 The last week in March, Dr Roger Herbert and Prof Richard Stillman led a research team to collect samples of mud and benthic invertebrates from salinas (saltworking sites) along the Atlantic coast of Portugal and Spain. The BU team comprised five Applied Sciences undergraduates – Caitriona Shannon, Jemma Fowler, Karen Saunders, David Hartnell, and Rebecca Brown – plus research assistant Chris Moody and PhD student Kathryn Ross. The team assisted with mud sampling, sieving, data logging and recording.
The last week in March, Dr Roger Herbert and Prof Richard Stillman led a research team to collect samples of mud and benthic invertebrates from salinas (saltworking sites) along the Atlantic coast of Portugal and Spain. The BU team comprised five Applied Sciences undergraduates – Caitriona Shannon, Jemma Fowler, Karen Saunders, David Hartnell, and Rebecca Brown – plus research assistant Chris Moody and PhD student Kathryn Ross. The team assisted with mud sampling, sieving, data logging and recording.
The trip was organised as part of the EcoSal Atlantis project – a European Interreg IVb project which is gathering information about the heritage and biodiversity of saltworking sites along the Atlantic Coast of Europe, to inform and promote sustainable management of the sites (http://ecosal-atlantis.ua.pt). The project has partners in Portugal, Spain, France, and the United Kingdom. Prof. Mark Brisbane at Bournemouth University is the UK national co-ordinator.
(http://www.bournemouth.ac.uk/applied-sciences/research/ecosal-atlantis/uk-project.html)

 The sites we visited varied from small-scale commercial enterprises to those more focused on tourism and biodiversity conservation, but all sites provided some interesting insights into how management can improve the quality of a site for certain bird species.
The sites we visited varied from small-scale commercial enterprises to those more focused on tourism and biodiversity conservation, but all sites provided some interesting insights into how management can improve the quality of a site for certain bird species.
The purpose of our trip was to collect information on the diversity and abundance of benthic invertebrate fauna in salinas. At each salina, 3 mud cores were taken from 5 sites within the reservoirs and evaporation ponds to examine the invertebrates and a further core was taken to determine the sediment composition. Samples for benthic invertebrates were sieved on-site and preserved, and further processing and species identification will be done at Bournemouth University. At each site the depth, temperature and salinity were recorded to determine the effect of these factors on invertebrate distributions. Results from the analysis combined with data obtained from other sites sampled in north Portugal, France and in the UK, will help to characterise the benthic fauna of lagoons and salinas and contribute to understanding of the ecological value of the sites.


Below is a short summary of the trip, including photographs from each of the sites visited and a list of bird species observed.
We arrived at Lisbon at 19.00 on Saturday 24th, and were greeted at the airport by the EcoSal national coordinator for Portugal, Renato Neves, who accompanied us to our first study site, Salinas dos Samaouco (http://www.salinasdosamouco.pt/), on the Tagus estuary, where we stayed the night at the field centre. Within the first few minutes of waking up in the morning we got spectacular views of black-winged stilts, avocets and an osprey. Butterflies such as the swallowtail were abundant at the site. A flock of juvenile flamingos were feeding in one of the reservoirs.
 From Sunday 25th – Tuesday 27th we stayed at the Arocha Trust field centre ‘Cruzhina’, (http://www.arocha.org/pt-en/index.html), where we were warmly welcomed by the Felgueiras family and other staff . Arocha is an international environmental charity that does a lot of bird ringing and other field survey work in the Algarve.
From Sunday 25th – Tuesday 27th we stayed at the Arocha Trust field centre ‘Cruzhina’, (http://www.arocha.org/pt-en/index.html), where we were warmly welcomed by the Felgueiras family and other staff . Arocha is an international environmental charity that does a lot of bird ringing and other field survey work in the Algarve.

While based at Arocha, we sampled the nearby abandoned Salinas at Odiáxere, where we found Kentish plovers displaying at a potential nesting sites. Black-winged stilts and redshank were also present at the site. Crested lark and corn bunting were also observed close by.
The Salinas at Castro Marim, close to the Portuguese/Spanish border were particularly good for bird life. We observed spoonbills, black-winged stilts, avocets, little stints, dunlin, common and spotted redshank and common sandpiper feeding in the Salinas. Birds of prey were very common and we were treated to some great views of marsh harrier, Bonelli’s eagle and short-toed eagle.

 For the remainder of the trip, we stayed at the Los Gallos Hotel in Cadiz. Unfortunately the Spanish weather was not quite as obliging as the Portuguese weather had been, and we spent much of the next few days making sure the wind did not blow away our equipment or the smaller members of the team.
For the remainder of the trip, we stayed at the Los Gallos Hotel in Cadiz. Unfortunately the Spanish weather was not quite as obliging as the Portuguese weather had been, and we spent much of the next few days making sure the wind did not blow away our equipment or the smaller members of the team.
Our first Spanish Salina, San Vicente, in Cadiz http://www.salinasanvicente.es/, was probably the most active site we visited, with mountains of salt and machinery dotted around the site. Slender-billed gulls were common at the site. The site was also a good example of how diversification is important for making Salinas commercially successful – the main building housed a function room that is used for wedding receptions, and a restaurant where the various mixtures of flavoured salt are showcased in the recipes. The premium product, ‘Flor de Sal’ is sold internationally, with Harrods in the UK being a major customer.


It was furiously windy when we did our sampling, but the site manager’s father still assisted us in gathering some samples of Artemia, the small saltwater crustacean that forms an important part of many birds, and is responsible for the pink colour of flamingos.
That same windy afternoon, we were offered a tour of a very different type of salina from Dr. Alejandro Pérez Hurtado from Cadiz University. La Esperanza Grande salina is partly owned and managed by Cadiz University, and is intensely managed for the benefit of the birds and rigourously monitored to determine the effects of various factors such as water levels, vegetation density, and height of the walls of the ponds, on the birds foraging behaviour and breeding success. From this year it will also be involved with various community projects to tackle the issue of high youth unemployment in Cadiz.
 The final site we surveyed, Salina de Chiclana http://www.salinasdechiclana.com/, was also predominantly focussed on education and conservation. There was a marvellous visitor’s centre explaining the process of saltmaking with a lot of information on birds. Like the previous site, Chiclana puts much effort into managing the site for birds. We were lucky enough to have some bee-eaters fly past us as we took our final mud samples for the trip – a perfect end to a memorable week.
The final site we surveyed, Salina de Chiclana http://www.salinasdechiclana.com/, was also predominantly focussed on education and conservation. There was a marvellous visitor’s centre explaining the process of saltmaking with a lot of information on birds. Like the previous site, Chiclana puts much effort into managing the site for birds. We were lucky enough to have some bee-eaters fly past us as we took our final mud samples for the trip – a perfect end to a memorable week.
Bird list for the trip.
While the Salinas provided us with some excellent views of various waders, wildfowl and gulls, we also took advantage of the time between fieldwork to explore some of the other local avifauna. A few of the species observed on the trip, such as the great and little bustards were ‘life ticks’, even for Richard and Roger, so it was an exciting and educational experience for all of us. The entire list of species observed on the trip is detailed below.
Acknowledgements
Renato Neves , Portugal National co-ordinator;
Márcia Pinto and staff at Samouco Salinas Foundation, Lisbon;
Marcial Felgueiras, Arocha Portugal;
Anabela Resende and Filipe Moniz at Castro Marim;
Manuel Ruiz and staff at Salinas de San Vicente, Cadiz;
Dr. Alejandro Pérez Hurtado from Cadiz University;
Inmaculada Saludo at Salinas de Chiclana, Cadiz;
Lola Alcon Mestre, Fundacion Andanatura, Seville.

Table 1. Bird list for Eco Sal Portugal/Spain trip March 24-31st, 2012.
| Common name |
Latin name |
Group |
| Bee-eater |
Merops Apiaster |
Bee-eater |
| Black-winged kite |
Elanus caeruleus |
Birds of prey |
| Bonelli’s Eagle |
Aquila fasciata |
Birds of prey |
| Kestrel |
Falco tinnunculus |
Birds of prey |
| Lesser kestrel |
Falco naumanni |
Birds of prey |
| Marsh harrier |
Circus aeruginosus |
Birds of prey |
| Montagu’s harrier |
Circus pygargus |
Birds of prey |
| Osprey |
Pandion haliaetus |
Birds of prey |
| Red kite |
Milvus milvus |
Birds of prey |
| Short-toed eagle |
Circaetus gallicus |
Birds of prey |
| Corn bunting |
Emberiza calandra |
Buntings |
| Great bustard |
Otis tarda |
Bustards |
| Little bustard |
Tetrax tetrax |
Bustards |
| Cormorant |
Phalacrocorax carbo |
Cormorants |
| Azure-winged magpie |
Cyanopica cyanus |
Crows |
| Carrion crow |
Corvus corone |
Crows |
| Magpie |
Pica pica |
Crows |
| Goldfinch |
Carduelis carduelis |
Finches |
| Greenfinch |
Chloris chloris |
Finches |
| Linnet |
Carduelis cannabina |
Finches |
| Serin |
Serinus serinus |
Finches |
| Black-headed gull |
Chroicocephalus ridibundus |
Gulls |
| Great black-backed gull |
Larus marinus |
Gulls |
| Slender-billed gull |
Chroicocephalus genei |
Gulls |
| Yellow-legged gull |
Larus michahellis |
Gulls |
| Cattle egret |
Bubulcus ibis |
Herons, storks, flamingos, spoonbills |
| Flamingo |
Phoenicopterus roseus |
Herons, storks, flamingos, spoonbills |
| Grey heron |
Ardea cinerea |
Herons, storks, flamingos, spoonbills |
| Little egret |
Egretta garzetta |
Herons, storks, flamingos, spoonbills |
| Spoonbill |
Platalea leucorodia |
Herons, storks, flamingos, spoonbills |
| White stork |
Ciconia ciconia |
Herons, storks, flamingos, spoonbills |
| Hoopoe |
Upupa epops |
Hoopoe |
| Common waxbill |
Estrilda astrild |
Introduced & escapees |
| Rose-ringed parakeet |
Psitticula krameri |
Introduced & escapees |
| Crested lark |
Galerida cristata |
Larks |
| Short-toed lark |
Calandrella brachydactyla |
Larks |
| Thekla lark |
Galerida theklae |
Larks |
| Barn owl |
Tyto alba |
Owls |
| Pheasant |
Phasianus colchicus |
Partridges & Pheasants |
| Quail* |
Cotumix coturnix |
Partridges & Pheasants |
| Red-legged partridge |
Alectoris rufa |
Partridges & Pheasants |
| Feral pigeon |
Columba livia |
Pigeons & Doves |
| Stock dove |
Columba oenas |
Pigeons & Doves |
| Wood pigeon |
Columba polumbus |
Pigeons & Doves |
| Coot |
Fulica atra |
Rails & Crakes |
| Moorhen |
Gallinula chloropus |
Rails & Crakes |
| House sparrow |
Passer domesticus |
Sparrows |
| Spotless starling |
Sturnus unicolor |
Starlings |
| Starling |
Sturnus vulgaris |
Starlings |
| Barn swallow |
Hirundo rustica |
Swallows and martins |
| House martin |
Delichon urbicum |
Swallows and martins |
| Swift |
Apus apus |
Swifts |
| Sandwich tern |
Sterna sandvicensis |
Terns |
| Blackbird |
Turdus merula |
Thrushes |
| Stonechat |
Saxicola torquatus |
Thrushes |
| Wheatear |
Oenanthe oenanthe |
Thrushes |
| Great tit |
Parus major |
Tits |
| Avocet (pied) |
Recurvirostra avocetta |
Waders |
| Black-tailed godwit |
Limosa limosa |
Waders |
| Black-winged stilt |
Himantopus himantopus |
Waders |
| Common sandpiper |
Actitis hypoleucos |
Waders |
| Dunlin |
Calidris alpina |
Waders |
| Greenshank |
Tringa nebularia |
Waders |
| Grey plover |
Pluvialis squatorola |
Waders |
| Kentish plover |
Charadrius alexandrinus |
Waders |
| Little ringed plover |
Charadrius dubius |
Waders |
| Little stint |
Calidris minuta |
Waders |
| Redshank |
Tringa totanus |
Waders |
| Ringed plover |
Charadrius hiaticula |
Waders |
| Spotted redshank |
Tringa erythropus |
Waders |
| Turnstone |
Arenaria interpres |
Waders |
| White (pied) wagtail |
Motacilla alba |
Wagtails |
| Yellow wagtail |
Motacilla flava |
Wagtails |
| Cetti’s warbler* |
Cettia cetti |
Warblers |
| Fan-tailed warbler |
Cisticola juncidis |
Warblers |
| Sardinian warbler |
Sylvia melanocephala |
Warblers |
| Gadwall |
Anas strepera |
Wildfowl |
| Garganey |
Anas querquedula |
Wildfowl |
| Mallard |
Anas platyrhynchos |
Wildfowl |
| Shoveler |
Anas clypeata |
Wildfowl |
| Wren |
Troglodytes troglodytes |
Wren |
*heard only
This repoirt was written by BU PhD student Kathryn Ross. All photos are courtesy of Kathryn Ross and Chris Moody.
 ne and then engage in stimulating discussion. Have a look at our website to find out more about the venue and future events.
ne and then engage in stimulating discussion. Have a look at our website to find out more about the venue and future events.
 Congratulations to
Congratulations to 




















 In the last few days, BU academics have achieved a series of major results by having their expertise featured in key national media outlets.
In the last few days, BU academics have achieved a series of major results by having their expertise featured in key national media outlets.
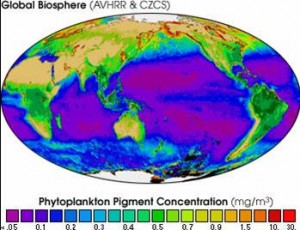
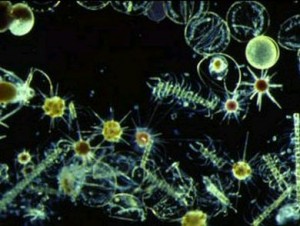
 Using this technology the scientists have built up a comprehensive picture of what grows where and how productive the different cells are.
Using this technology the scientists have built up a comprehensive picture of what grows where and how productive the different cells are.
 The research trip was made possible by the generosity of
The research trip was made possible by the generosity of  Dave Parham
Dave Parham
 The wreck has been featured on the One Show (6 April 2011) where presenter Dan Snow took part in a dive on the wreck in the mouth of Poole Bay alongside a team of BU Marine Archaeologists, led by Dave.
The wreck has been featured on the One Show (6 April 2011) where presenter Dan Snow took part in a dive on the wreck in the mouth of Poole Bay alongside a team of BU Marine Archaeologists, led by Dave. Dave will also feature in the fourth episode of Britain’s Secret Seas, The Bustling South, on 29 May at 8pm on BBC2.
Dave will also feature in the fourth episode of Britain’s Secret Seas, The Bustling South, on 29 May at 8pm on BBC2. After conservation, finds from the Wreck and all the information from the excavation will be passed on to
After conservation, finds from the Wreck and all the information from the excavation will be passed on to  I am delighted to tell you that BU has been awarded the AHRC Block Grant Partnership: Capacity Building Scheme grant that we applied for early this year. The final numbers are given below:
I am delighted to tell you that BU has been awarded the AHRC Block Grant Partnership: Capacity Building Scheme grant that we applied for early this year. The final numbers are given below:










 BU attendance at third annual GCPHR meeting in June
BU attendance at third annual GCPHR meeting in June Interactive Tangible and Intangible Heritage Applications – BU student work featured in new book chapter
Interactive Tangible and Intangible Heritage Applications – BU student work featured in new book chapter Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week
Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease