 The R&D People and Culture Strategy was published by the UK government in July 2021. The strategy sets out the government’s ambition to build the research and innovation workforce the UK needs, working in a positive and inclusive culture.
The R&D People and Culture Strategy was published by the UK government in July 2021. The strategy sets out the government’s ambition to build the research and innovation workforce the UK needs, working in a positive and inclusive culture.
People are at the heart of research and innovation. This strategy sets out a vision for attracting, retaining, developing and valuing the full diversity of people needed for an inclusive, vibrant research and innovation system that can fuel the UK’s recovery from the pandemic.
In her foreword, the then Science Minister Amanda Solloway described the strategy as a ‘call to action’. Building on work by people and institutions across the sector, the strategy sets out a step-by-step approach to foster the research and innovation culture needed.
The strategy has three priority areas: People, Culture, and Talent. The outcomes required are:
People: Redefining what it means to work in R&D in the 21st Century
Outcomes
• Attracting enough people with the right skills, across all roles
• Dynamic, varied and sustainable career paths
• Great leadership skills at all levels
Culture: Co-creating a vision of the culture we want to see in the sector
Outcomes
• A positive, inclusive and respectful culture
• Recognition and reward of all the people and activities that lead to excellent research and innovation
• Bullying and harassment is no longer an issue in the sector
• People feel confident to engage with and contribute to research and innovation
• Frameworks, assessment and incentives at an institutional level that encourage positive behaviours and support an inclusive culture
Talent: Renewing the UK’s position as a global leader in R&D by attracting, retaining and developing talented people
Outcomes
• People from all backgrounds are inspired into careers in research and innovation by the UK’s talent offer
• The UK will be the most exciting place in the world for top research and innovation talent
Short- and long-term goals are set out in the strategy.
UKRI is developing an ambitious programme of work to support the delivery of the strategy, working collaboratively with partners to drive forward lasting change.
UKRI First steps
Among the near-term actions set out in the strategy, UKRI will work to:
- create a good practice exchange to develop, test and evaluate ideas to improve culture sourced from the community, bringing together people from across the sector to work creatively
- launch a consultation on a new deal for post-graduate research students later this year, seeking input on funding, access, models and career routes
- pilot experimental approaches to public dialogue and community-led research and innovation
- co-design with partners a joined-up talent offer, open to a diversity of people across all career stages, connecting sectors, disciplines and working cultures.
 2 May 2018 (Wednesday)
2 May 2018 (Wednesday) The Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy has
The Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy has  The National Trust have published their research strategy for the next four years. You can read it in full
The National Trust have published their research strategy for the next four years. You can read it in full 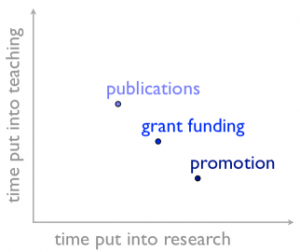











 The role of a university has been debated since the nineteenth century. In 1852 Cardinal Newman wrote that the sole function of a university was to teach universal knowledge, embodying the idea of ‘the learning university’. Newman believed that knowledge is valuable and important for its own sake and not just for its perceived use to society (this is very different from the current thinking on the importance of research impact, public accountability and the value of research findings to society at large, issues which I imagine Newman would have thought of as irrelevant!). There was not a great deal in Newman’s work about the importance of research in a university, but research was beginning to play the starring role in mainland Europe where Prussian education minister Wilhelm von Humboldt wrote of the concept of ‘the research university’ and eventually set up the Humboldt University of Berlin. After the Napoleonic Wars, von Humboldt’s view was that the research university was a tool for national rebuilding through the prioritisation of graduate research over undergraduate teaching. This model soon became the blueprint for the rest of Europe, the United States and Japan. Arguably the Russell Group universities are today still structured in a similar way to that envisaged by von Humboldt two hundred years ago.
The role of a university has been debated since the nineteenth century. In 1852 Cardinal Newman wrote that the sole function of a university was to teach universal knowledge, embodying the idea of ‘the learning university’. Newman believed that knowledge is valuable and important for its own sake and not just for its perceived use to society (this is very different from the current thinking on the importance of research impact, public accountability and the value of research findings to society at large, issues which I imagine Newman would have thought of as irrelevant!). There was not a great deal in Newman’s work about the importance of research in a university, but research was beginning to play the starring role in mainland Europe where Prussian education minister Wilhelm von Humboldt wrote of the concept of ‘the research university’ and eventually set up the Humboldt University of Berlin. After the Napoleonic Wars, von Humboldt’s view was that the research university was a tool for national rebuilding through the prioritisation of graduate research over undergraduate teaching. This model soon became the blueprint for the rest of Europe, the United States and Japan. Arguably the Russell Group universities are today still structured in a similar way to that envisaged by von Humboldt two hundred years ago. Moving into the twentieth century and we come across American educationalist Abraham Flexner who wrote of ‘the modern university’. In Flexner’s view universities had a responsibility to pursue excellence, with academic staff being able to seamlessly move from the research lab to the classroom and back again. The pursuit of excellence features in many universities strategies, and sounds very similar to the message conveyed by the REF team as part of the REF2014 guidance. The union of research and education also sounds similar to the current structure of many UK universities.
Moving into the twentieth century and we come across American educationalist Abraham Flexner who wrote of ‘the modern university’. In Flexner’s view universities had a responsibility to pursue excellence, with academic staff being able to seamlessly move from the research lab to the classroom and back again. The pursuit of excellence features in many universities strategies, and sounds very similar to the message conveyed by the REF team as part of the REF2014 guidance. The union of research and education also sounds similar to the current structure of many UK universities. The creation and sharing of new knowledge and new ideas has become the principal purpose of many modern universities. In Northern and Western Europe and North America the university has become the key producer of knowledge (through research) and the key sharer of knowledge (through teaching). The University of Bristol’s Vice-Chancellor Professor Eric Thomas claims that universities are the knowledge engines of our society having produced the vast majority of society’s breakthroughs and innovations, such as: the computer, the web, the structure of DNA, Dolly the Sheep, and the fibre optic cable. Where would we be without these breakthroughs, and would they have come about so quickly without university research?
The creation and sharing of new knowledge and new ideas has become the principal purpose of many modern universities. In Northern and Western Europe and North America the university has become the key producer of knowledge (through research) and the key sharer of knowledge (through teaching). The University of Bristol’s Vice-Chancellor Professor Eric Thomas claims that universities are the knowledge engines of our society having produced the vast majority of society’s breakthroughs and innovations, such as: the computer, the web, the structure of DNA, Dolly the Sheep, and the fibre optic cable. Where would we be without these breakthroughs, and would they have come about so quickly without university research?

 Last Friday BU held an internal Research Impact event to share the success of the excellent research that has been undertaken by BU academics. The focus of the event was on how this research has had an impact outside of academia, for example an impact on society, the economy, quality of life, culture, policy, etc.
Last Friday BU held an internal Research Impact event to share the success of the excellent research that has been undertaken by BU academics. The focus of the event was on how this research has had an impact outside of academia, for example an impact on society, the economy, quality of life, culture, policy, etc.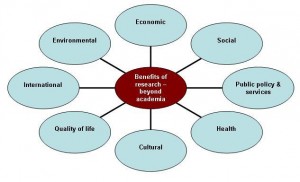


 Part of the presentation focused on the BU Research Themes which are currently being identified and defined through academic consultation via the Research Blog. This is still in the early stages but Matthew presented the ten draft themes that are emerging. You can comment on the emerging themes
Part of the presentation focused on the BU Research Themes which are currently being identified and defined through academic consultation via the Research Blog. This is still in the early stages but Matthew presented the ten draft themes that are emerging. You can comment on the emerging themes 
 Attendees were encouraged to go to impact case study presentations from different UOAs/Schools to find out about research that is undertaken in different areas of the University. Stronger impact case studies can also be developed with input from different disciplines.
Attendees were encouraged to go to impact case study presentations from different UOAs/Schools to find out about research that is undertaken in different areas of the University. Stronger impact case studies can also be developed with input from different disciplines. The event was also attended by key staff from Marketing & Communications who will be working with UOA Leaders to develop and enhance impact case studies between now and the REF submission in autumn 2013.
The event was also attended by key staff from Marketing & Communications who will be working with UOA Leaders to develop and enhance impact case studies between now and the REF submission in autumn 2013. There has been much positive feedback received from attendees and we are considering whether this should now be an annual event, celebrating the success of BU research and its benefit to society.
There has been much positive feedback received from attendees and we are considering whether this should now be an annual event, celebrating the success of BU research and its benefit to society. Many thanks to all the presenters and attendees, and everyone who supported the event and made it such a success! 😀
Many thanks to all the presenters and attendees, and everyone who supported the event and made it such a success! 😀
















 REF Code of Practice consultation is open!
REF Code of Practice consultation is open! BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project
BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University
Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease