lots more to explore in the data dashboard.
OfS also published their new Equality of Opportunity Risk Register (EORR) and expect universities to consider the listed range of equality risks when planning. It includes risks relating to the perception that HE might not be right for people from disadvantaged backgrounds, or concerns about academic and personal support for those at university, students’ mental health, the continuing impact of the pandemic on education opportunities, and pressures on living costs.
OfS has also published the outcome and analysis of responses to their consultation on a new approach to regulating equality of opportunity plus a commentary from OfS Fair Access and Participation Director.
Impact of online teaching on student outcomes
TASO published online teaching and learning – lessons from the pandemic. Executive summary here; rapid evidence review here.
Here are their key findings:
- Existing evidence is mixed; there are a small number of studies which suggest online teaching and learning can maintain or improve outcomes for some groups, but overall, the move to online learning appears associated with worse student outcomes.
- Pre-pandemic literature (compared to purely online learning) suggests ‘blended’ learning (e.g., a combination of face-to-face and online learning) is more likely to improve student attainment. Whereas the literature produced during the pandemic demonstrates that the rapid shift to an online format had a negative impact on student outcomes.
- In the post-pandemic literature, there is some evidence that, prior to applying any type of ‘no detriment’ control in an attempt to account for the impact of the pandemic on students’ performance, learners from low-income backgrounds and academically at-risk students may be most likely to be negatively impacted by the shift online. However, this was not universal in the case studies they reviewed.
- Course design is an important factor to consider when planning online learning, as its efficacy is highly dependent on a number of design choices. However, this planning was not possible with the emergency switch to remote learning, where the priority was to adapt promptly to unforeseen crisis circumstances.
- Design features – the existing evidence suggests that courses which encourage active engagement through planned student-student interactions and opportunities for feedback between teaching staff and students increase student attainment.
- Digital poverty is thought to be the largest barrier to the success of online teaching and learning and will most likely disproportionately impact disadvantaged groups. Students from more privileged backgrounds may have better access to the internet and more sophisticated devices.
Recommendations:
- The design of online courses is important: A concerted effort should be made to design online courses rather than simply moving face-to-face materials into the online environment. Effective design features include:
- Coordinated student-to-student interaction via discussion boards and chat rooms.
- Feedback between teaching staff and students.
- Appropriate frequency and timing of online teaching and assessment to avoid student fatigue.
- HEIs should make use of their institutional data and differing pedagogical approaches to design and conduct evaluations that allow us to draw strong conclusions about what works in the UK context. Our data analysis provides a foundation and blueprint for future work of this sort.
- As students from disadvantaged backgrounds may be more likely to be adversely impacted by the shift to online teaching, learning and assessment, future research should focus on their experiences and outcomes.
A & P Blogs:
Graduate Careers
Wonkhe report on the Institute of Student Employers’ annual report on development programmes for graduates and apprentices. 54% of employers surveyed agreed that graduates were “career ready” at the point of hire (31% unsure). The report covered 162 responses from student employers who collectively hired over 26,000 graduates in 2021–22.
HESA published National Careers Week: Career trends of graduates from the class of 2019/20.
Careers: Wonkhe blog – The idea that a postdoc is a route to an academic career downplays other career possibilities. Lucy Williams and James Howard have been helping postdocs prosper with tailored advice and support.
International
Wonkhe report that: there has been a 65% increase in the number of international students at English higher education providers over the past four years, with growth of over 100,000 in the past year alone. The figures come from the delayed Office for Students’ Higher Education Students Early Statistics survey (HESES), which provides an early indication of the number of higher education students studying in 2022-23.
They also show that the home v international split for postgraduates in the English system is now roughly 50:50, and that providers are forecasting that circa 320k students will not complete by the end of the year, up from 300k a year ago.
Blog: New English student numbers figures show how rapidly universities are changing size and shape. David Kernohan and Jim Dickinson consider if the regulation can keep up
Scottish Minister for Higher Education and Further Education, Youth Employment and Training Jamie Hepburn answered questions on international students and accommodation.
Wonkhe: Home Office proposals to limit the number of international student dependant visas are receiving a “major pushback” from the Treasury, i News reports. It says Chancellor Jeremy Hunt is resisting Home Secretary Suella Braverman’s proposals, arguing they would inflict “major damage” on the British economy.
HEPI
The Higher Education Policy Institute has published a range of interesting blogs and briefings recently. You may be interested in:
Degree Apprenticeships
- The OfS confirmed £16m of recurrent fundingto expand the development and delivery of HE qualifications, of which £8m will support the development of Level 6 degree apprenticeship training programmes and £8m to increase the provision of Level 4 and 5 qualifications. Minister for Skills, Apprenticeships and Higher Education Robert Halfon said: Degree apprenticeships offer people of all backgrounds an alternative route to achieving their career goals than doing a traditional three-year degree. They enable students to earn while they learn the skills needed to build a successful career. I’m delighted that the OfS is continuing to support and encourage HE providers to expand their degree and degree level apprenticeship offer…This investment will help us continue to build a skills and apprenticeship nation and extend the ladder of opportunity to even more people.
- Wonkhe report that the Independent has been investigatinghow some universities are still using the apprenticeship levy to part-fund MBAs.
- The Science Industry Partnership published a manifesto for skills in the science industries. The report outlines four priorities for technical education and workplace learning. It includes making the apprenticeship levy work for employers and increasing equity through diverse career pathways.
- The UCL Centre for Education Policy and Equalising Opportunities published their evidence-led policy priority calls which they believe are essential to equalising opportunities in society. They call for:
- reform to apprenticeship rules to ringfence a proportion of the levy for young people with lower qualification levels, they also entertain that if other changes were made levy funds could be entirely ringfenced for school leavers. This to reduce the number of apprenticeships going to existing employees instead of other internal training.
- Expand accountability to all providers of post-16 education to help reduce NEET rates. To make these metrics meaningful and minimise ‘gaming’, providers should be compared against other providers offering similar courses, in areas with similar socio-economic characteristics.
- Introduce an annual “Social Mobility Scorecard” for universities, showing the proportion of students from disadvantaged backgrounds attending each university, and the earnings associated with each degree. This should be released by the government to confer official status…There is wide variation in earnings across different degrees, and disadvantaged students are less likely to attend those with high labour market returns, even when they have the qualifications to get in. If we judge universities and courses based only on their outcomes, rather than their intake, their contribution to social mobility will be limited.
- Introduce a post-qualification applications (PQA) system for post-18 education (including further education) so that students would make applications after they sit exams and receive the results. A PQA system could be achieved with minimal disruption to the school year (or college/university start date), by condensing the exam period to four weeks (as was planned during the pandemic), and accelerating marking to 7-8 weeks. Examinations would take place in early May. Students would then return to school, receiving results in mid-July, in time for an in-school ‘applications week’. Universities and colleges would have over a month to process and make offers at the end of August, and students would then have time to accept their favoured choice… allowing students to make these life changing applications based on full information.
- Finally, UCAS stated they’re collaborating with the Institute for Apprenticeships and Technical Education (IfATE) to enable apprenticeships to qualify for UCAS points. They anticipate UCAS points may be attached to apprenticeships by the end of 2023. Dods report: The plans represent another step on UCAS’ bid to give parity between apprenticeships and other post-16 study routes, however it is not yet clear how many points apprenticeships may be eligible for, or whether they will secure as many as other level 3 routes. The Department for Education said that offering the ability to apply for apprenticeships through UCAS from 2024 is part of a wider ambition to develop a “one-stop-shop” for education and training options that it hopes will eventually include apprenticeships, T Levels, skills bootcamps, higher technical qualifications and degree apprenticeships.
Other news
The DfE published a policy paper on the use of generative artificial intelligence (AI), including large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT or Google Bard, within the education sector. Snippets:
- Although generative AI is not new, recent advances and public access to the technology mean that the general public can now use this technology to produce AI-generated content. This poses opportunities and challenges for the education sector.
- When used appropriately, technology (including generative AI), has the potential to reduce workload across the education sector, and free up time, allowing a focus on delivering excellent teaching.
- Schools, colleges and universities, as well as awarding organisations need to continue to take reasonable steps where applicable to prevent malpractice, including malpractice involving use of generative AI and other emerging technologies.
- The education sector must continue to protect its data, resources, staff and students, in particular:
- Personal and sensitive data must be protected and therefore must not be entered into generative AI tools.
- Education institutions should review and strengthen their cyber security, particularly as generative AI could increase the sophistication and credibility of attacks.
- Education institutions must continue to protect their students from harmful content online, including that which might be produced by generative AI.
Strategic Skills planning: The DfE Unit for Future Skills published the UK labour market projections up to 2035 (national, regional and local). You can display the data by LEP or other choices and it provides information to support local skills plans, careers guidance, and provides a projected picture of the type of jobs in the UK labour market (and the skills needed) up to 2035. Data here.
Carbon capture curriculum: The Scottish Affairs Committee has published a report on hydrogen and carbon capture in Scotland. It warns that the UK will fail to meet its net zero targets, and transition away from fossil fuels, unless carbon capture is rolled out at scale. The report calls for the UK and Scottish Governments should jointly set out work they are undertaking to ensure that colleges, training providers and businesses within the hydrogen and CCUS sectors are able to offer appropriate routes into employment and training, and providing this information should be viewed as a priority.
President UUK: UUK announced that Professor Dame Sally Mapstone FRSE, Principal and Vice-Chancellor of University of St Andrews, has been elected as its next President. The role runs for two academic years from 1 August 2023 and is elected through a ballot of UUK’s 140 members. Dame Sally will succeed current President, Professor Steve West CBE, Vice-Chancellor of UWE Bristol. Before her appointment as Principal and Vice-Chancellor of the University of St Andrews in 2016, Dame Sally lectured and held several leadership roles at the University of Oxford, including Pro-Vice-Chancellor for Personnel and Equality and Pro-Vice-Chancellor for Education. She has served as a Board Member of UUK since 2016 including currently as Vice-President for Scotland, by virtue of being Convener of Universities Scotland.
Late retirement: The Times reports that graduates could work longer under plans to allow people in manual jobs to claim their state pensions earlier (Wonkhe).
Subscribe!
To subscribe to the weekly policy update simply email policy@bournemouth.ac.uk. A BU email address is required to subscribe.
External readers: Thank you to our external readers who enjoy our policy updates. Not all our content is accessible to external readers, but you can continue to read our updates which omit the restricted content on the policy pages of the BU Research Blog – here’s the link.
Did you know? You can catch up on previous versions of the policy update on BU’s intranet pages here. Some links require access to a BU account- BU staff not able to click through to an external link should contact eresourceshelp@bournemouth.ac.uk for further assistance.
JANE FORSTER | SARAH CARTER
VC’s Policy Advisor Policy & Public Affairs Officer
Follow: @PolicyBU on Twitter | policy@bournemouth.ac.uk
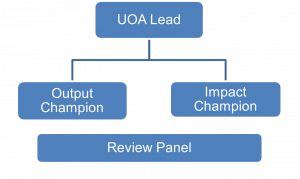 We are currently preparing submissions to thirteen units (otherwise known as UOAs). Each unit has a leadership team with at least one leader, an output and impact champion. The leadership team is supported by a panel of reviewers who assess the research from the unit. This includes research outputs (journal articles, book chapters, digital artefacts and conference proceedings) and impact case studies.
We are currently preparing submissions to thirteen units (otherwise known as UOAs). Each unit has a leadership team with at least one leader, an output and impact champion. The leadership team is supported by a panel of reviewers who assess the research from the unit. This includes research outputs (journal articles, book chapters, digital artefacts and conference proceedings) and impact case studies. Would you like to play a key role in supporting preparations for the Engagement & Impact element of BU’s REF2029 submission?
Would you like to play a key role in supporting preparations for the Engagement & Impact element of BU’s REF2029 submission?
 As part of the RKEDF Impact Essentials programme, booking is now open for the Impact Essentials: creating your impact development plan 2-hour in-person workshops. There are 4 dates to choose from and they will be delivered on both Talbot and Lansdowne campuses, so hopefully there will be a date and time that is convenient for everyone who would like to attend.
As part of the RKEDF Impact Essentials programme, booking is now open for the Impact Essentials: creating your impact development plan 2-hour in-person workshops. There are 4 dates to choose from and they will be delivered on both Talbot and Lansdowne campuses, so hopefully there will be a date and time that is convenient for everyone who would like to attend.

 An opportunity has arisen for an Impact Champion for Unit of Assessment (UOA) 23 (Education) to help drive preparations for the next REF. This role would initially be until summer 2022.BU is making early preparations towards units of assessment (UOAs) for the next Research Excellence Framework (REF) exercise. Each UOA has a UOA Leader, supported by Impact and Outputs Champions. The roles are recruited through an open and transparent process, which gives all academic staff the opportunity to put themselves forward for UOA Leader roles.We are currently seeking expressions of interest (EoI) from academic staff interested in supporting impact development for UOA 23 (Education). Impact Champions play a key role in shaping the impact element of their UOA’s submission, working closely with their Faculty’s Impact Advisor.Key responsibilities of the Impact Champion role include:
An opportunity has arisen for an Impact Champion for Unit of Assessment (UOA) 23 (Education) to help drive preparations for the next REF. This role would initially be until summer 2022.BU is making early preparations towards units of assessment (UOAs) for the next Research Excellence Framework (REF) exercise. Each UOA has a UOA Leader, supported by Impact and Outputs Champions. The roles are recruited through an open and transparent process, which gives all academic staff the opportunity to put themselves forward for UOA Leader roles.We are currently seeking expressions of interest (EoI) from academic staff interested in supporting impact development for UOA 23 (Education). Impact Champions play a key role in shaping the impact element of their UOA’s submission, working closely with their Faculty’s Impact Advisor.Key responsibilities of the Impact Champion role include:










 Read and sign up to BU’s Policy Influence Digest
Read and sign up to BU’s Policy Influence Digest Upcoming opportunities for PGRs – collaborate externally
Upcoming opportunities for PGRs – collaborate externally BU involved in new MRF dissemination grant
BU involved in new MRF dissemination grant New COVID-19 publication
New COVID-19 publication MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024 Horizon Europe News – December 2023
Horizon Europe News – December 2023