The Migration Advisory Committee review is out!
The report was released on 14th May as planned.
Firstly, because you are all interested in this, the recommendations, Worth reading and set out (in more detail but lightly summarised) at the end of this update, but broadly:
- They propose keeping the post study work visa because numbers will fall anyway as a result of the other changes (dependants for students and salary thresholds for skilled workers) will reduce the numbers of students coming and those staying for the long term in any event. They note the impact on universities of removing it, particularly universities outside London and the South East in the context of no increase in tuition fees.
- The government wants the graduate visa route to support the UK labour market (mainly graduate roles and STEM, they are not happy about international students working in non graduate roles in social care). In response to this, rather than suggesting subject level caps, as some had predicted, they merely suggest that the government and the sector should “collaborate” on integrating international students into work in priority sectors.
- But there are some recommendations for change, particularly in relation to agents and data monitoring. On agents, they recommend that “universities should be required to publish data on their spend on international recruitment agents and the number of students recruited through agents annually”. They also suggest that the voluntary code for agents is probably insufficient and therefore recommend a mandatory registration system for international recruitment agents and subagents which includes quality controls, and enforced removal of agents from the system for compliance breaches, and a data sharing framework to monitor compliance. They want universities to have to say which agent they have used on a CAS application.
- On data, they want universities, who already have to report completion of a programme, to report on degree class. This would inform applications to the Graduate route. They want the Home Office to sort out its own data and use HMRC data.
It is also important to note that the introduction makes it clear that they do not believe that there is significant abuse of the Graduate route.
Context: The MAC quote the government’s purpose when setting up the graduate route:
- In 2021, the Home Office outlined the key objectives of the Graduate route. It is worth quoting this in full: “The Graduate route is introduced to enhance the offer to international students who choose, or are considering choosing, to study in the UK. It is intended to retain their talent upon graduation thus contributing to the UK economy. Through increasing the attractiveness of the UK as a destination of study, the policy will ensure the UK remains internationally competitive, assist to achieve the Government’s ambition to increase the number of international students in higher education and increase the value of education exports.
The questions: the committee summarise their instructions (important because of what has been said since)
- The letter made clear the intent of the government to continue attracting “the brightest and best” international students to study in the UK consistent with the International Education Strategy, and the important role the Graduate route has played in this ambition. However, there was a concern in the commissioning letter that the Graduate route may be attracting migrants to come to the UK primarily for post-study work opportunities, rather than to access a quality education and the secondary opportunity to gain experience in the UK labour market.
- The government asked us to provide evidence in answer to 5 questions:
- Any evidence of abuse of the route including the route not being fit for purpose (covered in Chapter 3); (see above; no)
- Who is using the route and from what universities they graduated (covered in Chapter 1);
- Demographics and trends for students accessing a study visa and subsequently accessing the UK labour market by means of the Graduate route (covered in Chapters 1 and 2) (see above);
- What individuals do during and after their time on the Graduate route and whether students who progress to the Graduate route are contributing to the economy (covered in Chapter 2); and,
- Analysis of whether the Graduate route is undermining the integrity and quality of the UK Higher Education system. This includes an understanding of how the Graduate route is or is not effectively controlling the quality of international students, such that it is genuinely supporting the UK to attract and retain “the brightest and best”, contributing to economic growth, and benefiting British higher education and soft power – in the context of the government’s wider International Education Strategy (covered in Chapters 3 and 4)
Recommendations:
The future of the Graduate route
…. Based on our analysis, the Graduate route is broadly achieving its objectives and supporting the International Education Strategy. We recommend retaining the Graduate route in its current form.
In making this recommendation, our key considerations follow.
- The government’s concerns about misuse of the route and its aim to reduce net migration:
- The restrictions on dependants on the Student route only came into force in January 2024. This change of policy on the Student route is in effect a restriction to the Graduate route, as dependants are only eligible for the Graduate route if they have been dependants on the Student route. Early indications show that this change will reduce the number of international students coming to study in the UK later this year, though it is not yet possible to assess the full impact given its recent implementation. In time, this change should reduce the numbers of both main applicants and dependants on the Graduate route as the student cohorts move into the route.
- We also expect the share of people moving from the Graduate route to long-term work visas in the UK to decline due to significant increases in salary thresholds on the Skilled Worker route. It is possible that this could potentially disproportionately affect some groups of international students and we would expect that the Home Office would have considered this whilst conducting an Equalities Impact Assessment before changes were made to the route.
- The impact of closing or further restricting the route on the higher education sector:
- Under the current higher education funding model, closure or additional restrictions could put many universities at financial risk. There has been a substantial fall in the real value of domestic fees since their introduction and many HE providers are becoming increasingly reliant on international student fees as the business model to fund increasing losses on domestic student provision (driven primarily by inflation) and research. If the government were to prioritise different objectives and restrict the route significantly, it should only do so once the full impact of the change to the dependants rules on the Student route and therefore the Graduate route can be seen and once it has addressed the current HE funding model which is driving the dependence on international student fees.
- The government’s levelling up agenda:
- Based on where the expansion of student numbers has occurred and the reliance of regional economies upon universities, a decrease in international student numbers due to the restriction or closure of the Graduate route could disproportionately impact local and regional economies outside London and the South East.
- For these reasons, our recommendation is to retain the Graduate route in its current form.
- However, we do suggest that greater collaboration between government and the HE sector could be fostered to support the government’s desired labour market objectives for the route. International graduates provide a potential pool of underutilised labour and could be better integrated into priority occupations and sectors. Universities benefit from the Graduate route, and they could further support the integration of international graduates into work and do more to raise awareness of the route among employers.
International Recruitment Agents and the Agent Quality Framework (AQF)
- It is important to protect international students from abuse and exploitation and to ensure that UK HE and our available study routes are being represented accurately by international recruitment agents. While we recognise the valuable role that many agents play in supporting international students and HE providers, we have heard from student representatives and Graduate visa holders about poor practice amongst some agents and sub-agents, such as providing misleading information about UK HE to prospective students.
- There is limited transparency around the extent to which universities are using agents. We recommend that universities should be required to publish data on their spend on international recruitment agents and the number of students recruited through agents annually as a starting point to improving disclosure.
- Whilst we welcome the voluntary Agent Quality Framework (AQF) to control for the quality of agents going forward, the current lack of a mandatory data sharing framework makes it difficult to understand which agents are working in the best interests of UK HE and students and the scale of poor practices. Based on experience of voluntary schemes within the immigration system, there is insufficient evidence that this voluntary code will prove effective against deliberate poor practice. We recommend that the government establishes a mandatory registration system for international recruitment agents and subagents which encompasses the quality controls in the voluntary AQF, consulting with the Devolved Administrations to ensure UK-wide coverage. Where agents and subagents are shown to have engaged in non-compliance, they should be removed from the system.
- We also recommend that a new data sharing framework encompassing key parties including universities, the British Council, and UK Visas and Immigration (UKVI), should be established to monitor agent and subagent practices effectively. This could include a requirement for universities to submit which agent has been used in an application for a Certificate for Acceptance of Study, allowing UKVI to collect comprehensive data on agents.
Recommendations on data and monitoring
- …. the introduction of the Graduate route in 2021 was a major policy change and we find it extraordinary that the government appeared to have very limited plans for data collection, monitoring and evaluation when the route was launched. Until this review, there was for example no data readily available looking at what universities those on the Graduate route had attended. In future, we recommend that the government should only open new migration routes or make significant policy changes when it has a clear plan for how it will collect and monitor data to assess the effectiveness of the route against its objectives and understand wider impacts. ….
- We also recommend that the Home Office introduces a requirement for universities to provide confirmation of the course outcome (e.g. class of degree) on the Student route, in addition to confirmation that a course has been successfully completed which is currently required. This should be part of the process for international students applying for the Graduate route, and that the data are collected in a way that will enable statistical analysis. This will enable an understanding of whether the government’s objective of retaining talented students has been achieved.
- We have also come across significant issues on the misunderstanding or mislabelling of Home Office data, … We recommend the Home Office undertakes a review of the data variables used for analytical purposes across the largest visa routes (including the Skilled Worker route, Student route and Graduate route) to develop a clear definition of what these data represent, and the quality of each variable collected. …We recommend that the government explore and make further use of the HO/HMRC matched data. … Data which follows the migrant journey over time linking between visas and HM Revenue & Customs (HMRC) earnings data is useful for analysing long term migrant progression and impact over time. …
Other data
Alongside the report, the Home Office published some data on migrants use of the Graduate route
Student perspectives
The Home Office also published some research on the sponsored study route to understand the broader context including the motivation of students and HEI perspectives.
So what next?
Well of course, just because the MAC report says keep the post study work visa doesn’t mean that the government will. There appeared, from some of the media reports, to be a fair level of unhappiness with the outcome of the report. There was a distinct lack of formal response though. Those in the sector rushing to celebrate should be cautious.
The BBC:
- The prime minister thinks there is “further to go” to bring down legal migration numbers, according to Rishi Sunak’s spokesman. “British students should be the priority for our education system and universities – and student visas must be used for education, not immigration,” he said. “We are focused on driving down migration whilst ensuring the UK attracts the best and the brightest.”
That sounds like doubling down.
The FT:
- Prime Minister Rishi Sunak is still looking to restrict the UK’s graduate visa scheme to cut legal migration to Britain, even after he was strongly advised by the government’s migration adviser not to abolish the programme. Sunak’s spokesperson has insisted ministers were not obliged to accept recommendations from the independent Migration Advisory Committee.
- …Senior Tories have been divided over whether to restrict the route. Chancellor Jeremy Hunt and education secretary Gillian Keegan have privately lobbied to retain the scheme in light of the severe financial strain many universities are under, said people familiar with the matter. But former migration minister Robert Jenrick and former health minister Neil O’Brien, who released a scathing report attacking the Tory government’s legacy on migration last week, criticised the MAC’s findings. Both former ministers argued on social media platform X that the report was guided by misleading parameters set by the government. This included not asking the MAC to review the government’s goal of attracting 600,000 foreign students per year and asking it to assess the extent of abuse in the visa system, rather than the social and economic impact of this type of migration. Jenrick and O’Brien reiterated calls for the graduate route to be scrapped immediately.
- …Industry figures cited in the report indicated the number of international students paying a deposit to study in the UK had fallen 57 per cent in May compared with a year earlier.
The Guardian
- The report’s release has stoked an internal Conservative party row over net migration, with senior rightwing MPs describing it as a “whitewash”.
- Robert Jenrick, a former immigration minister, wrote that the committee’s inquiries were tightly controlled by the commission from James Cleverly, the home secretary. “The MAC’s conclusions have clearly been constrained by the narrow terms of reference deliberately set by the government. If you order white paint, you get a whitewash,” he wrote on X, formerly Twitter.
- Neil O’Brien, a Tory MP who is an ally of Jenrick, described the report as a “whitewash” on Substack: “We are pursuing an arbitrary target, and the expansion of universities for their own sake.”
- Another Conservative MP said backbenchers were “piling pressure” on Rishi Sunak to ignore the committee’s conclusions.
- The government has so far declined to say whether it will accept the MAC recommendations. A source close to the home secretary said he would read the review thoroughly and listen to Prof Brian Bell, the committee’s chair, carefully before he makes any decision. They were due to meet on Tuesday afternoon.
Wonkhe has a piece summarising the findings which notes:
- Whether government will issue a suitably studied response is the next question for the sector. Next week’s Office for National Statistics data will bring a headline figure for net migration in 2023, a number which UK politics seems to have lost the ability to contextualise over the last few bi-annual releases, opening itself up instead to a furious buffeting from the press.
Research Professional also has a piece by Nick Hillman
- I am not a natural fan of the Migration Advisory Committee. It is said to be “independent” but has often seemed part and parcel of Whitehall—more specifically, the Home Office.
- The chair and members are picked by the Home Office, who decide the terms of reference of the committee and the work it undertakes, while the secretariat includes Home Office officials.
- But on this occasion, I am happy to eat my hat. The MAC has begun to strike out on its own. Even though it didn’t want the graduate route introduced in the first place, it now wants it kept in place. It has even floated some sensible-sounding—and, in truth, probably overdue—ideas on regulating agents. These could maintain confidence in the pathways followed by potential international students, although they won’t placate the Tory right.
- …There are two possible responses from ministers and the opposition to the MAC. One would be to throw their toys out of the pram. When advisers don’t give the advice that ministers want, they can be sacked and the government can do as it pleases. But another response would be to recognise the MAC has indeed come of age and that the child sometimes knows better than the parent.
 Dr. Pramod Regmi in the Centre for Wellbeing & Long-Term Health published two new academic papers just before Christmas on health and migration. The first one was called ‘Health and Wellbeing Among Nepali Migrants: A Scoping Review’ [1], and the second one has the title ‘Returning Home to Nepal after Modern Slavery: Opportunities for Health Promotion’ [2]. Both papers are Open Access and, hence, freely available online!
Dr. Pramod Regmi in the Centre for Wellbeing & Long-Term Health published two new academic papers just before Christmas on health and migration. The first one was called ‘Health and Wellbeing Among Nepali Migrants: A Scoping Review’ [1], and the second one has the title ‘Returning Home to Nepal after Modern Slavery: Opportunities for Health Promotion’ [2]. Both papers are Open Access and, hence, freely available online!





































 Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian
Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian NIHR-funded research launches website
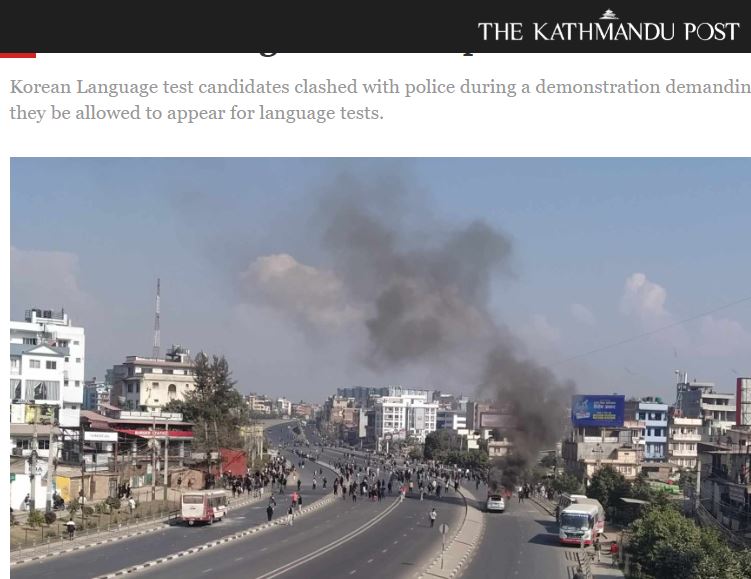
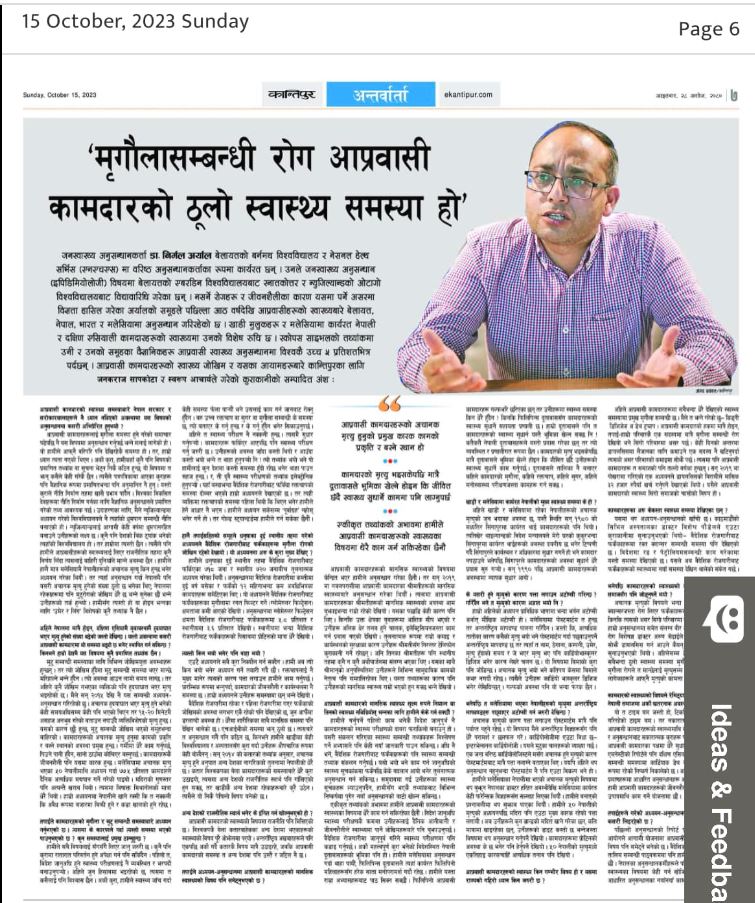
NIHR-funded research launches website Academics write for newspaper in Nepal
Academics write for newspaper in Nepal New paper published on disability in women & girls
New paper published on disability in women & girls MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease