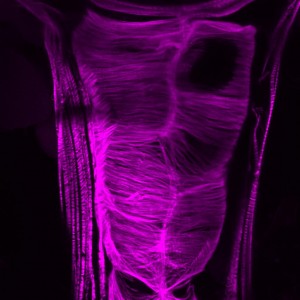
The heart of a fly. Two cells wide and capable of beating five times per second, the fly heart is helping us unlock the secrets governing our own heart’s function.
Research funded by the British Heart Foundation and conducted both here and at the Sanford-Burnham-Prebys Medical Discover Institute near San Diego in California, is to be published in the American Heart Association’s journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Genetics.
The work identified a genetic pathway linking cardiac function with expression of a protein called SPARC (Secreted Protein Acidic and Rich in Cysteine). In humans, increases in SPARC accompany cardiac ageing, inflammatory disease, obesity and cancer. As a consequence SPARC is a potentially very important therapeutic target in a wide range of important clinical settings. Our work, which utilised the fly Drosophila, demonstrated that heart dysfunction (cardiomyopathy) could be cured by reducing SPARC gene expression. Establishing this link allows us to ascertain the mechanism by which SPARC contributes to cardiac function in humans. Whilst the human heart is significantly more complex than that of a fly, their early development and function are controlled by similar genetic pathways; evolution may have added to the human heart but it has not changed its fundamentals. Hence, we’re able to learn a lot about ourselves by studying this simple, yet very sophisticated, little insect.
 Molecular basis for a healthier heart…new work published by BU
Molecular basis for a healthier heart…new work published by BU










 BU attendance at third annual GCPHR meeting in June
BU attendance at third annual GCPHR meeting in June Interactive Tangible and Intangible Heritage Applications – BU student work featured in new book chapter
Interactive Tangible and Intangible Heritage Applications – BU student work featured in new book chapter Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week
Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease