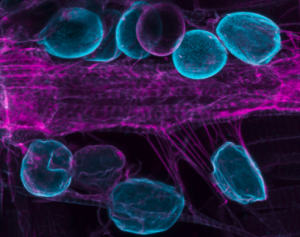
 Whether its in you, a blue whale or a tiny insect, circulating fluids bathe and nourish organs, tissues and cells. To avoid compromising organ function, these ‘bloods’ are filtered and kept free of unwanted molecules. Studying these clearance mechanisms informs us about normal physiology, as well as disease across a vast array of organisms, from flies to humans.
Whether its in you, a blue whale or a tiny insect, circulating fluids bathe and nourish organs, tissues and cells. To avoid compromising organ function, these ‘bloods’ are filtered and kept free of unwanted molecules. Studying these clearance mechanisms informs us about normal physiology, as well as disease across a vast array of organisms, from flies to humans.
In a new paper led by BU, it has been established that a mechanism common to flies and humans involving a protein called Amnionless, relies on a cell’s calcium level being controlled by genes known as Stim and Orai. Using powerful fruit fly genetics and dynamic cellular imaging techniques, the researchers found that as calcium levels change, Amnionless is turned-over at the cell surface where is helps to remove unwanted molecules. This new information is important because of its relevance to the human kidney’s role in blood filtration. Additionally, research is showing that the mechanism can be targeted by environmental toxins and this may explain why some insect species are struggling in the wild.
It is sobering to think that aspects of human cardiovascular disease and the ‘insect apocalypse’ may actually have common origins. Understanding these biological systems therefore has a dual purpose by informing medical, biomedical and ecological research fields.
(The image shows insect filtration cells in blue, adjacent to the heart, coloured magenta).












 Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU
Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU 3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching
UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease