There are several different methods or approaches to help researchers when evaluating of complex public health interventions or programmes. Our recent paper ‘Most Significant Change Approach: A Guide to Assess the Programmatic Effects’ [1] describes the Most Significant Change (MSC) participatory technique to monitor and evaluate programmatic effects. The MSC is a form of monitoring because it occurs throughout the programme’s lifecycle and provides information to manage it. Unfortunately, MSC as a participatory evaluation technique using qualitative methods is not widely used nor known. 
We hope to convince relevant funders and evaluators of the value of the MSC technique and application. Our paper offers step-by-step guidelines on how to use the MSC technique when evaluating a large-scale intervention covering perspectives of different beneficiaries within a limited period. The MSC process involves purposively selecting the beneficiaries, collecting the Most Significant (MS) stories, which are then systematically analysed by designated stakeholders and or implemented partners, selected through internal vetting, and external process by involving beneficiaries and stakeholders.
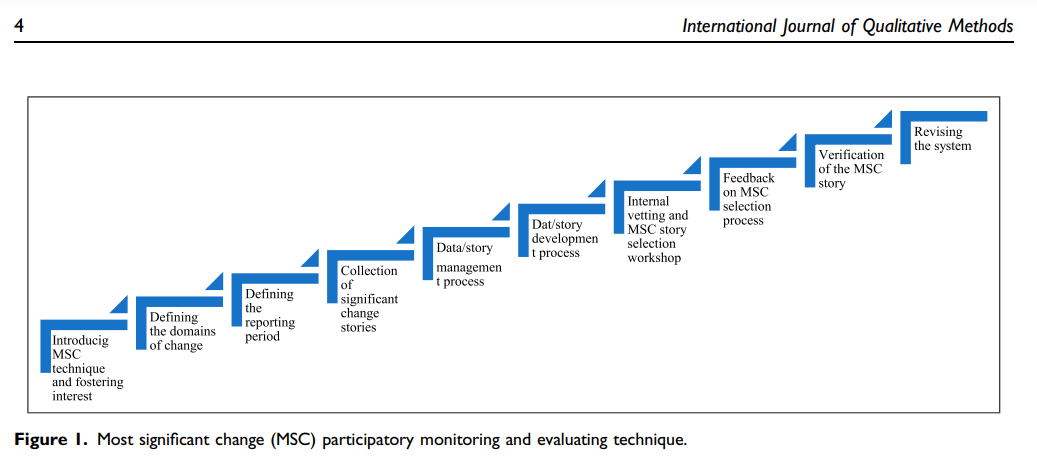 The central question focuses on changes in the form of stories such as ‘Who did what?’; ‘When did the change occur?’; and ‘What was the process?’ Additionally, it seeks feedback to explain why particular a story was selected as MS and how the selection process was organised. The MSC technique further attempts to verify the validity, significant, relevant, sustainability of the change, and impact on marginalized or Gender Equality and Social Inclusion (GESI) groups brought by the programme. Furthermore, the technique seeks verification of the MS story by triangulating comprehensive notes and recordings.
The central question focuses on changes in the form of stories such as ‘Who did what?’; ‘When did the change occur?’; and ‘What was the process?’ Additionally, it seeks feedback to explain why particular a story was selected as MS and how the selection process was organised. The MSC technique further attempts to verify the validity, significant, relevant, sustainability of the change, and impact on marginalized or Gender Equality and Social Inclusion (GESI) groups brought by the programme. Furthermore, the technique seeks verification of the MS story by triangulating comprehensive notes and recordings.
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health

Reference:
- Sharma, M. K., Khanal, S. P., & van Teijlingen, E. (2024). Most Significant Change Approach: A Guide to Assess the Programmatic Effects. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 23. https://doi.org/10.1177/16094069241272143











 New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease