Some people in academia (and many outside it) don’t appreciate the importance of PhD supervision . An academic supervising PhD students is not merely for the educational purposes, or in other words, for the benefits of the postgraduate student. The value of postgraduate supervision lies in pushing the boundaries of knowledge, about testing new ideas, new approaches or even new methods.
Interestingly, enough it means that PhD supervision for an academic is also about developing their own ideas, expanding one’s CV, and developing one’s career. Whilst for the university it is also for the wider benefit of research for the wider society. The latter means that PhD students help improve the REF (Research Excellence Framework) scores for a university, through metrics such as number and proportion of PhD completions, but also through papers based on PhD research co-authored with staff. It always amazes me how some outsider regard PhD supervision as simply more of the same, i.e. not that different from supervising an undergraduate student.
Looking at my ow CV, some of my best papers have been co-written with PhD students, including my most cited paper on SCOPUS [1]. Moreover, as the graph of my h-index [checked SCOPUS for May 19th 2025] shows four of my top eight highest cited papers were co-authored with postgraduate students [1-4]. Papers that would not have been written without the postgraduate student conducting knowledge-advancing research! 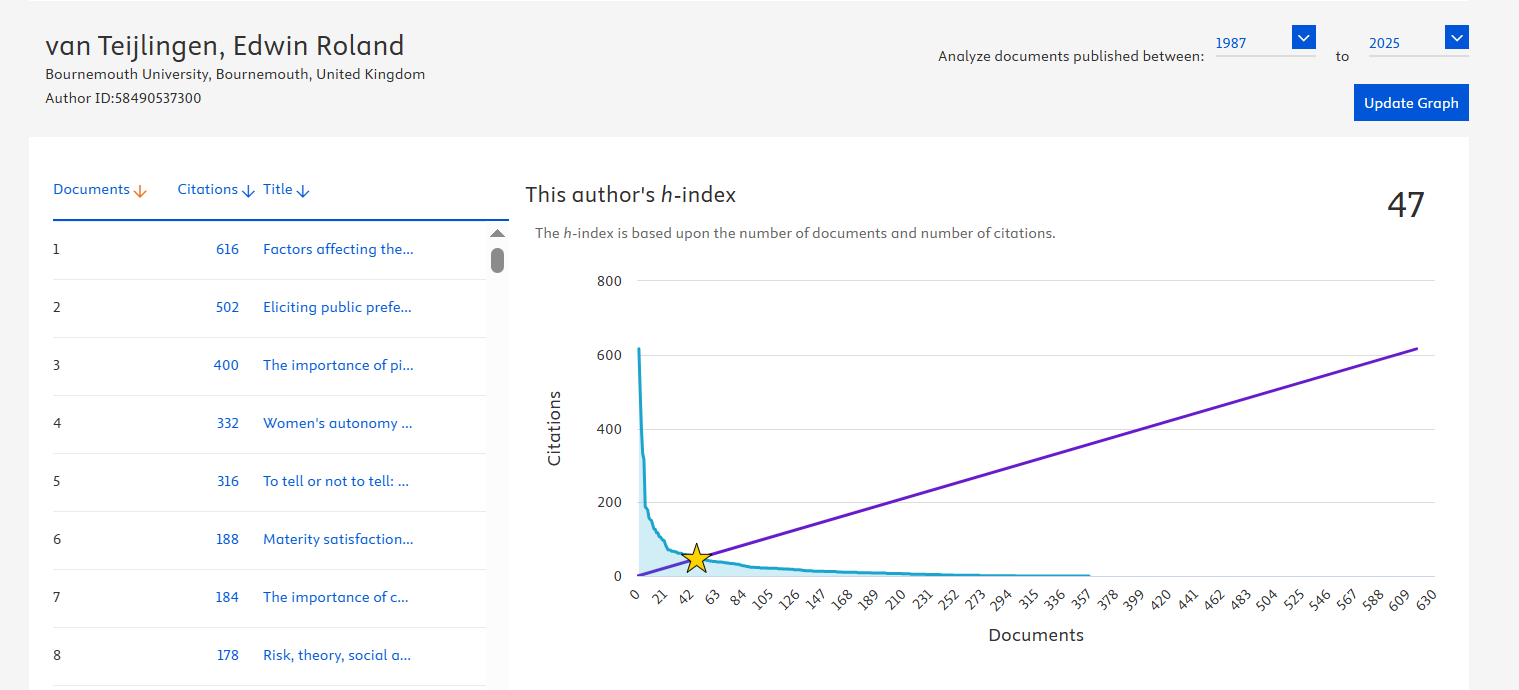
Not surprisingly, three of the four former PhD students who co-authored these highly-cited papers are now in academic positions across the UK (the fourth one has retired). These four highlighted papers are not just looking good on my CV, they are also highly ranked within their respective journals. The first paper [1] is the 28th most cited paper in the Journal of Advanced Nursing, an impressive 28th position out of 12,762 articles ever published by this international journal. Similarly, the paper ‘Women’s autonomy in decision-making for health care: Demographic study in Nepal’ [2] is the 10th most cited paper in Reproductive Health, whilst ‘ To tell or not to tell: Barriers and facilitators in family communication about genetic risk’ [3] is the 20th most article in Clinical Genetics. Last, but not least, ‘Risk, Theory, Social & Medical Models: critical analysis of the concept of risk in maternity care’ [4] is the 17th most cited article (out of 3,910) in the international journal Midwifery.
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health
References:
- Simkhada, B., van Teijlingen E., Porter, M., Simkhada, P. (2008) Factors affecting the utilisation of antenatal care in developing countries: a systematic review of the literature, Journal of Advanced Nursing 61(3): 244-260.
- Acharya, D.R., Bell, J., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E, Regmi, P.R. (2010) Women’s autonomy in decision-making for health care: Demographic study in Nepal. Reproductive Health 9(15) reproductive-health-journal.com/content/pdf/1742-4755-7-15.pdf
- Forrest, K., Simpson, S., Wilson, B.J., van Teijlingen E, McKee L, Haites, N., Matthews E. (2003) To tell or not to tell: Barriers and facilitators in family communication about genetic risk,Clinical Genetics, 64: 317-26.
- MacKenzie Bryers H., van Teijlingen, E. (2010) Risk, Theory, Social & Medical Models: critical analysis of the concept of risk in maternity care, Midwifery 26(5): 488-496.
 Some thoughts about PhD supervision in Public Health
Some thoughts about PhD supervision in Public Health Pilot studies methods paper cited 500 times
Pilot studies methods paper cited 500 times More pilots please!
More pilots please! FHSS academics’ paper cited 1,000 times
FHSS academics’ paper cited 1,000 times










 Missing Persons Indicator Project Recruitment
Missing Persons Indicator Project Recruitment Celebrating our Research: Postgraduate Research Showcase 2026
Celebrating our Research: Postgraduate Research Showcase 2026 Nursing Research REF Impact in Nepal
Nursing Research REF Impact in Nepal Fourth INRC Symposium: From Clinical Applications to Neuro-Inspired Computation
Fourth INRC Symposium: From Clinical Applications to Neuro-Inspired Computation ESRC Festival of Social Science 2025 – Reflecting back and looking ahead to 2026
ESRC Festival of Social Science 2025 – Reflecting back and looking ahead to 2026 3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Cookies – Tuesday 13 January 10-11am
3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Cookies – Tuesday 13 January 10-11am ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease