Dr Ellie Jennings and Dr Alice Hunter write for The Conversation about the problems that can occur when young people are treated as athletes rather than children…
The problem with seeing young sportspeople as athletes first, children second

Ellie Gennings, Bournemouth University and Alice Hunter, Bournemouth University
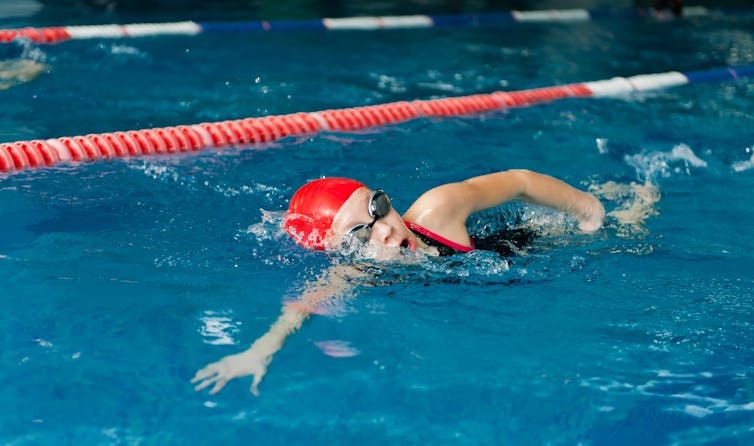
A recent report commissioned by Swim England, the national governing body for swimming in England, has found evidence of a “culture of fear” in swimming clubs. The report finds that children involved in competitive swimming can be treated like professional athletes, and the importance of sporting performance held above all else.
Sport can be a positive influence on young people’s wellbeing. Children are encouraged to participate in sport, and the aspiration to become an elite athlete is widely seen as an admirable goal.
Many children will find competitive sport enjoyable and rewarding. But problems can occur when the athletic identity of a young person overshadows their identity as a child. There is a risk that clubs, coaches and parents may treat young people as athletes rather than as children. And this can take place at all levels of sport, from children taking part in sports like swimming at local clubs to those who compete at the highest level.
One participant in the Swim England report said that a focus on swimming performance led to their social and academic life suffering, and that they would frequently push themselves in training to the point of vomiting or collapse to please their coach. “The way in which the sport is delivered to children and hiding under the label of ‘high performance athletes’ is driving people away from the sport they once loved,” they said.
“We’re not here to have fun, we’re here to win!” one parent told a researcher for the Swim England report.
A focus on sporting success above all can compromise children’s wellbeing and safety. Young people may be exposed to environments that are highly pressurised, psychologically demanding and often tolerant of abuse.
Certain practices that take place in youth sports, such as coaches and parents screaming on the sidelines, that would be considered unacceptable in other settings. A teacher would be unable to behave like this towards their charges in a school setting, for instance.
In football academies, child athletes are potential future stars – and money spinners. A business mindset shifts the focus from nurturing children to moulding them into “assets” for potential profit.
Treating children like products rather than unique individuals with their own childhood experiences overshadows children’s vital developmental needs.
Accelerated adulthoods
Liverpool manager Jurgen Klopp recently spoke about the need to protect young football players, including from media attention, as academy youth players made their debut in senior-level games. “But from tomorrow, leave the boys in the corner, please. And don’t ask: ‘Where are they now? Where are they now? Where are they now?’” he told reporters after Liverpool’s FA cup win over Southampton.
Darts player Luke Littler competed in the World Darts Championships and other major darts tournaments at the age of 16. Littler has received intense levels of public scrutiny that extended beyond the reaches of sport: his private life, including his relationship status, has made headlines.
Attention on the personal life of a minor rushes them towards adulthood but also shows a lack of respect for the privacy of young athletes: a significant safeguarding concern.
Children’s names have even been included in reports about doping. Kamila Valieva, a Russian figure skater, experienced the unwelcome publicity of having her positive test revealed at the age of just 15, causing controversy at the 2022 Beijing Winter Olympics.
This stands in stark contrast to practices elsewhere, such as in courts of law. Article 16 of the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child outlines children’s right to privacy.
A balanced approach
Children have the right to be protected from all forms of harm in sport. This extends to their right to participate in sports within a safe and enjoyable environment. There are evidently distinct challenges that arise when young people compete in elite and often adult-dominated sporting spaces.
The abuse of children in sports is a concern at both community and elite levels. It is essential to address these concerns to ensure that the pursuit of athletic excellence does not come at the cost of the fundamental rights and safety of young people.
When children are treated solely as athletes, the excitement around their potential means that the fact that they are still minors may be forgotten. They must be recognised as children first, especially when their performance in elite sports takes place prior to reaching adulthood.
It is the moral obligation of all adults involved in sport to develop an approach that keeps children in sport safe, even when they are classed as elite athletes.![]()
Ellie Gennings, Senior Lecturer in Sport Coaching, Bournemouth University and Alice Hunter, Senior Lecturer in Sports Coaching, Bournemouth University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.


















 BU academics in the news in Nepal
BU academics in the news in Nepal New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease