On Monday 4th November 2019, as part of the ESRC festival of social science, Dr Emma Kavanagh and Dr Adi Adams (Faculty of Management) alongside final year sport student Terri Harvey, curated and hosted an arts based installation to showcase their research on inter-personal violence in sport. The event adopted an innovative, immersive, sensory art-based method not traditionally utilised in sport coach education (but widely used in other ‘caring’ professions) to bring their research knowledge to life and allow coaches and other practitioners to engage with data in a dynamic manner. This was achieved through re-presenting research data collected by the BU academics in audio and visual forms.
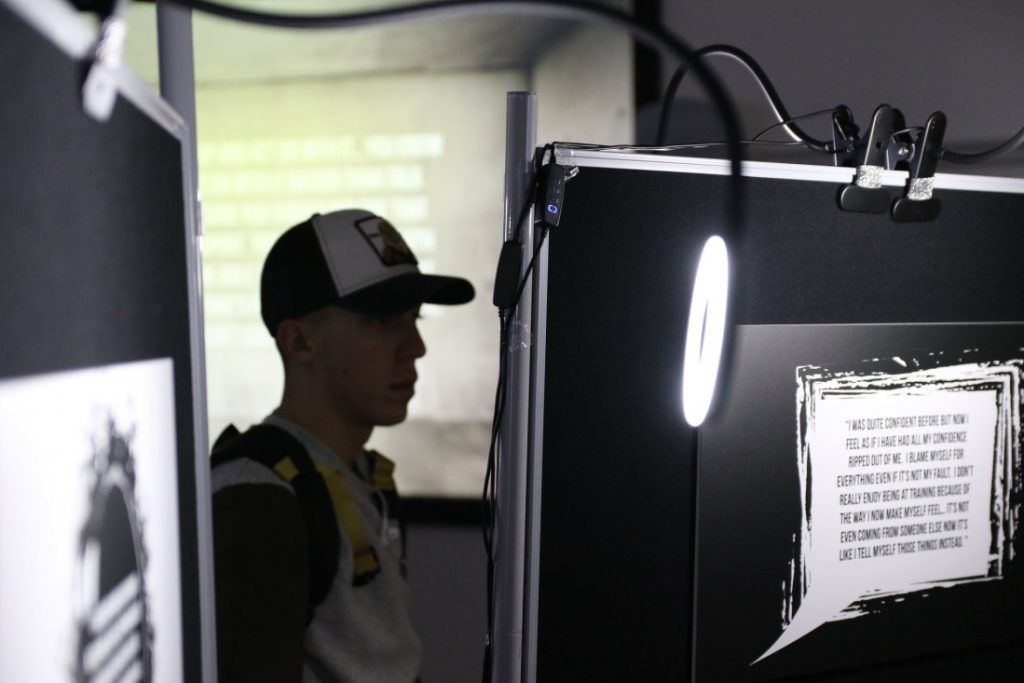

Abuse, intimidation and violence in sport and coaching remains a significant global problem. In 2017 the British Government published the Duty of Care in Sport Review, sharing the findings of a critical inquiry into the culture and climate of elite sport in the United Kingdom. High performance sport came under significant scrutiny linked to a number of high profile accounts in the media that raised serious questions concerning the safety of elite sporting spaces and the threats they can pose to athlete welfare. Allegations of bullying, racial, sexual and gender abuse alongside other forms of discrimination have been made across Olympic and Paralympic sports. This ESRC event provided an opportunity to engage practitioners in debates surrounding the safety of sporting spaces as a way of promoting the duty of care in practice.
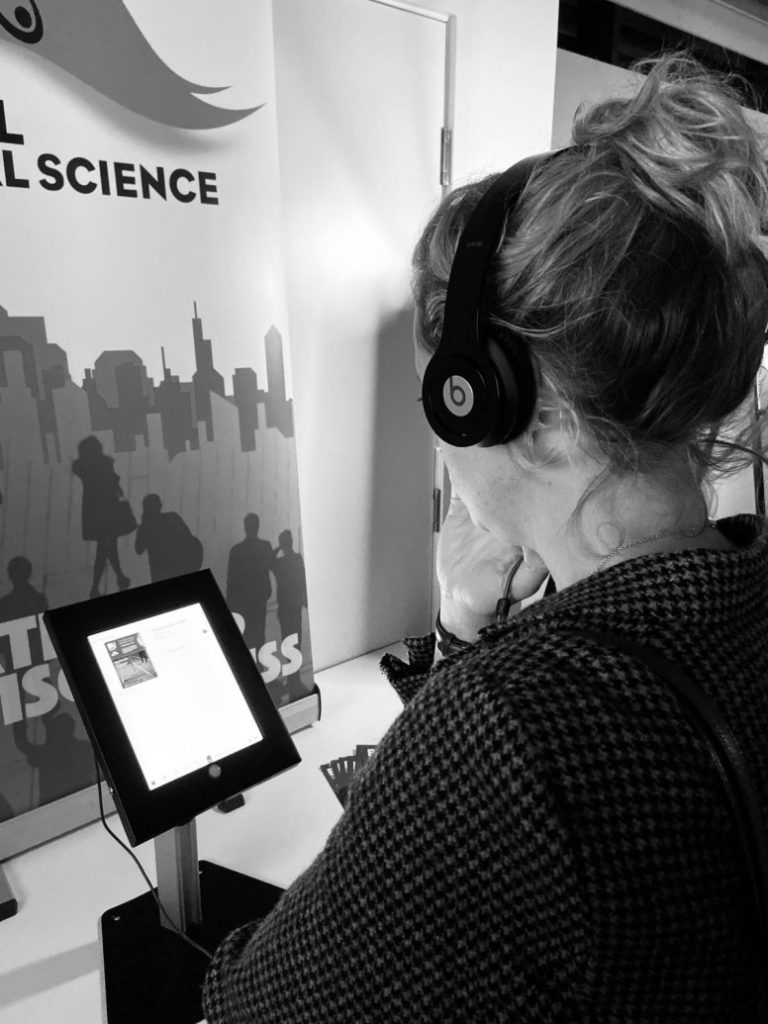
The event brought to life qualitative social science research data, currently available to academics through peer-reviewed journal articles through the production of an immersive arts-based installation. The data was used to enable those who attended to see/hear/feel and confront the contemporary issue of inter-personal violence in the world of sport coaching, from the perspective of ‘others’. The event aimed to bring sport coaches (and other practitioners) together around a shared concern/problem in the sport industry, with the aim of inspiring awareness, understanding, empathy, care and practical solutions to reducing interpersonal-violence. An arts and media-based approach is often adopted in the education of other ‘caring’ professions engaged in complex, difficult, ‘social’ and emotional work (e.g. nurses, medical practitioners, social workers, palliative care workers), yet has gained limited application in the sporting profession.
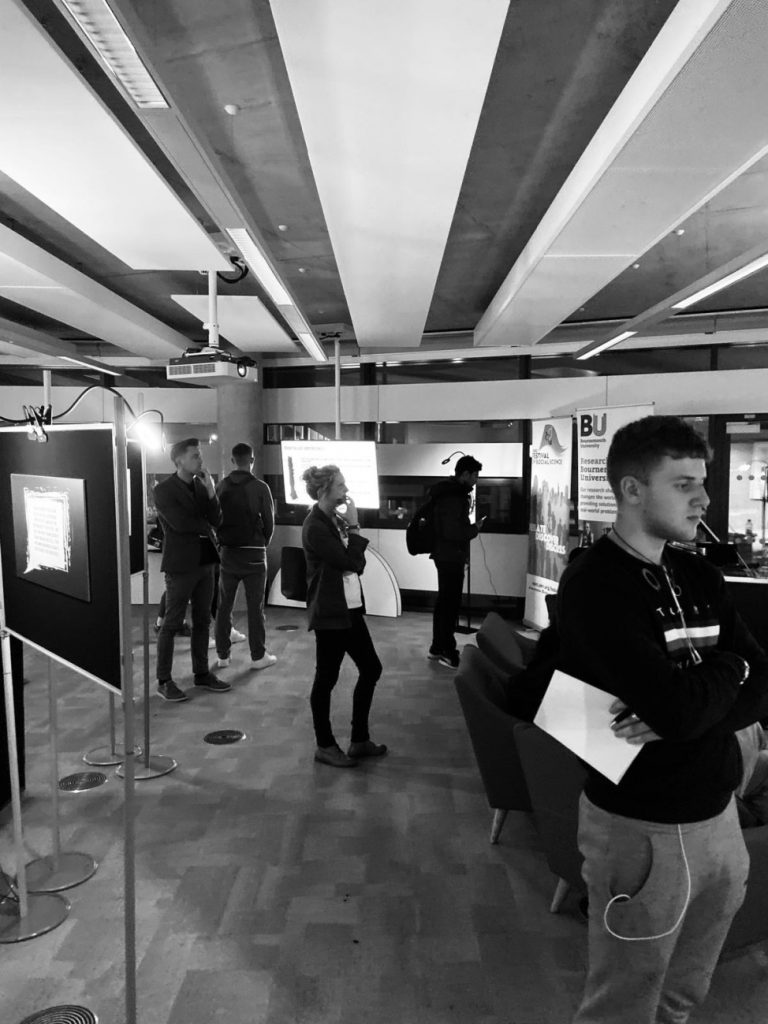

The event attracted significant attention from external practitioners, students and local organisations. Participants moved around and shared the immersive space with others, experiencing the ‘felt difficulty’ (Trevelyan et al., 2014) of ‘what it feels like’ to experience violence and intimidation as a participant in sport. It is anticipated that experiencing this ‘felt difficulty’, provoked by engaging with material that is ‘perplexing’ or ‘disorientating’ has the potential to provide a platform for coaches to reflect authentically on and transform their own practice. The impact of attending the installation is currently the topic of Terri’s dissertation and the team are excited to understand more about how participants experienced the event.
The event would not have been a success without the support of the ESRC team and, in particular, Adam Morris who helped drive the installation forward. In addition, thanks goes to the sport students who volunteered on the evening and actively engaged in the project through ‘becoming voices’. All of these people shared one passion; making sport a safer space for all those who participate in it.













 Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration
Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration 3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March
Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward?
Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward? ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease