 On World Refugee Day 2025, Friday 20 June, the new Maternal and Infant Health Equity Research Centre (MIHERC) website was launched. MIHERC is a hub for research, collaboration and action on maternal and infant health equity. MIHERC) is a collaborative effort between Sheffield Hallam University, Bournemouth University and City of Doncaster Council working to reduce health inequalities for mothers and babies. This year’s World Refugee Day’s theme, hashtagSolidarity, reflects MIHERC’s mission to stand with all mothers and babies – especially those facing health and social inequalities or barriers to care.
On World Refugee Day 2025, Friday 20 June, the new Maternal and Infant Health Equity Research Centre (MIHERC) website was launched. MIHERC is a hub for research, collaboration and action on maternal and infant health equity. MIHERC) is a collaborative effort between Sheffield Hallam University, Bournemouth University and City of Doncaster Council working to reduce health inequalities for mothers and babies. This year’s World Refugee Day’s theme, hashtagSolidarity, reflects MIHERC’s mission to stand with all mothers and babies – especially those facing health and social inequalities or barriers to care.
Category / BU Challenges
BU seeking input from ethnic minority and migrant communities
 Bournemouth University has received funding from the NIHR to support an internship for a Social Work student to seek views and perception of women from ethnic minority and migrant communities. Therefor, we are seeking volunteers to take part in a small group on-line workshop to hear from women from ethnic minority and migrant communities. They are invited to share their thoughts, insights and experiences of engaging in health research so that we can better understand what would work when conducting research with this population. This work sits within a larger NIHR-funded project that aims to reduce health inequalities for marginalised mothers and babies. BU Profs Huseyin Dogan and Professor Vanora Hundley are leading workstreams within this prestigious NIHR Maternity Disparities project over the next five years (more information about the bigger project can be found here!).
Bournemouth University has received funding from the NIHR to support an internship for a Social Work student to seek views and perception of women from ethnic minority and migrant communities. Therefor, we are seeking volunteers to take part in a small group on-line workshop to hear from women from ethnic minority and migrant communities. They are invited to share their thoughts, insights and experiences of engaging in health research so that we can better understand what would work when conducting research with this population. This work sits within a larger NIHR-funded project that aims to reduce health inequalities for marginalised mothers and babies. BU Profs Huseyin Dogan and Professor Vanora Hundley are leading workstreams within this prestigious NIHR Maternity Disparities project over the next five years (more information about the bigger project can be found here!).
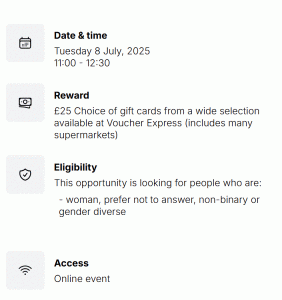
 We would like to hear from women from ethnic minority and migrant communities, also referred as women from the global majority. You do not need to be pregnant or have had a baby to participate in the workshop. If you are a woman from an ethnic minority and migrant community in the UK and you would like to take part please apply here! The event will be online on Tuesday 8th July from 11.00-12.30. No specific experience of involvement in research is required.
We would like to hear from women from ethnic minority and migrant communities, also referred as women from the global majority. You do not need to be pregnant or have had a baby to participate in the workshop. If you are a woman from an ethnic minority and migrant community in the UK and you would like to take part please apply here! The event will be online on Tuesday 8th July from 11.00-12.30. No specific experience of involvement in research is required.
Dr. Orlanda Harvey and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Faculty of Health & Social Sciences
PhD supervision is good for you
Some people in academia (and many outside it) don’t appreciate the importance of PhD supervision . An academic supervising PhD students is not merely for the educational purposes, or in other words, for the benefits of the postgraduate student. The value of postgraduate supervision lies in pushing the boundaries of knowledge, about testing new ideas, new approaches or even new methods.
Interestingly, enough it means that PhD supervision for an academic is also about developing their own ideas, expanding one’s CV, and developing one’s career. Whilst for the university it is also for the wider benefit of research for the wider society. The latter means that PhD students help improve the REF (Research Excellence Framework) scores for a university, through metrics such as number and proportion of PhD completions, but also through papers based on PhD research co-authored with staff. It always amazes me how some outsider regard PhD supervision as simply more of the same, i.e. not that different from supervising an undergraduate student.
Looking at my ow CV, some of my best papers have been co-written with PhD students, including my most cited paper on SCOPUS [1]. Moreover, as the graph of my h-index [checked SCOPUS for May 19th 2025] shows four of my top eight highest cited papers were co-authored with postgraduate students [1-4]. Papers that would not have been written without the postgraduate student conducting knowledge-advancing research! 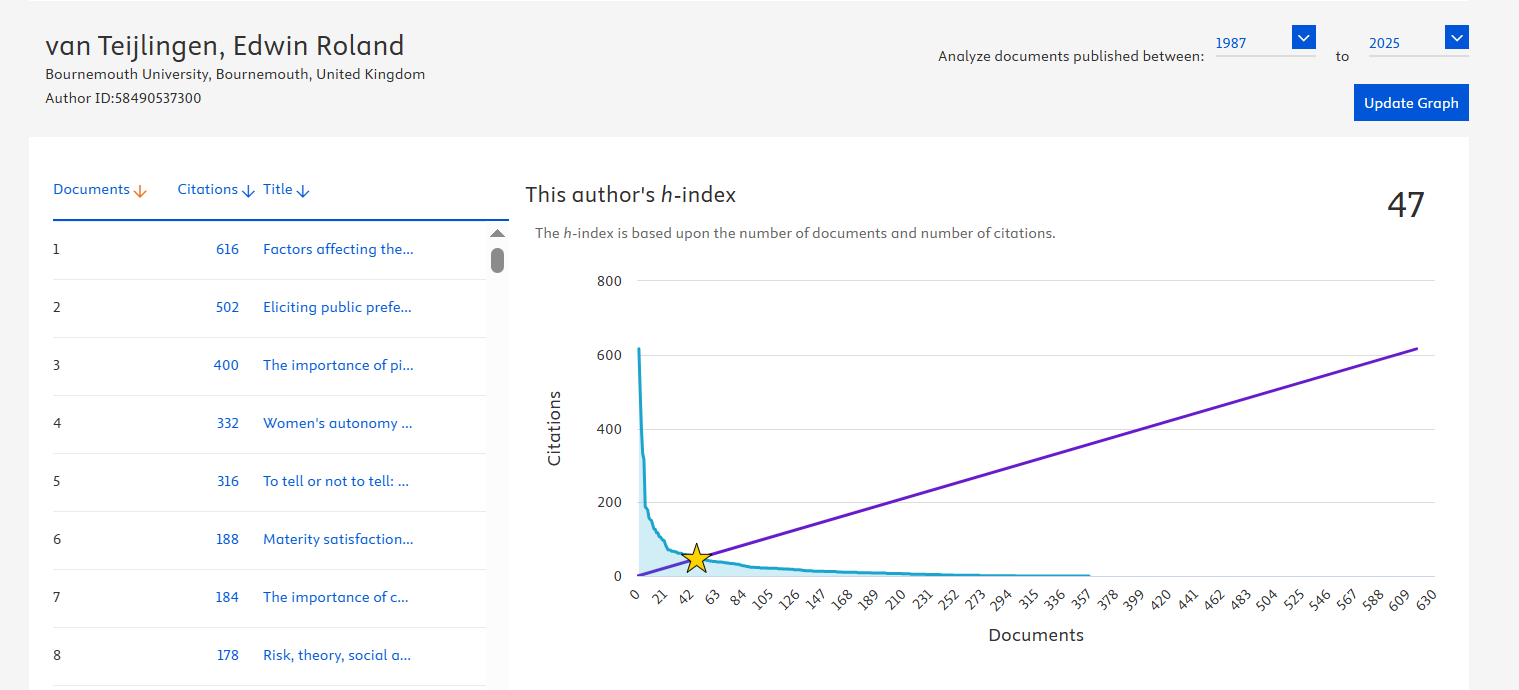
Not surprisingly, three of the four former PhD students who co-authored these highly-cited papers are now in academic positions across the UK (the fourth one has retired). These four highlighted papers are not just looking good on my CV, they are also highly ranked within their respective journals. The first paper [1] is the 28th most cited paper in the Journal of Advanced Nursing, an impressive 28th position out of 12,762 articles ever published by this international journal. Similarly, the paper ‘Women’s autonomy in decision-making for health care: Demographic study in Nepal’ [2] is the 10th most cited paper in Reproductive Health, whilst ‘ To tell or not to tell: Barriers and facilitators in family communication about genetic risk’ [3] is the 20th most article in Clinical Genetics. Last, but not least, ‘Risk, Theory, Social & Medical Models: critical analysis of the concept of risk in maternity care’ [4] is the 17th most cited article (out of 3,910) in the international journal Midwifery.
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health
References:
- Simkhada, B., van Teijlingen E., Porter, M., Simkhada, P. (2008) Factors affecting the utilisation of antenatal care in developing countries: a systematic review of the literature, Journal of Advanced Nursing 61(3): 244-260.
- Acharya, D.R., Bell, J., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E, Regmi, P.R. (2010) Women’s autonomy in decision-making for health care: Demographic study in Nepal. Reproductive Health 9(15) reproductive-health-journal.com/content/pdf/1742-4755-7-15.pdf
- Forrest, K., Simpson, S., Wilson, B.J., van Teijlingen E, McKee L, Haites, N., Matthews E. (2003) To tell or not to tell: Barriers and facilitators in family communication about genetic risk,Clinical Genetics, 64: 317-26.
- MacKenzie Bryers H., van Teijlingen, E. (2010) Risk, Theory, Social & Medical Models: critical analysis of the concept of risk in maternity care, Midwifery 26(5): 488-496.
Sarah Morton, PhD student short listed for Nursing Times Award.
 Congratulations to Sarah Moreton, PhD student at Bournemouth University, who was nominated and shortlisted for her research into the challenges faced by the nursing workforce in implementing the COVID-19 vaccination programme during the pandemic. A great achievement Sarah – very well done.
Congratulations to Sarah Moreton, PhD student at Bournemouth University, who was nominated and shortlisted for her research into the challenges faced by the nursing workforce in implementing the COVID-19 vaccination programme during the pandemic. A great achievement Sarah – very well done.
The awards bring together the nursing community to celebrate the brightest talent in the profession and to recognise innovation, inclusivity, and patient-centred care. The event aims to honour individuals who go above and beyond to inspire excellence across the nursing and midwifery community, contributing to the advancement of patient care and the healthcare profession as a whole.
The awards showcase innovation, perseverance, and outstanding contributions across 25 categories, spanning a diverse range of nursing specialties—including mental health, community care, inclusivity, and sustainability in nursing and midwifery.
Building Research Capacity: The key role of PhD students
Postgraduate students, especially PhD students dramatically expand a university’s research capacity. They contribute significantly to data collection, analysis, the day-to-day management of research projects, and publications that might otherwise be impossible to sustain. Postgraduate students are central to progressive research-active communities. PhD student also frequently serve as mentors to undergraduate researchers or Masters’ students, creating a cascade of learning that benefits all participants.
Beyond individual projects, postgraduate students help build research infrastructure through their contributions to lab management, protocol development, the exchange of innovative ideas, and so on. These contributions create lasting benefits to staff as well as higher education institutions. Academic communities with PhD students often promote collaboration, provide emotional and intellectual support, and create spaces where ideas can be tested and analyses refined before wider dissemination.
This expanded capacity allows universities to pursue more ambitious research agendas and respond to complex challenges requiring multidisciplinary approaches. The postgraduate journey requires carefully planned mentorship, giving students increasing autonomy, and ownership of their scholarly contribution. This apprenticeship model has proven remarkably effective in preparing the next generation of academics for centuries.
This blog was created as part of the Professional Discourse in the Age of AI: an interactive writing workshop facilitated by Prof. Debbie Holley and Prof. Carol Clark in the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences at Bournemouth University. Since last week’s workshop was on the topic, we have used the help of AI in the writing of this BU Research Blog!
Dr. Kathryn Collins, Prof. Vanora Hundley & Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Federalisation & health research presented in Nepal
- Koirala, B., Rushton, S., Adhikary, P., Balen, J., et al. (2024) COVID-19 as a challenge to Nepal’s newly federalised health system: capacities, responsibilities, and mindsets, Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health (online first) https://doi.org/10.1177/1010539524125012.
- Sapkota, S., Rushton, S., van Teijlingen, E., et al. (2024) Participatory policy analysis in health policy and systems research: reflections from a study in Nepal. Health Research & Policy Systems, 22 (No.7) https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-023-01092-5 .
- Wasti, S.P., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P., et al. (2023) Selection of Study Sites and Participants for Research into Nepal’s Federal Health System, WHO South-East Asia Journal of Public Health 12(2):116-119.
- Sapkota, S., Dhakal, A., Rushton S., et al. (2023) The impact of decentralisation on health systems: a systematic review of reviews. BMJ Global Health 8:e013317. doi:10.1136/bmjgh-2023-013317.
- Wasti, S.P., van Teijlingen, E., Rushton, S., et al. (2023) Overcoming the Challenges Facing Nepal’s Health System During Federalisation: An Analysis of Health System Building Blocks, Health Research Policy & Systems 21(117) https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-023-01033-2
- Sapkota, S., Panday, S., Wasti, S.P., et al. (2022) Health System Strengthening: The Role of Public Health in Federal Nepal, Journal of the Nepal Public Health Association 7(1):36-42.
- Adhikary, P., Balen, J., Gautam, S., et al. (2020) The COVID-19 pandemic in Nepal: Emerging evidence on the effectiveness of action by, and cooperation between, different levels of government in a federal system, Journal of Karnali Academy of Health Sciences 3 (3): 1-11.
- Rushton, S., Pandey, S., van Teijlingen, E., et al. (2021) An Investigation into the Impact of Decentralization on the Health System of Nepal. Journal of Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences, 7(1): 3–14. https://doi.org/10.3126/jmmihs.v7i1.43146
Corruption and Financial Constraints, SME Firm Productivity Growth in European Economic Crisis and Conflict by BU EACES PKES Member
To address these topical themes, I am truly proud and feel honoured to be part of BU’s visionary impactful research contributions and I have personally actioned:1A) an abstract poster presentation for the BU Conference [27 November] in person attendance all warmly welcomed, BU Talbot Campus, Fusion FG06 Posters on show viewing and Share theatre (oral presentations), 9-4pm and incorporated into it: 1B) my own very original topical preprint article [12 November] ii) attended (after last year see my RDS Blog ‘BU live with USA, Germany and Kyiv’) the 3rd International IZA/OECD online workshop [21 November] of top international themes alongside 101 zoom participants from USA, UK, Germany, Italy, Spain, France and more.
1A) poster abstract presentation (BU Conference and Researchgate link)
Poster and Abstract – Fiona Vidler
Abstract
Financial Constraints and Bribery Impact upon SME Firm Productivity in Economic Crisis and Conflict
Do economic destabilisation factors link to conflict even war? Only now in the explosive mid2020s are finance economists breaking the silence, raising this critical question. The author proposed early 2022, a ‘turning point’ notion of 2019 – thirty years after the Berlin Wall fell, seventy years after NATO formed; pre-covid 2020; before ‘Zeitenwende’ 240222 – seeking missing descriptive and empirical regression evidence beyond speculation for predictive indicators: financial constraint and bribery incidence within financialisation, competitivity and corruption. Findings demonstrate significant negative heterogenous effects across 27 Eastern European countries upon SME firm productivity outcomes with co-operative alliances adding business transformation value.
1B) Preprint Abstract and Article Download
Preprint Abstract and Article Download – Fiona Vidler
Vidler, Fiona,
Keynes World War, Prophecies And Productivity Growth In Economic Crisis -A Critical Review (November 12, 2024).. A review style paper that links current relevant themes in a novel readable socio-economic scholarly critique relating to a resurgent interest in Keynes’ original work and finishing with elements of the author’s own original research – so debating Keynes’ own predictive words even prophecies with words from a hundred years ago in 1919 to a 2019 proposed ‘turning point,’ leading into consequences for the current 2020s and future. Available at Elsevier SSRN:
https://ssrn.com/abstract=5018719 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.5018719
Also available on research gate with poster and abstract files (note preprint article first available 13 November 2024 although categorised 2024 on Researchgate itself). Also, already additionally early listings (featured) so far early days in other more general ejournals- European Economics: Macroeconomics & Monetary Economics eJournal and Development Economics: Microeconomic Issues in Developing Economies eJournal with interest from The Journal of Research Development.
ii) 3rd OECD/IZA Workshop
3rd OECD/IZA International Workshop
Link to IZA/OECD program with group photo shot (BU top right corner of image), where it was a great opportunity to this time, listen participate seek first to understand and find out what the IMF (International Monetary Fund), OECD, ILO United Nations, IZA (Institute of Labour Economics, HQ Germany – with its links to EACES) latest news is and more – where researchers linked face to face with policy makers on the 21 November.
Furthermore, to ask one’s own question related to productivity and received an answer too. A lateral one as hot topics were related to productivity intrinsic factors ‘within firms’; a consideration different but relevant to my own theme considering 10,000 SME firms as entities and their extrinsic productivity outcomes in measures of output per worker in SME firms. Intriguingly, 2019 was also a turning point down turn found by IMF researchers in Europe beyond relative prosperity of 2015-2018.
On the theme of publishing research that makes a difference and gaining inspiration to keep writing further articles (how does one do it one may ask): A leading publications ranked world class esteemed BU Professor (Marketing Strategy Innovation and Tourism), Dimitrios Buhalis, far greater than myself, recently circulated for reflection by colleagues: 'the attributes of distinguished scholars' (McKercher, 2024) where consensus was that inquisitiveness, insights, passion were top criteria, followed by other criteria including: connections, taking a risk with a joined up 'whom, what, how, why' strategy for truly original research with relevant impactful publications that make a difference or reach the target audiences – linking themes of topical current real interest in an intellectual scholarly manner often with practitioner or policy maker relevance, on the leading edge, meeting needs, connections, collaborations, often interdisciplinary considerations to expand thinking – inspiring and enabling memorable research publications as opposed to churning or common mediocre scholarly research which is common.
Making a (real) difference in the world with recognition in many fields is one of BU's themes and forte in the 2020s. I personally find these criteria inspiring for researchers publishing, would also add return on investment or with relevance or benefits with solutions towards solving issues in the economy/economies (from a finance economic perspective of the world is a reality of how we live today, where sustainability the flipside of economic destabilisation is the golden elixir matrix required). So gratitude and thank you so much for reading as always.
So Let us All be NICE = Noteworthy Inspiring Connecting Energising for yourself, others, and the world!
Fiona ‘Stewart’ Vidler MBA MSc MLIBF
Former MIPR (media) and financial advisor, Decision-Making Business Strategy (Corporate and SME Director roles) and Financial Times Business Winner
Corruption and Financial Constraints Impacts upon SME Firm Productivity – European Transition Economies in Crisis (Finance Economics – Advanced Researcher and British Author)
Bournemouth University Business School (BUBS) – Catalyst Growth Fusion 2022-26
MSc Green Economy – Bournemouth University, UK, 2021-2022
MBA Finance Macroeconomics (One of best dissertations 2020 – joint Oxford Magna Carta/New Bucks. Universities)
PLUS Level 7 – Accounting, Auditing, Strategic Financial Management and Investment Strategies
Driver Award – Highest Achiever (Faculty) Cognitive Psychology (RHUL,UK)
Financial Times Business Award Winner
– ‘ROI + media publishing success made us stand out win’
Previously Senior Researcher (over decade experience), RHUL, Defra (as prior MAFF), DSTL (as prior MOD), International Crisis Management Researcher (Burson-Marsteller A-team) and Director Education/ Marketing/ Research /Media/Conference/Round-table programs for professors leading lights networks creation and bidding team budgets writing programs £10K to £3M.
Impact of virtual reality on the well-being and travel experiences of people affected by dementia
I am undertaking a research placement as part of my studies on the MSc Foundations of Clinical Psychology. In my role as a research assistant, I have been working on a project that aimed to introduce the idea of travelling using Virtual Reality headsets for people with dementia and their caregivers/ family members. Virtual reality (VR) technology presents a promising means of bridging geographical divides and empowering individuals with dementia to participate in their communities in ways that were not possible prior to diagnosis. Additionally, research has demonstrated the value of virtual reality in helping people with dementia remember their past, revisit their hometown, or most treasured vacation spots. The purpose of this project is to evaluate how virtual reality can support people with dementia with travel and explore the impact on their wellbeing.
This is a collaborative pilot research study involving BU staff from the Ageing and Dementia Research Centre (ADRC) (Dr. Michelle Heward, Dr. Catherine Talbot, Dr. Michele Board, Dr Aisling Flynn, Lyndsey Bradley) and the International Centre for Tourism and Hospitality Research (ICTHR) (Dr. Daisy Fan, Prof. Dimitrios Buhalis) alongside colleagues from PramaLife (Sue Warr and Jo Keats) and is funded with QR funding from the Department of Psychology. We collected data on campus, and I was able to support this and had an opportunity to engage with the participants. The participants were asked to come to 2 sessions. The first session consisted of a session in the Blended Learning Interactive Simulation Suite, also known as the BLISS room. In this room, the participants and their caregivers were given the chance to play interactive VR games of their choice on the walls or visit different parts of the UK, such as London and Oxford. The second session consisted of using the VR headsets, where the participants were able to use the headsets themselves, which allows them to virtually experience other parts of the world, by looking around and having access to a 360 view, of a location of their choosing, whether that be somewhere they had never been to or reminisce about places they have been.

Given this immense opportunity to relive and reminisce about their previous experiences around the world, and their respective homes, the reception was overall a positive one. The participants left feeling positive about having virtually visited places from their past and having engaged with places they have never been to or would like to go to in the future. They provided some useful insights and feedback to inform future research in this area. We now move towards analysing and publishing the data.
Roshin Sibu
For more information about this project please email Michelle mheward@bournemouth.ac.uk
GLOW poster presentation by CMWH’s Dr. Rebecca Neal
Dr. Rebecca Neal in the Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH) who has a poster accepted for presentation at the prestigious GLOW conference later this month. This poster ‘Heat resilience and midwives: Bridging the gap for women’s health in a changing global climate. The 2024 GLOW conference, supported by the Medical Research Council, will focus on the effects of the ongoing global crises of climate change, infectious diseases, mental health, and conflict and migration on women’s and newborn health.
 Insights from the Nepal Family Cohort Study (NeFCoS). NeFCoS is a multidisciplinary, longitudinal family cohort study designed to be one of its kind, informative research conducted in various geographical areas of Nepal. NeFCoS, led by Dr. Om Kurmi at the University of Coventry is part large-scale epidemiological study supported by BU and several other universities in the UK and elsewhere.
Insights from the Nepal Family Cohort Study (NeFCoS). NeFCoS is a multidisciplinary, longitudinal family cohort study designed to be one of its kind, informative research conducted in various geographical areas of Nepal. NeFCoS, led by Dr. Om Kurmi at the University of Coventry is part large-scale epidemiological study supported by BU and several other universities in the UK and elsewhere.

Why Productivity Growth and Eastern Europe Matters by BU, EACES Member on Transition and Finance Economics
Why is ‘growth’ magical, mysterious and elusive in Eastern Europe, throughout most of Europe, in the spotlight as the recent buzz word. It is even more critical to those governments in debt or deficit crisis now? How do some economies have it and others not? Especially since 2008/9 GFC (Global Finance Crisis)? Without growth, it impacts on economies. Its effects are slow growth, stagnation, lower standards of living experiences, overcrowding, emerging diseases, competition over scarce resources, ultimately emerging into protest riots, conflicts even wars.
Who creates critical growth? Answer is the 90% of businesses in Eastern Europe, which are the fastest growing SMEs (small medium enterprises) including innovative manufacturing processes and complex value chains. It is businesses SMEs, which are thought to be critical to research 2024 and beyond – the top theme after the biggest health (though is mainly tangible ROI devices diagnostic tests equipment advances) and greater than innovation and tech, as ranked in the UK 2024.
Informal relationships and collaborative alliances are now viewed as growing importance as subfactor determinants alongside main indicators to attain growth. Moreover seemingly innocent barriers inhibitors to growth – relating to top agendas of governments like financial constraints and bribery incidence (corruption) – are speculated by my study to flatten recent past productivity outcomes in stress times.
So, does one of the keys to the conundrum of productivity, my study proposes lie in removing barriers, so creating freedoms to growth prosperity sustainability and business transformation? Is it by uncovering what is hidden within and possible to achieve, as opposed to injecting new resources services or aid either monetary or non-monetary which reduce ROI (return on investment made) which assisted in the past? Is this the lesson of Eastern Europe for the West, which is growing faster albeit off a slightly smaller baseline total than most of the top of the G7. However, perceptions need testing with empirical evidence where none or little exists – so these are the themes of this British author and her own research at Bournemouth University.
This leads to the implications of how do you create successful models for growth adaptations relevant to the 2020s and Eastern Europe, another theme of resurging interest in the 2020s, for example EACES 2024, a keynote programme theme by a leading light, Post-Keynesian Economics, Professor Stockhammer (King’s College, London)? The Eastern front is protecting us, for this is unheard for Europe since zeitenwende 24022022, where Kyiv reminds me of cultured Vienna. Whereas other parts of the world outside Europe continent, it is a different scenario, it does not change, it is the norm and have always been at barbaric medieval war continuously flaring with low rights freedoms, long before I was born.



If you think your working and personal life is tough going count yourself lucky:
i) Professor Kyiv School Of Economics says to me (BU) online IZA seminar (in a break from drones overhead in a skeletal department) he knew the Durrells of Bournemouth. [Note: Famous Gerald Durrell linked to famed family with Margo’s Durrell Boarding House of Bournemouth (in fact, Gerry’s collection of animals were initially housed in back garden garage before new premises), a feature film 2019].
ii) SME mainly female businesses work in Kyiv, Ukraine (all partners men 25-59 age bar minimum essential are conscripted mandatory onto the front lines.
iii) 08072024 41 killed as Russian Missile hit children maternity hospital Kyiv, Ukraine
iv) SME sanity she escapes Kyiv shelling work/home to Ukraine’s beautiful mountains.
Sources: copyright my own/donated freely sent to me – ‘Everyday Academic and SME business life in Eastern Europe’ on our Eastern Frontier 2022-2024 – Lest anyone forget what is protecting our own peace and way of life here.
Alternatively, a further complex conundrum exists where the economy may have possibly continued to generate income all along, with inequalities of wealth growth evident or disappearing abroad or into offshore havens, so it does not grow the host economy and is not traceable non-productive, so not providing surpluses for developing society, even drains resources in an increasing debt ratio as it draws but does not give back, so is hidden invisible. It could also even be part of a growing ‘shadow economy’ (outside personal scope due to income below legally tax thresholds or creative tax accounting to pay less taxes and other avenues, but it is a growing interest theme researched by another at AFE, BUBS, Bournemouth University).
What does it look like this growth? Government budgets and announcements in Europe currently revolve around it. So, what? READ ON IF WISH TO FIND OUT AND A LITTLE OF MY STUDY FINDINGS IN DEVELOPMENT – IF NOT THANK YOU FOR READING THIS EYE OPENING OVERVIEW WHERE EAST MEETS WEST, AND WEST GETS AN AWAKENING AS MEETS EAST.
So, as an example of the past decade 2008/9 to 2019 post GFC (Global Financial Crisis) from Eastern Europe, my own research study data. It reveals how in the past decade that economic growth has become more complex and no longer necessarily is related directly as before to productivity growth. So, I am finding that potentially being more productive is not necessarily the answer to ultimate economic growth anymore but increasing it could be one factor determinant towards boosting overall growth in the economy – which needs financial surpluses not debt and clean scores not corruption to thrive. Furthermore, my study provides evidence for heterogenous (diverse) different productivity outcomes related to financial constraints and bribery corruption across Eastern Europe compared to more accepted homogenous (similar) flattening productivity trends in ‘the West.’
The Productivity Gap = hierarchy economic states for top 30% and bottom 30% in my study findings 2019 and 2008/9 of 27 transition economies Eastern Europe
smaller gap 2008/9 to 2019 shows productivity growth%
has slowed down the most in higher productivity economies of study SME firms
top8 30% total sample gap [log] 0.42
bottom8 30% total sample gap [log] 1.23
Source: Author own construct
The Productivity Gap = hierarchy economic states for top 30% and bottom 30% in my study findings 2019 and 2008/9
Typical Most prominent
Top 8 group
30% total samples firm-level study largest yet slowest growing Productivity
2008/9 and 2019 (not in precise order as changes over decade)
Czech Slovenia Lithuania Poland Latvia Estonia Hungary Slovak rep
Typical Most prominent Bottom 8 group 30% total samples firm-level study smaller yet fastest growing Productivity
2008/9 and 2019 (not in precise order as changes over decade)
Azerbaijan Ukraine Armenia Georgia Kosovo Uzbekistan Kyrgyz rep Tajikistan
Source: Author own construct
*Although at a lower starting point, the bottom third hierarchy of economies in my study, the third decade of independence in Eastern Europe where there is a gap as relatively no extensive large cross countries evidence exists, before the turning point of 2019, findings are it has grown faster and seen far less flattening in productivity than the top third economies, suggesting something different is happening here between Northern and Southern economies in Eastern Europe (ECA borders) especially.
So, the implications could be that these are the economies with growing economies that investors are attracted towards either i) the top most productive with least corruption most stability or ii) despite lower baseline are fastest growing for greatest yields, so achieving a real return on investment (ROI) when offering FDI (foreign direct investment). However, the top performers are flattening or the most attractive performers have higher risk impacted upon by geopolitical geo-economic volatility, conflict, geopolitical instability and corruption, so delaying foreign investments made which impacts hardest upon Eastern Europe that depends more on FDI more so than ‘the West.’
Eastern Europe matters most to us in Britain too, not just Eastern Europe itself, this is because Europe is pragmatically our geographically closest advanced protective neighbour with cost-effective tangible benefits and historic long-term finance economic alliances. Research reports in 2024 shows Eastern Europe gains spill-overs by closely collaborating trading on its own borders with its neighbours. Also, advantages are closest geo-economic (geographical) alliances brings economies of scale savings. Further more as in 11092024 world news and UK reported too: “most proud of the unity, we and all our allies have shown in support for Ukraine,” furthermore “reiterating that Ukraine’s freedom is crucial for Europe” as well. For it holds up the Eastern front for European peace that includes financial economic order against destabilisation – in addition to the benefits of Europe retaining access to its vast required precious minerals especially lithium ions think mobile phones EV energy and vast food grains store which are recently providing sources of competitive conflict for scarce precious resources.
Critically, the whole of Europe itself should not be diminishing as seen in the 2020s but needs to stand up and increase now in its own continental priorities for survival and striving for growth. Like it did so before GFC (Global Financial Crisis) 2008 and before EU even existed pre1991 (for those who remember either born and travelling Europe/USA easily safely even when very young freely or perhaps working flying travelling before then too – so it can’t be blamed on recent Brexit 2020 although Brexit has left a quagmire legacy of increased technocrat, bureaucracy, restrictions, trading barriers and red tape attached still as not being in the EU unlike pre1991. But countries do survive without the EU, hence some of Eastern Europe’s cynicism.
The productivity growth trends can be seen in both my study tables 2008/9 to 2010 and following independent source tables 1997-2007 and 2008/9 to 2019:
Comparison OECD G7 (important contrast outside Eastern Europe study focus)
Since the 2008/9 economic downturn, growth rates have been slower in all G7 countries, with the UK and US having the largest slowdowns. Even closer to home, outside of my study scope, the UK’s productivity (outside of my study scope) has fallen away from most of the other G7 countries during this period, which corresponds to my Eastern European study’s turning point notion of 2019 being predictive of the 2020s and what lessons can be learnt.
It is interesting to look outside of my research scope in context briefly at the G7, the ‘so called advanced economies’ compared to the transition economies too who are rapidly catching up converging or a few top economies overlapping now too with the G7.
G7 Economies – Compound average annual growth rate of output per hour worked (a measure of productivity is output per worker too preferred by this researcher compared to total productivity factor measurement), before and after 2008/9 economic downturn due to GFC mainly.
Average annual growth (%) 1997 to 2007 (left)
Average annual growth (%) 2009 to 2019 (centre)
Difference (right)
US 2.3 0.8 -1.5
UK 1.9 0.7 -1.2
France 1.6 0.9 -0.7
Canada 1.5 1.0 -0.5
Japan 1.6 1.2 -0.4
Germany 1.4 1.1 -0.3
Italy 0.4 0.4 0.0
G7 mean 1.9 0.9 -1.0
Source: OECD data, Office for National Statistics calculations
Notes
1. The figures for the UK in this table differ slightly to ONS National Statistics estimates of output per hour worked.
2. Sources suggest that measurement units used may differ but produce similar trend lines.
3. Note: the homogenous similarities of growth too in G7 compared to heterogeneity of Eastern Europe.
To quote the past famous economists from Kings College, Cambridge with Keynes who was also a practitioner treasurer advisor to British Government too with relevance:
“Whether this account is true or fanciful, there can be no doubt as to the immense change in public sentiment over the past two years” (Keynes, 1919; 1931).
“But perhaps it is only possible in England to be so unconscious. In continental Europe the earth heaves. Not just about extravagance or “labour troubles”; but of life and death, of starvation and existence (‘including disease and poverty’), and of the fearful convulsions of a dying civilization” (Keynes, 1919). Analogous to productivity and today’s society environment.
“Ending up very soon facing a monumentally unjust inequality of income and wealth; a conflictual world with warring regions, religions and ethnic groups; a depleted, desertified [sic] and unviable planet, dominated by squalor, ignorance, want, idleness and disease.” (Nuti, 2018C, p. 15 Nuti 1937-2020). This is it in a nutshell, one hundred years later, as echoes Keynes in 2019. So, what lessons have we learnt is contentiously dubious debatable?
“Mario Nuti was a major theoretical and policy figure in economics; perhaps the last of the major UK post-Keynesians in a line of significant Cambridge economists. Notably – Mario questioned the success of the transition economies, terming it more as “a development into a ‘mutant’ economic system. “Due to “seismic faults” in the European Union – including Brexit, austerity policies, tiny EU budget, premature introduction of the Euro, migrations, tax competition, tolerance of illiberal regimes, divergence of welfare policies – its institutions and policies are equivalent to “tectonic plates sliding over each other and colliding” (Nuti, 2018b). Mario particularly condemned the persistence of austerity policies, demonstrating that fiscal consolidation can actually increase, instead of decreasing, public debt/GDP ratio.” (Estrin and Uvalic, 2020; 2021; 2022, 2023, 2024). Nuti and his thinking is a top appreciation theme of EACES (European Association of Comparative Economics Studies) 2024.
This adds weight to the imperative of this researcher in conducting further imperative finance economics research as part of the quest like a holy grail mission to contribute towards advancing knowledge required ultimately towards peace stabilisation, balanced not so volatile finance economics equilibrium required for international order, sustainability and growth for survival. So, ultimately to meet now an expanding ever demanding (beyond supplies is Keynesian) overpopulated world competing for resources on the planet in the so called ‘dependent advanced civilised society,’ unless one wishes to return to the alternative of literally the relative dark ages of existing simple indigenous independent self-sufficient people and roaming nomads on the planet. Therefore, the researcher’s contribution to the words of magical mysterious elusive ‘growth’ and the proposed subfactor of productivity outcomes.
To end on a lighter note and the takeaway mini-bite, especially for the non-finance economists (if mathematics, finance, economics, statistics and modelling blow your mind and goes over your head) then maybe you can relate all of this to extracted lines from a memorable theme song:
“Millenium” song by Robbie Williams:
We’ve got stars directing our fate (Millennium)
And we’re praying it’s not too late (Millennium)
Some say that we are players
Some say that we are pawns
But we’ve been makin’ (takin’) money
Since the day that we were born
Cos we’re low down (low down)
Run around in circles
Then we’ll slow down (Slow down)
Before we fall down
We all enjoy the madness
Cos we know we’re gonna fade away
(And we won’t stop)
Songwriters: Robert Peter Williams, John Barry, Leslie Bricusse, Guy Antony Chambers.
For the optimists there is the movies like ‘Sliding Doors’ with its two parallel universes (an increasingly popular concept), one golden returning progressing ‘happy places making beautiful memories’ outcomes is “the new trend now” and one universe the dark side black hole which is very volatile dark just like financial economic pain society disorder. Or the iconic star trek movie, where Spock the Vulcan from another planet, replies to the captain of the starship enterprise on charting a new course forward, ‘there is life, but not as we know it.’
Mario Nuti (Cambridge economist, researcher, opinion leader) once wrote: ‘I used to reproach myself for not doing enough work, for I only regarded research as true work, but now I regret not having spent more time on a beach’ (Nuti, 1992a). Indeed, wherever he was, Mario was always surrounded in solitude by books, papers, notes, and he never stopped working (on his research matters), up to his very last days.” Likewise, Bournemouth and Dorset offers great opportunities for combining its microclimate with amazing beaches, ideal for reflective higher thinking alongside its dedicated research and publication offerings.
So ideally realistically, the best research it is intrinsically driven (not extrinsic) with passion dedicated determination as when ‘the going gets tough only the tough get going’ (theme song film used in USA business),’ so always like an ongoing daily mission to climb a mountain expedition to its peak and ongoing beyond this, only for critical subjects in demand that create a real difference impact relevant in 2024 and onwards, for a significant number in the real world on local, national, international levels (not peripheral often loud background noise minorities), which only then has long been proven to deliver ££££’s benefit contribution for every £1 invested in research (Return on Investment) back to the UK society, planet and the economy (to add growth to the source investment resources made) otherwise it dissipates disappears, destroying ‘the goose that laid the golden eggs (fable and often USA business expression).
In line with this, all eyes are upon trend setting, Canadian PM, Trudeau, September, 2024 is looking for a critical significant contribution to strengthening the economy, its priorities, its workforce to even include advanced research in education to protect the integrity of the system itself and dramatically already reducing transient permits (including spouses)’ where specifically “changes are part of a larger effort to ensure a well-regulated and sustainable system.” “Not everyone who wishes to come to Canada will be granted entry, and not everyone currently residing here will be able to remain indefinitely. It is our duty to safeguard the integrity of our policies, and we are committed to adapting them to meet today’s evolving challenges,” he and his minister told Business Insider.’ This will achieve sustainability and ultimately strive for the government priorities of growth.

Source: Just Breathe
My current research life journey truly looks like this as reach a top peak phase
(those who truly know it is as is for themselves too as growth is internal and external)
Thank you, this is a longer blog essay account on the current topical buzz word of ‘growth,’ because finance economics articles often take longer to publish in AFE subjects, so are rarer in BU than some prolific publishing disciplines with shorter time frames more publications – as we all await the research contributions to be made, in the next insightful cluster of awaited exciting future pipeline research publications and creative media outputs by the BUBS and AFE (accounting, finance and economics) 2024 even 2025 as well as ideally by myself too makes a welcomed contribution then too.
Disclaimer: The themes are of top current relevance, but independent viewpoints not necessarily reflecting others connected with Bournemouth University. Notably, “Economist Keynes later admitted after 2019 the ‘consequences of the peace’ in reflection that his (words) prophecies were far more successful than his persuasion influence.”

Fiona ‘Stewart’ Vidler
MBA MSc MLIBF
Former MIPR (media) and Financial Advisor, Decision-Making Strategy (Corporate and SME) Director roles – Financial Times Business Winner (media ROI winning difference)
Corruption and Financial Constraints Impacts upon SME Firm Productivity – European Transition Economies in Crisis
(Finance Economics Advanced Researcher –research annual review rated ‘Excellent’ 2024)
Bournemouth University Business School (BUBS) – ‘Catalyst for Growth Fusion’ 2022-26.’
Previously British Senior Researcher (over a decade/s experience): RHUL, Defra (as prior MAFF), DSTL (as prior MOD), International Crisis Management Researcher (Burson-Marsteller A-team) and Director Education/ Marketing/ Research /Media /Conference /Round-table programs for professors leading lights networks creation and bidding team budgets writing programs £10K to £3M
‘
BMJ Global Health Blog online
 Today BMJ Global Health posted a blog (read it here!) about our recently publish paper ‘Socio-economic experiences of female community health volunteers matter: insights from Nepal’ which appeared last month in the Open Access journal PLOS Global Public Health [1]. In Nepal, about 50,000 Female Community Health Volunteers (FCHVs) are a vital human resource for both government and non-government agencies delivering primary healthcare at community level. Their contribution to maternal and child health is recognised globally. Being an active volunteer brought some interesting issues for the FCHCs. For example, the social experience of working in one’s own village was not the same for all. While community recognition of volunteers’ work was seen as a motivator, most volunteers thought they were not given due respect by fellow community members. Too often community members mistook volunteers as paid health workers often due to their involvement in medicine distribution, a rare bi-annual activity.
Today BMJ Global Health posted a blog (read it here!) about our recently publish paper ‘Socio-economic experiences of female community health volunteers matter: insights from Nepal’ which appeared last month in the Open Access journal PLOS Global Public Health [1]. In Nepal, about 50,000 Female Community Health Volunteers (FCHVs) are a vital human resource for both government and non-government agencies delivering primary healthcare at community level. Their contribution to maternal and child health is recognised globally. Being an active volunteer brought some interesting issues for the FCHCs. For example, the social experience of working in one’s own village was not the same for all. While community recognition of volunteers’ work was seen as a motivator, most volunteers thought they were not given due respect by fellow community members. Too often community members mistook volunteers as paid health workers often due to their involvement in medicine distribution, a rare bi-annual activity. 
Our recent paper in BMJ Global Health was highlighted in an earlier BU Research Blog (to read this click here!). This latest paper is the third one based on Dr. Sarita Panday’s PhD research conducted at the University of Sheffield [2-3]. It is the fourth Bournemouth University paper on FCHVs with last weeks publication in the Journal of Manmohan memorial Institute of Health Sciences [4]
Professor Edwin van Teijlingen

References:
- Panday, S., Barnes, A., van Teijlingen, E. (2024) Exploring the motivations of female community health volunteers in primary healthcare provision in rural Nepal: a qualitative study, PLOS Global Public Health 4(8): e0003428
- Panday, S., Bissell, P., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P. (2017) The contribution of female community health volunteers (FCHVs) to maternity care in Nepal: a qualitative study, BMC Health Services Research 17:623 be/vz9C
- Panday, S., Bissell, P., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P. (2019) Perceived barriers to accessing female community health volunteers’ services amongst ethnic minority women in Nepal: a qualitative study, PLoS ONE 14(6): e0217070 https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0217070
- Bhattarai, S., van Teijlingen, E. (2024). Nepal Needs A Two-Pronged Approach to Secure Future of Its Female Community Health Volunteers (FCHVs). Journal of Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences, 9(1), 43–48. https://doi.org/10.3126/jmmihs.v9i1.68640
Student numbers in the next decade
In contrast to recent student numbers intake across the country FT has published an article stating that, undergraduate numbers will see a rise in England in the next decade. [APRIL 7 2024. Looming rise in student numbers sparks calls for skills reform in England. Peter Foster and Anna Gross. © The Financial Times Limited 2013. All Rights Reserved].

Total numbers have a direct relation to several factors including but not limited to overseas students, and both financial and planning challenges faced by international students. Various geographical regions for example South and Southeast Asia are conventionally more leaning towards traditional degrees for example engineering and medicine. Particular interest in these degrees is stemmed by primary and secondary education systems, national skill gaps and more widely societal impacts. Despite, a brief decline in the numbers of international students a pattern in terms of various disciplines varies according to available data. In order to attract and sustain international student numbers core engineering and medical/ medicine degrees will remain significant centripetal force.
FT also reported that, this year universities will make a loss on each domestic student unless there is a change in fees policy [APRIL 7 2024. Looming rise in student numbers sparks calls for skills reform in England. Peter Foster and Anna Gross. © The Financial Times Limited 2013. All Rights Reserved]. In addition, a more diverse repositioning in terms of educational provisions is needed, such as strategic priorities for engineering & technology degrees, innovation in delivery models and methods of gradually but completely decoupling from textbooks taught system to a more flexible intuitive, research informed and practice-based education in partnership with industry which is fit for solving real world impact bearing problems. In turn safeguarding graduates’ future, placing their learning experience at the heart of education-research interface to guarantee higher levels of employability and job satisfaction.
HEIs are also facing a challenge in terms of financial sustainability as reported, the sector is struggling to recruit the higher-paying foreign students it relies on to subsidise lossmaking domestic places [FT 07 April 24]. A two-pronged approach would be needed to address these challenges. Firstly, repositioning in terms of facilities and resources to introduce, apply and integrate more state-of-the-art modelling and simulation techniques for practice, practical and experimental elements of teaching in engineering and technology degrees and initiating a phased transition from dependency on conventional hardware tools e.g. expensive machines to realise releasing economies of scale. Secondly, more robust, simpler and well understood parallels and transitioning pathways between HEIs and primary to higher secondary education are needed.

FT added that, “At the same time, government spending on skills will be 23 per cent below 2009—10 levels, according to analysis by the Institute for Fiscal Studies think-tank.” [APRIL 7 2024. Looming rise in student numbers sparks calls for skills reform in England. Peter Foster and Anna Gross. © The Financial Times Limited 2013. All Rights Reserved]. Collaborating closely with industrial partners and stakeholders’ skills gaps can be strategically prioritised for medium to long term needs, and educational provisions would need reshaping to integrate with research portfolio, UNSDGs, socio-economic, environmental impacts and relevant REF Unit of Assessment (UoA).
FT reported that, “The apprenticeship levy introduced in 2017 has also failed to deliver the expected boost to training, according to London Economics.” [APRIL 7 2024. Looming rise in student numbers sparks calls for skills reform in England. Peter Foster and Anna Gross. © The Financial Times Limited 2013. All Rights Reserved]. This is an important pathway for filling the skill shortages and also bridging the gap between theory and practice. A steady rise in flexible learning engineering degree students’ numbers, have been observed. These students are industry professionals who join these degrees at L5/6 level for a BEng/MEng flexible learning program. In addition to academic benefits these professionals achieve academic benchmark qualifications for professional registrations with professional institutions. This is one of the best available models to address skill shortages with a flexible high-quality delivery and academic provisions underpinned by research.
A stronger and broader engineering sector in collaboration with industry partners and professional institutions to develop futuristic engineering degrees to contribute to economic growth and its sustainability with an upward trajectory to address real concerns that, “tackling (of) the UK’s entrenched skills shortages and low economic productivity.” [APRIL 7 2024. Looming rise in student numbers sparks calls for skills reform in England. Peter Foster and Anna Gross. © The Financial Times Limited 2013. All Rights Reserved] is important.
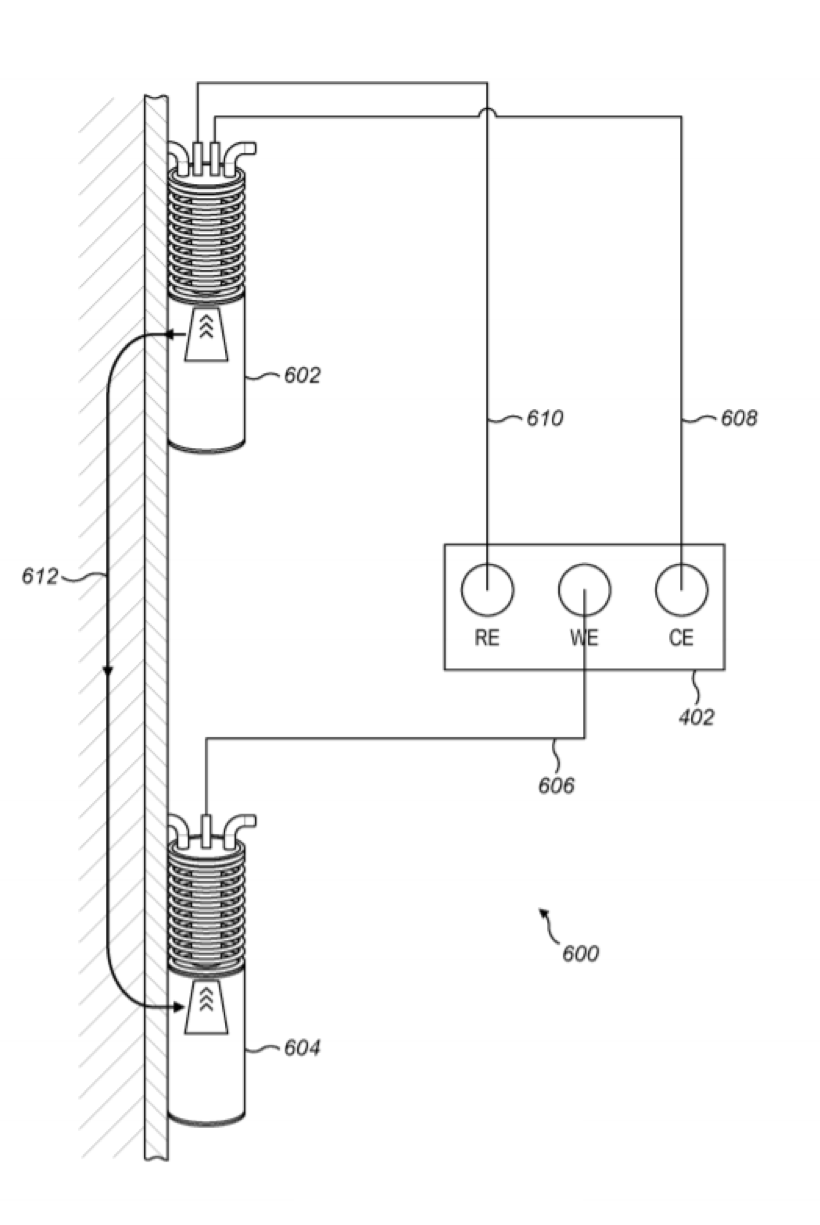
Telescopic Electrochemical Cell (TEC) for Non-Destructive Corrosion Testing of Coated Substrate. Patent number GB2018/053368
FT also mentioned in its latest article that, “Policymakers should also remove the cap on FE college places in order to “level up” education, (Lord Jo Johnson), added, providing more opportunities.” [APRIL 7 2024. Looming rise in student numbers sparks calls for skills reform in England. Peter Foster and Anna Gross. © The Financial Times Limited 2013. All Rights Reserved]. This can be looked into within the context of above-mentioned points in terms of establishing more defined parallels between HEIs and from primary to higher secondary education. A rethink to consider schools’ post code model for HEIs entry will help in levelling up.
Keywords: education, numbers, overseas students, engineering, skills, industry, professions.
Professor of Design, Engineering & Computing
NanoCorr, Energy & Modelling Research Group Lead
Email: zkhan@bournemouth.ac.uk
Dr Mili Shrivastava awarded Outstanding Women Researcher Award
Dr Mili Shrivastava received an Outstanding Women Researcher Award for her impactful research and contribution to policy briefings on women entrepreneurship and technology for sustainable business and society.

Dr Mili Shrivastava’s research delves into pivotal inquiries concerning gender dynamics, specifically focusing on women’s entrepreneurship and their presence in the tech industry. Driven by a passion for fostering sustainable business practices and societal progress, her work sheds light on pressing issues in these domains.
She has made contributions to the UK Parliament Committee’s examination of enhancing diversity in STEM fields, drawing on insights from her research.
The VIWA Awards Foundation honours and spotlights exceptional women researchers from across the globe.
Expressing her gratitude, Dr Mili Shrivastava remarked, “I’m deeply honoured and energised to see the impact of my research initiatives and endeavours in the realm of women and technology, as they serve to inspire and empower other women.”
New paper on Digital Nomads and Smart destination strategies, innovation and competitiveness for regional development
New paper on Digital Nomads
Zhou, L., Buhalis, D., Fan, D., Ladkin, 2024, Attracting digital nomads: Smart destination strategies, innovation and competitiveness, Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, Volume 31, March 2024, 100850, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdmm.2023.100850
Highlights
Digital nomads are an attractive market segment for global destinations
Smart destinations cater for the work, leisure & lifestyle needs of digital nomads
Digital nomad destinations innovate at structural and agency levels
International, destination-based & institutional stakeholders involve in innovation
Digital nomad visa regimes reinforce the global north and global south divide
Destinations assertively portray digital nomads as a homogenous group
Abstract
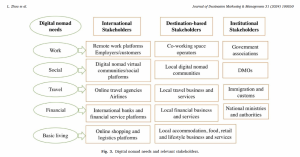
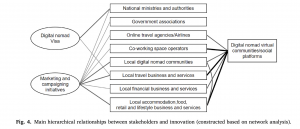
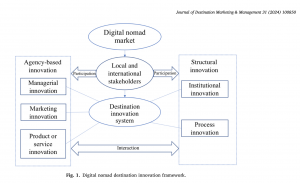
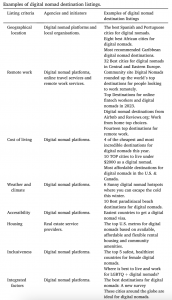
Digital nomadism, as a new form of tourist mobility, brings opportunities and challenges for destination management. To attract this new market, smart destinations need to innovate to develop readiness and competitiveness. This research examines 225 digital nomad destination web articles, from multiple sources and different continents. The study aims to identify innovative strategies and practices using semantic content analysis and hierarchical network analysis. It explores relevant stakeholders and their importance, and pinpoints digital nomad trends. Findings suggest that smart destinations cater for the work, travel, social, financial and basic-living needs of digital nomads. These are different from those of short-term leisure and business tourists. Destinations tend to portray digital nomads as a homogenous group, although different segments have been identified. The long-term impacts of digital nomads on local economies and societies have yet to be fully explored. The theoretical significance of this study lies in the provision of an agency-structural perspective of destination innovation and competitiveness. Practically, the study contributes to digital nomad management and marketing within smart tourist destinations.

Professor Dimitrios Buhalis has recently published a new service robots research paper based on a global survey in the hospitality industry
Professor Dimitrios Buhalis has recently published a new service robots research paper based on a global survey in the hospitality industry
Pizam, A., Ozturk, A.B., Hacikara, A., Zhang, T., Balderas-Cejudo, A., Buhalis, D., Fuchs, G., Hara, T., Vieira de Souza Meira, J., García Revilla, R., Sethi, D., Shen, Y. and State, O. (2024),
The role of perceived risk and information security on customers’ acceptance of service robots in the hotel industry, International Journal of Hospitality Management, Vol.117, 103641 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2023.103641
Highlights
•Perceived risk negatively and information security positively impacted intention to use service ts.
•Self-efficacy negatively influenced perceived risk, and positively influenced perceived information security.
•Innovativeness and facilitating conditions were positively associated with information security.
ABSTRACT This study proposed and tested a theoretical framework that investigated the influences of perceived risk and information security on hotel customers’ intention to use service ts. In addition, the impacts of self-efficacy, innovativeness, and facilitating conditions on perceived risk and information security were examined. Structural equation modeling (SEM) was used to test the proposed model by utilizing data collected from eleven countries including the United States, United Kingdom, Turkey, Spain, Romania, Japan, Israel, India, Greece, Canada, and Brazil. The study results demonstrated that perceived risk had a negative impact on customers’ intention to use services ts while information security had a positive impact. In addition, the study results indicated that self-efficacy negatively influenced perceived risk, and positively influenced perceived information security; and innovativeness and facilitating conditions positively influenced information security. The study findings offer several important contributions to the hospitality tics technology adoption literature and present valuable implications for hospitality practitioners and service vendors.
IMIV MRI Research Project Scheme 2023 – 2nd call closing 1st Oct
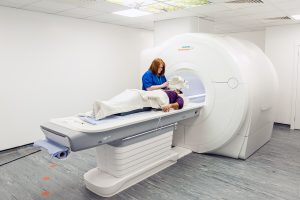 Earlier this year, we were delighted to award 80 hours’ scanning time to a study examining the impact of cold water immersion on depression, under the IMIV MRI Research Scheme 2023.
Earlier this year, we were delighted to award 80 hours’ scanning time to a study examining the impact of cold water immersion on depression, under the IMIV MRI Research Scheme 2023.
The second call for applications for the Scheme is currently still open, but closes on 1st October.
Under the scheme, imaging research projects can apply for up to 100 hours of scanning time on the IMIV’s state-of-the-art 3T Siemens Lumina MRI scanner.
- The focus of the scheme is on multi-disciplinary and cross-institutional projects, and priority will be given to projects with a clinical partnership.
- All research projects must have a Bournemouth University researcher as lead or co-lead applicant.
- Projects must be able to demonstrate how they will lead to peer-reviewed academic outputs and external funding applications for further MR imaging studies.
Please note: the award does not cover any additional expenses related to scanning, or other aspects of the project.
For further information and an application form, please email imiv@bournemouth.ac.uk.
IMIV MRI Research Project Scheme 2023 – Call Re-opens
The Institute of Medical Imaging and Visualisation (IMIV) has re-opened its call for applications for the IMIV MRI Research Project Scheme 2023.
Under the scheme, imaging research projects can apply for up to 100 hours of scanning time on the IMIV’s state-of-the-art 3T Siemens Lumina MRI scanner.
- The focus of the scheme is on multi-disciplinary and cross-institutional projects, and priority will be given to projects with a clinical partnership.
- All research projects must have a Bournemouth University researcher as lead or co-lead applicant.
- Projects must be able to demonstrate how they will lead to peer-reviewed academic outputs and external funding applications for further MR imaging studies.
Please note: the award does not cover any additional expenses related to scanning, or other aspects of the project.
Deadline for applications: 1st October 2023.
For further information and an application form, please email imiv@bournemouth.ac.uk.
Hampshire Constabulary and Bournemouth University Team Collaboration: Blue Light App
Police officers often work long, unsocial hours in a highly pressurised environment and may experience difficulties managing their health and well-being. Their jobs can be highly stressful and have unusual working hours and multiple shift patterns. When we think of the policing environment of today, many roles that were previously the domain of warranted officers are now carried out by non-warranted police staff equivalents. These police staff roles are relatively new to policing but put staff under some of the same stresses as police officers.
A research project affirmed that the working environment for officers makes it harder for those affected to make healthy choices. The problem not only includes thinking of a solution to help manage personalised risk issues, but also ensuring it won’t be intrusive for users during and outside of work.
Hampshire Constabulary is collaborating with the team at BU to investigate technologies that could be used to improve health and well-being and research how these technologies could be used to measure and track health behaviour change. A multi-disciplinary project team has been assembled to work on this project. Working with Dr Huseyin Dogan (Principal Investigator), Dr Festus Adedoyin and Professor Nan Jiang from the Faculty of Science and Technology, Professor Jane Murphy and Dr Andy Pulman from the Faculty of Health and Social Science as well as representatives from Hampshire Constabulary.


This project has developed and launched a fully functioning application (HantsPolHealth App) monitoring the members of the force’s health and well-being. This application is available in Android and iOS formats. Going forward, the App has been updated with new features covering shift patterns, financial well-being, and good mental health, and considerations are in place for its use by other blue light forces. Additionally, longitudinal usability data will be collected with the continuous use of the App. This demonstrates the potential expansion of the project and longer-term use by the funder.
As part of the collaboration effort, Dr Festus Adedoyin from Bournemouth University attended the 2023 Families Day event hosted by Hampshire Constabulary to explore further partnerships, funding, and collaboration.



 This is one of several news articles from this project which have appeared in both English and Nepali in national media in Nepal.
This is one of several news articles from this project which have appeared in both English and Nepali in national media in Nepal.  Our interdisciplinary research project ‘
Our interdisciplinary research project ‘












 Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian
Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian NIHR-funded research launches website
NIHR-funded research launches website Academics write for newspaper in Nepal
Academics write for newspaper in Nepal New paper published on disability in women & girls
New paper published on disability in women & girls Global Consortium for Public Health Research 2025
Global Consortium for Public Health Research 2025 MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
Explore our work, meet our partners, and find out how you can collaborate with us by clicking here! MIHERC is led by Sheffield Hallam University, with Bournemouth University as a key partner and the important funding coming from NIHR (National Institute for Health and Care Research) Maternity Challenge Initiative. The BU key academics are: Huseyin Dogan, Vanora Hundley, Edwin van Teijlingen, and Deniz Çetinkaya. Please share with all who may be interested.