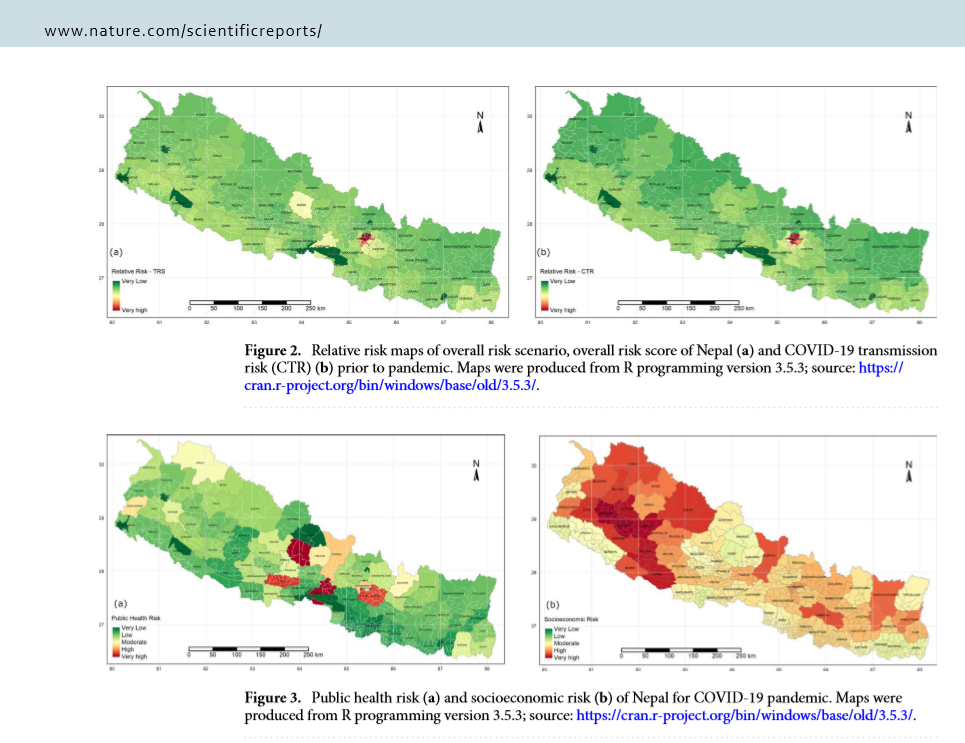
 An evidence-based, multidisciplinary approach on risk zoning, personal and transmission risk assessment in near real-time, and risk communication would support the optimized decisions to minimize the impact of coronavirus on our lives. This interdisciplinary paper [1], pubished today in Scientific Reports, offers a framework to assess the individual and regional risk of COVID-19 along with risk communication tools and mechanisms. Relative risk scores on a scale of 100 represent the integrated risk of influential factors. The personal risk model incorporates age, exposure history, symptoms, local risk and existing health condition, whereas regional risk is computed through the actual cases of COVID-19, public health risk factors, socioeconomic condition of the region, and immigration statistics. A web application tool (http://www.covira.info) has been developed, where anyone can assess their risk and find the guided information links primarily for Nepal. This study provides regional risk for Nepal, but the framework is scalable across the world.
An evidence-based, multidisciplinary approach on risk zoning, personal and transmission risk assessment in near real-time, and risk communication would support the optimized decisions to minimize the impact of coronavirus on our lives. This interdisciplinary paper [1], pubished today in Scientific Reports, offers a framework to assess the individual and regional risk of COVID-19 along with risk communication tools and mechanisms. Relative risk scores on a scale of 100 represent the integrated risk of influential factors. The personal risk model incorporates age, exposure history, symptoms, local risk and existing health condition, whereas regional risk is computed through the actual cases of COVID-19, public health risk factors, socioeconomic condition of the region, and immigration statistics. A web application tool (http://www.covira.info) has been developed, where anyone can assess their risk and find the guided information links primarily for Nepal. This study provides regional risk for Nepal, but the framework is scalable across the world.
 The authors comprised researchers from the University of Bristol, Science Hub (Nepal), University of the West of England, Public Health Perspective Nepal, Nepal Open University, Center for Molecular Dynamics Nepal, Mid Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust, the University of Huddersfield and Bournemouth University.
The authors comprised researchers from the University of Bristol, Science Hub (Nepal), University of the West of England, Public Health Perspective Nepal, Nepal Open University, Center for Molecular Dynamics Nepal, Mid Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust, the University of Huddersfield and Bournemouth University.
Reference:
- Parajuli, R.R., Mishra, B., Banstola, A. Multidisciplinary approach to COVID-19 risk communication: a framework and tool for individual and regional risk assessment. 21650 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78779-0













 BU attendance at third annual GCPHR meeting in June
BU attendance at third annual GCPHR meeting in June Interactive Tangible and Intangible Heritage Applications – BU student work featured in new book chapter
Interactive Tangible and Intangible Heritage Applications – BU student work featured in new book chapter Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week
Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease