NEW METAVERSE PAPER JUST PUBLISHED
Kılıçarslan, Ö., Yozukmaz, N., Albayrak, T., Buhalis, D., 2025, The impacts of Metaverse on tourist behaviour and marketing implications, Current Issues in Tourism, Vol.28(4), pp.622–642 https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2024.2326989
ABSTRACT
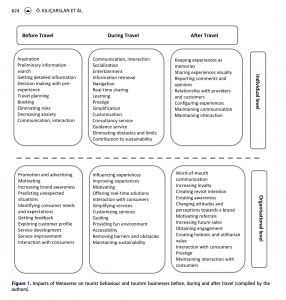
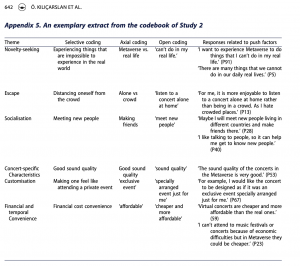
Metaverse is expected to deeply affect the travel and tourism industry and requires a dearth of empirical research. In this investigation, two exploratory qualitative research studies were conducted to fill this gap. The first research explored the potential impacts of Metaverse on the travel and tourism industry by interviewing tourism academics. Findings revealed that Metaverse could be used for marketing, CRM, and HRM by hospitality organisations, while it would be useful for marketing and sustainability of destinations. It could also influence tourist behaviour before, during, and after travel experiences. One of the notable findings was related to the close relationship between Gen Z and virtual events. The second research identified the motivations of Gen Z individuals to attend a concert organised in Metaverse. Accordingly, novelty-seeking, escape, fun and excitement, and socialisation were the most significant push factors to use Metaverse. Metaverse-specific characteristics, accessibility, and availability were the important pull factors to attend a Metaverse concert.


















 Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration
Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration 3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March
Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward?
Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward? ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease