Dr Dan Franklin, Associate Professor in Environmental Science, and Annesia Lamb, Post-Doctoral Research Assistant/Senior Research Associate, write about RaNTrans, an Interreg project addressing the issues of excess nutrients in coastal waters…
The Interreg (Rapid Reduction of Nutrients in Transitional Waters) project is a partnership of several UK and French organisations addressing the issues of excess nutrients (particularly nitrogen) in coastal waters. Human modification of the nitrogen cycle is recognised as one of the “planetary boundaries” beyond which humanity currently operates. Excess nitrogen in coastal ecosystems can cause dramatic ecological changes and significantly alter how ecosystems function.
RaNTrans has had a strong focus on the use of seaweeds and oysters to mitigate excess nitrogen conditions. Seaweeds and oysters take up and store nutrients in their tissues and when harvested can act as a removal mechanism to offset human nutrient discharges from agriculture and wastewater treatment works. They are also the subject of large-scale ecosystem restoration projects through European coastal waters.
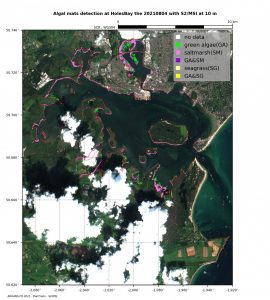
Green seaweeds (such as Ulva) are often very abundant in high-nutrient estuaries. They can form “mats” and shade other species of seaweeds, potentially change dissolved oxygen conditions, and can also change the amount of food available to wading birds in the underlying sediments. Improving our understanding of mat species and biochemical composition, mat dynamics and computer modelling, and mat detection with remote sensing are other aspects of the project.
This year RaNTrans successfully completed a large-scale seaweed collection trial in Holes Bay, Poole Harbour, which removed several hundred kilos of seaweed mat. This effort involved up to 10 project personnel working at our Hole’s Bay experimental site.
We are now monitoring the impact of this collection effort on bird ecology, sediment macrofauna (the clams, worms etc that live in the mud) and we are quantifying how fast the seaweed mat returns to the harvested plots. We have found that the growth conditions for green mat-forming species of seaweeds in Holes Bay are especially benign, resulting in an almost single-species mat which is relatively straightforward to harvest.
The project runs until June 2023 and we hope that our findings will lead to a better understanding, and greater innovation, in how we manage an environmental issue that is significant throughout the coastal waters of the world.












 From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event REF Code of Practice consultation is open!
REF Code of Practice consultation is open! BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project
BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease