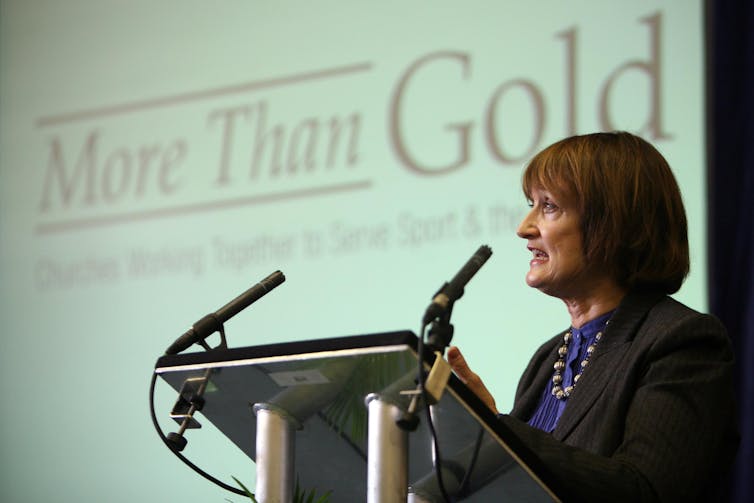

Forward thinker: Tessa Jowell in 2007. More Than Gold UK, CC BY-NC
By Dr Richard Wallis, Bournemouth University
The untimely death from cancer of former UK Labour cabinet minister, Dame Tessa Jowell, has triggered a wave of tributes from across the political spectrum. Her vision for securing the 2012 Olympics for London, her formative role in New Labour’s flagship Sure Start scheme, and most recently, her campaign for cancer research, have all been given many column inches.
By contrast, Jowell’s less certain legacy as principal advocate for media literacy is barely given a mention. It seems to have been quietly forgotten that it was Jowell, as secretary of state for Culture, Media and Sport, that pushed through parliament the Communications Act 2003 which enshrined media literacy in law, and gave to Ofcom – the (then new) media “super-regulator” – the responsibility to “promote” the idea.
Media literacy existed as a New Labour policy well before Jowell’s turn at the Department for Culture Media and Sport (DCMS). Her predecessor, Chris Smith, believed that the concept was a useful one for “arming the citizen-consumer” of media, to make responsible choices in a period of increasing deregulation.
To the dismay of some of her own policy advisors, Jowell seized the concept, made it her own, and became a fervent advocate at every opportunity. In an address given at BAFTA the year following the Communications Act, she referred to media literacy as “a coming subject” and one that “in five years’ time will be just another given”.
Misplaced optimism
With the benefit of hindsight, Jowell’s optimism seems to have been misplaced. Media literacy, arguably, has never been lower on the political agenda. The plethora of initiatives that sprang up in the wake of the Communications Act have largely withered on the vine – and the process of recent reforms to the popular Media Studies A-level have seen the subject savagely “strangled”.
Yet Jowell’s argument for media education has never been more relevant. “It is important,” she insisted, “that we know when we are watching ‘accurate and impartial’ news coverage and when we are not”. These are prescient comments when you consider that they were made more than a decade before “post-truth” became the Oxford Dictionary’s Word of the Year (in 2016) and when terms such as “fake news” or “Leveson Inquiry” had yet to pass anyone’s lips.
Jowell believed that education in media opened opportunities that could enrich the experience of individuals and society – but she was equally exercised about the role that education had to play in protecting against some of the dangers of modern media. She thought that media were dominated by powerful and potentially harmful commercial and political interests. She believed that children, in particular, should be provided with “critical life skills” to guide their media consumption.
“It is transparently important,” she told a media literacy seminar in 2004, “that they should be helped to get the most from all those screen hours, and be protected from what we know are some of the worst excesses”. She went on to ensure that, from 2006, the BBC Charter also contained requirements to promote media literacy.
Where did it go so wrong?
The key to understanding the marginalisation of media literacy as government policy is the role of the Department for Education – once known as the Department for Education and Skills(DfES). Media education was not seen as a serious curriculum priority at the DfES, and – despite New Labour’s early insistence on “joined-up government” – enthusiasm for media literacy never spread beyond the confines of DCMS.
There was widespread ignorance about media education among civil servants within DfES, many of whom had had highly traditional educational experiences themselves. A preoccupation with “driving up” standards, measurability and international comparison provided little incentive for the promotion of a field of study concerned with recognising and understanding forms of popular (or “low”) culture. This was despite the apparent economic value being attributed to the “creative industries” at the same time.
Read more:
Tessa Jowell’s call for greater access to experimental cancer treatments is right – here’s why
The byzantine operation of the DfES also made change of any kind difficult – particularly where it touched on what was actually taught in schools. In this case, there was the added disincentive of a policy being driven by a separate –and junior – department. Ultimately, media literacy was never to be widely embraced as an educational project in the way that Jowell had hoped.
Media literacy remains on the statute book and Ofcom continues to have a responsibility to promote it. But the way it is defined – and the level of resources provided to support it – ensure that it has largely been reduced to a form of market research, an undead policy. Jowell once proclaimed:
I believe that in the modern world, media literacy will become as important a skill as maths or science. Decoding our media will become as important to our lives as citizens as understanding literature is to our cultural lives.
It may be too much to hope that media literacy could yet be reclaimed as one of Tessa Jowell’s essential legacies.
Richard Wallis, Principal Academic in Media Production, Faculty of Media & Communication, Bournemouth University
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.



























 From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event REF Code of Practice consultation is open!
REF Code of Practice consultation is open! BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project
BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease