It feels like only yesterday that I was writing a research blog reflecting on social impact entrepreneurship amongst students at Bournemouth University Business School (BUBS) in the Faculty of Business and Law. A year on, this work continues to evolve, offering further evidence of how entrepreneurship education can act as a catalyst for social impact, inclusion and sustainable development.
This year’s final-year 20-credit module on the Entrepreneurship pathway, called Entrepreneurship and Business Ventures, ran yet another elevator pitch event, resulting in 22 new mentoring opportunities for students developing socially and environmentally minded business ideas. This builds on 24 mentoring opportunities created the previous year, highlighting not only the consistency of outcomes but also the growing strength of the entrepreneurial ecosystem surrounding BU.
The module has now been running for over seven years and has undergone deliberate pedagogical redesign during that time. It now operates as an in-class incubation and ideation space for social and impact entrepreneurship, rather than a traditional lecture-led module. Students are supported in developing, testing, and refining venture ideas within a structured environment that prioritises both business viability and social impact.
Central to the unit’s design is the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs). Rather than treating the SDGs as abstract global ambitions, students are encouraged to use them as a practical framework for opportunity recognition. The SDGs help students to identify real-world problems, consider systemic impacts, and design business models that create economic, social and environmental value simultaneously. In this sense, sustainability is positioned not as an ethical add-on, but as a source of legitimacy, resilience and competitive advantage.
Across two days of live elevator pitches, final-year students presented a diverse range of ideas addressing challenges at local, national and global levels. The quality and ambition of the pitches demonstrated a notable shift in entrepreneurial mindset. While financial feasibility remained central, many students framed entrepreneurship in terms of long-term value creation, legacy and responsibility, with profit understood as a means to enable impact rather than an end in itself.
As a module-level assessment, this activity could have been delivered entirely within the classroom. However, entrepreneurship is inherently experiential and relational. Each year, the assessment is therefore designed as a live engagement exercise, with students pitching to an external panel of judges drawn from industry, policy and practice. The panel provides immediate feedback and, crucially, offers mentoring and access to professional networks. These outcomes are particularly significant in relation to inclusive entrepreneurship practice at BU. By embedding incubation, mentoring, and ecosystem engagement within a credit-bearing module, access to entrepreneurial opportunities is expanded. Students do not need prior entrepreneurial experience, social capital or financial resources to participate. Instead, all students on the pathway are given structured access to support, feedback and visibility.
Inclusive entrepreneurship is also evident in the nature of the ideas themselves. Many ventures draw directly on students’ lived experiences, cultural backgrounds and community contexts, demonstrating how diversity can be a driver of innovation. The breadth of the judging panel—including expertise in sustainability, inclusive enterprise, ethnic minority entrepreneurship and venture coaching—further reinforces inclusive role modelling and challenges narrow stereotypes of who entrepreneurs are and what they do. None of this would be possible without the entrepreneurial ecosystem that supports this work. Over seven years, that ecosystem has grown significantly, reflecting shared commitment to impact-driven and inclusive entrepreneurship. The sustained willingness of external partners to mentor students demonstrates that meaningful inclusion is built through relationships and trust, not rhetoric alone.
Reflecting on these outcomes raises an important question for higher education more broadly. If such impact—mentoring, confidence building, inclusive participation and SDG-aligned venture development—can be achieved within a single 20-credit module, what more might be possible with structured, longitudinal support for student social entrepreneurs? At Bournemouth University, this module offers a practical example of how entrepreneurship education can contribute to inclusive growth and sustainable development, aligning teaching, research and external engagement with the Global Goals.







 Coating Innovation for Tough Environments
Coating Innovation for Tough Environments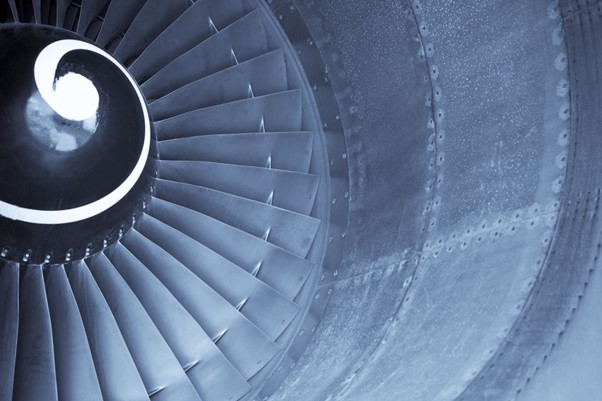






























 Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop
Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching
UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives
SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives BRIAN upgrade and new look
BRIAN upgrade and new look Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh
Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease