Ahead of the London Marathon this weekend, Dr Ben Powis co-authors this article for The Conversation which explains the variety of techniques used by visually impaired runners, as well as the societal barriers that stop visually impaired people from getting involved in the sport.
London Marathon: how visually impaired people run
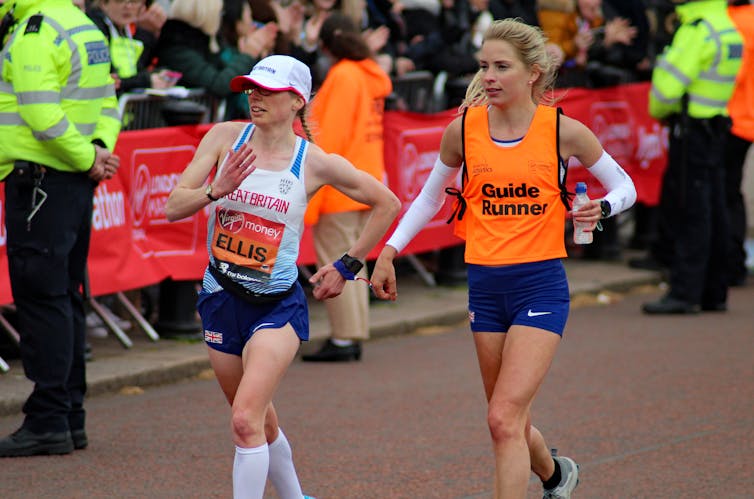

Dave Smith/Shutterstock
Jessica Louise Macbeth, University of Central Lancashire and Ben Powis, Bournemouth University
In this weekend’s London Marathon, nearly 50,000 runners will hit the capital’s streets in one of the world’s most iconic races. For the visually impaired (VI) runners on the start line, their approach to this famous route will differ from their sighted counterparts. Just as there are misconceptions about blindness itself, many people are confused about how VI people run.
Some assume that all VI runners are blind with no usable vision, have superhuman compensatory skills and are passively guided around running routes by sighted guides. The reality is that, like all runners, VI runners have diverse experiences, preferences and needs.
In our research, we’ve conducted in-depth interviews with eight blind and partially sighted runners about their running practices. Some navigate routes independently, while others run with a guide – using a tether, holding their elbow or running in close proximity.
VI running can be a rich and creative experience, engaging all the senses. But, as one of our participants stated, this process is not innate: “People say, ‘Oh your smell becomes better, your hearing becomes better’. I don’t think it does, I just think you tune into it a little bit more… it just becomes more of a natural thing.”
As research on the runner-guide partnership shows, it can take practice and trying different strategies for runners to make sense of their surroundings and figure out what works for them.
Through touch, hearing, smell and usable vision, VI runners actively develop unique relationships with the routes they run. Our participants described how they identify landmarks, such as the sound of a river or the feel of changing terrain, to construct maps inside their heads. As one runner explains: “I could subconsciously tell you where every crack on the pavement is.”
Barriers to running
With VI people being one of the most inactive minority groups, running can be inclusive, empowering and provide a range of social and physical benefits.
But there are a number of societal barriers to VI people getting and staying involved in running. Ableist assumptions about who can and cannot run, are frequently internalised by VI people themselves.
One of our participants, who is blind from birth, explained: “I’d never even considered running before really… I just thought I couldn’t do it.” Having acquired sight loss in adulthood, another participant said: “I thought I’d never be able to run again, which was a massive blow when I first started losing my sight.”
To combat these assumptions and spread awareness about opportunities, runners like Kelly Barton and her guides share running content online. A recent video of her 250th parkrun, which she completed without being tethered to a guide, attracted national media coverage.
Our participants reported struggling to find guide runners, who can support VI people to run safely by guiding them along a route using verbal instructions, tethers or physical contact.
One VI runner who owns a guide dog contacted a local running event for a guide and was told they “haven’t found a guide yet, but we’ve got a dog sitter”. While there are local groups connecting VI runners and guides in some areas, such as VI Runners Bristol, this is not consistent across the UK.
The challenge of finding guides was also exacerbated during the pandemic. In the US, an innovative project using guide dogs trained for running has led to positive outcomes for both runners and dogs. But such projects are not yet widespread and require additional training for the guide dogs.
For VI runners who prefer running indoors, the treadmills used in many gyms are inaccessible. The charity Thomas Pocklington Trust and UK Coaching are working to address this through the inclusive facilities toolkit.
How you can get involved
For many VI runners, including our participants, parkrun has become a popular place to get started. The event’s inclusive ethos and specific efforts to encourage VI runners have created a welcoming and accessible environment.
The Great Run Series has introduced VI runners challenges at the Bristol 10K and Manchester Half Marathon, the only dedicated events for severely sight-impaired runners and guides in the UK.
If you are in search of a guide, British Blind Sport and England Athletics operate a database to connect VI runners with guides licensed by England Athletics. And if you are a sighted runner thinking about becoming a guide, you can complete a sight loss awareness and guide running workshop to get listed on the database.
Prospective runners and guides can also connect informally through parkruns, running clubs, local VI organisations or running organisations like Achilles International.![]()
Jessica Louise Macbeth, Senior Lecturer in Sports Studies, University of Central Lancashire and Ben Powis, Senior Lecturer in Sport, Bournemouth University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.



































 BU attendance at third annual GCPHR meeting in June
BU attendance at third annual GCPHR meeting in June Interactive Tangible and Intangible Heritage Applications – BU student work featured in new book chapter
Interactive Tangible and Intangible Heritage Applications – BU student work featured in new book chapter Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week
Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease