FMC Cross-Departmental Seminar Series 2015-16
The Faculty of Media and Communication at BU
Venue: CG17, Christchurch House, Talbot Campus, Bournemouth University, Fern Barrow, Poole, Dorset, BH12 5BB
Wednesday 10 February 2016, 3pm-4pm, CG17
Pollyanna Ruiz, University of Sussex
Twitter, Transparency and Surveillance
Transparency is central to an understanding of the public sphere as a universally accessible arena characterised by reason, inclusivity and sincerity (Habermas, 1974). Consequently, the refusal to be seen is invariably interpreted as a threat to the principles that underpin the democratic process (Engles, 2007). However, if one experiences the public sphere not as a utopia of transparency (Johnson, 2001), but as a nightmare of surveillance and coercion then the desire to evade surveillance can be read very differently (Foucault, 1995). These dynamics are especially fraught in socio political environments in which the power relations that usually construct the relationship between the individual and the nation state are being blurred and eroded by criminal forces.
These complexities will be illustrated by a case study from Mexico in which a citizen journalist used a pseudonymous Twitter account to crowd source information about the movements of the drugs cartels in the state of Tamaulipas. Within this context Twitter can be read as a technological mask concealing the identity of multiple dissenting voices whilst also seeking recognition for the injustices being suffered by a people left unprotected by their state. As such ‘Felina’, who used a masked cat woman as her avatar, drew upon of long history of semi-folkloric figures who have used the protective qualities of the mask to speak to power (Ruiz, 2013).
However in January of this year ‘Felina’ was publically unmasked. Her Twitter account was commandeered by the cartel, her cat woman avatar was replaced by an image of her dead body and her followers were warned of retributions to follow. The brutal murder of Felina and the dissemination of threats through her social network is part of a cartel led counter offensive, which uses the fear of transparency to repress an emerging culture of sousveillance in cartel held territories. Consequently this paper will conclude by arguing that the optimism that characterised the rise of citizen journalism in oppressive regimes is being modified by the realisation that while online dynamics can be socially and politically productive, they can never disembody acts of dissent.
Bibliography
Engle, K. (2007) The face of a terrorist. Cultural Studies Critical Methodologies. Vol. 7 p.397-424.
Foucault, M. (1995) Discipline and Punish: The Birth of the Prison. New York Vintage Books.
Habermas, J. (1974) ‘The public sphere: an encyclopaedia article’, New German Critique, Vol. 3, pp.49-55.
Johnson, J.H. (2001) Versailles, meet les Halles: masks, carnival and the French revolution. Representations, Vol. 73 pp. 89-116.
Ruiz, P. (2013) ‘Revealing Power: Masked Protest and the Blank Figure.’ The Journal of Cultural Politics. Dukes Journals.
Pollyanna Ruiz is interested in the media’s role in the construction of social and political change. Her research focuses on the ways in which protest movements bridge the gap between their own familiar but marginal spaces, and a mainstream which is suspicious at best and downright hostile at worst. In doing so, she looks at the communicative strategies of contemporary political movements, such as the anti-globalisation movement, the anti-war movement and coalitions against the cuts. Her new project Protest, Technology and the Dynamics of Intergenerational Memory extends these dynamics over time.
Pollyanna is a Lecturer in Media and Communication at the University of Sussex. Her recently published book Articulating Dissent; Protest and the Public Sphere examines the ways in which coalition movements access the mainstream media.
Wednesday 10 February 2016, 4pm-5pm, CG17
Dr Lincoln Geraghty, University of Portsmouth
Constructing Childhood Memories: Nostalgia, Fandom and the World of LEGO Collecting
LEGO’s shift to producing product tie-ins has been supported by a very popular range of video games (eg. LEGO Star Wars) and the creation of online fan clubs aimed at both children and adults. One of them, the VIP Program, boasts a members’ only website, special offers and a point rewards system, specifically targeting grown-ups and encouraging them to collect LEGO rather than play with it, display it rather than pack it away. This convergence of popular fandom, new media, nostalgia and contemporary toy culture suggests that the lines between past and present, technology and culture, childhood and adulthood are increasingly porous. Memory is an important component of being a fan and the remediation of childhood toys like LEGO through video games, animated television shows and online communities helps to reconstruct memories of youth that are subsequently used to negotiate digital collaborative spaces shared by other fans. These spaces also serve as the means to add to and promote the often vast collections of adult collectors. In these web spaces personal memories and official histories of children’s culture are constantly negotiated and reshaped, taking on new meanings, as collections grow and collectors determine the subcultural and economic value of old and new LEGO sets. LEGO, a children’s toy originally based on the physicality of construction, has taken on new significance in contemporary media culture as it allows adult collectors/fans to reconnect with their past and define a fan identity through more ephemeral and digital interaction. Now that the LEGO “system” incorporates global franchises like Star Wars it means collectors/fans of one brand crossover to become collectors/fans of the other. The LEGO Star Wars universe develops a fandom of its own with the minifigure versions of Han Solo and Darth Vader (animated with comic effect in the video games and TV episodes) becoming just as iconic and desirable amongst collectors as the “real” toy originals. Therefore, I argue in this presentation that LEGO’s shift from educational children’s toy to transmedia adult collectible is characteristic of contemporary convergence culture. It highlights the importance of nostalgia in the influencing of what childhood media and commodities get collected but also how nostalgia acts to limit the original potentials of those remediated texts and commodities. There is an inherent conflict between how childhood texts are rebranded by producers and how fans choose to remember and negotiate those texts online. As a consequence, this presentation will also consider the reconstruction of personal and public memories of childhood in the digital sphere and assess the difficulties associated with the archiving and collecting of children’s media.
Lincoln Geraghty is Reader in Popular Media Cultures in the School of Media and Performing Arts at the University of Portsmouth. He serves as editorial advisor for The Journal of Popular Culture, Reconstruction, Journal of Fandom Studies and Journal of Popular Television with interests in science fiction film and television, fandom, and collecting in popular culture. He was recently appointed as a Senior Editor for the new online open access journal from Taylor Francis, Cogent Arts and Humanities. He is author of Living with Star Trek: American Culture and the Star Trek Universe (IB Tauris, 2007), American Science Fiction Film and Television (Berg, 2009) and Cult Collectors: Nostalgia, Fandom and Collecting Popular Culture (Routledge, 2014). He has edited The Influence of Star Trek on Television, Film and Culture (McFarland, 2008), Channeling the Future: Essays on Science Fiction and Fantasy Television (Scarecrow, 2009), The Smallville Chronicles: Critical Essays on the Television Series (Scarecrow, 2011), and, with Mark Jancovich, The Shifting Definitions of Genre: Essays on Labeling Film, Television Shows and Media (McFarland, 2008). He is currently serving as Editor for multi-volume Directory of World Cinema: American Hollywood from Intellect Books (2011 & 2015), and his most recent collection, entitled Popular Media Cultures: Fans, Audiences and Paratexts, was published by Palgrave in 2015.
About the series
This new seminar series showcases current research across different disciplines and approaches within the Faculty of Media and Communication at BU. The research seminars include invited speakers in the fields of journalism, politics, narrative studies, media, communication and marketing studies. The aim is to celebrate the diversity of research across departments in the faculty and also generate dialogue and discussion between those areas of research.
Contributions include speakers on behalf of
The Centre for Politics and Media Research
The Centre for the Study of Journalism, Culture and Community
Promotional Cultures & Communication Centre
Public Relations Research Centre
Narrative Research Group
Journalism Research Group
Advances in Media Management Research Group
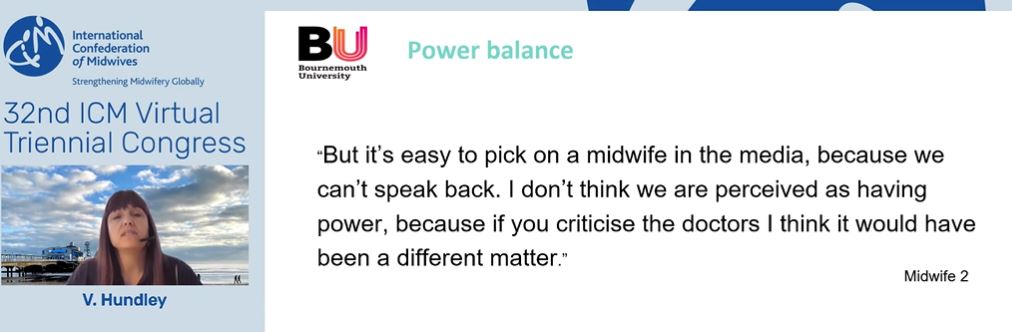 Today Prof. Vanora Hundley, based in the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences, gave a well-received presentation on ‘Changing the narrative around childbirth: whose responsibility is it?’ at the 32nd ICM (International Confederation of Midwives) Virtual Triennial Congress. Prof. Hundley presented online a BU collaboration published in the journal Evidence-based Midwifery [1]. This presentation is part of a larger body of interdisciplinary work between media and heatlh scholars at Bournemouth University [see 2-6].
Today Prof. Vanora Hundley, based in the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences, gave a well-received presentation on ‘Changing the narrative around childbirth: whose responsibility is it?’ at the 32nd ICM (International Confederation of Midwives) Virtual Triennial Congress. Prof. Hundley presented online a BU collaboration published in the journal Evidence-based Midwifery [1]. This presentation is part of a larger body of interdisciplinary work between media and heatlh scholars at Bournemouth University [see 2-6].




 Our
Our 











 REF Code of Practice consultation is open!
REF Code of Practice consultation is open! BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project
BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University
Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease