
On Wednesday, 25th October 2017, BU’s Research and Knowledge Exchange Office (RKEO) will be hosting a STEAMLab on Food Security.
Which means…?
We have renamed ‘Sandpits’ to the new name of ‘STEAMLab’. This demonstrates the purpose of the STEAMLabs as being open to all disciplines and encouraging truly interdisciplinary research ideas. The ‘Lab’ part demonstrates the working environment that leads to the creation of novel research ideas and partnerships. In a nutshell, the STEAMLabs offer the opportunity to meet new people from all disciplines and sectors, and to spend dedicated time developing novel ideas for research projects.
For this STEAMLab, we’re seeking to come up with novel research which addresses challenges in food security. With increasing pressure on food sources and the food industry, we need to consider how food security can be guaranteed for the future. Potential areas to address this challenge may include but are not limited to, malnutrition/nutrition, agriculture, logistics, robotics, supply chain, new forms of food, sustainability, political/economic problems, food policy, food waste & recycling, and climate & the environment.
So, who should attend?
STEAMLabs cover broad themes to ensure that they are open to everyone from all disciplines. So if you think you have something to contribute then come along. If you think that they don’t include you then please have a chat with your RKEO Facilitator who can explain how your research could make a vital contribution to new ideas and approaches. In order to encourage wider partnerships, each STEAMLab will include academics from other universities, as well as representatives from industry and other sectors.
What do I need to prepare in advance? What will the STEAMLab entail?
Absolutely nothing in advance. During the session, you’ll be guided through a process which results in the development of research ideas. The process facilitates creativity, potentially leading to innovative and interdisciplinary research ideas. These ideas will be explored with other attendees, and further developed based on the feedback received.
What if I don’t have time to think about ideas in advance?
You don’t need to do this but it will help. Attendees will come from a range of backgrounds so we expect that there will be lively conversations resulting from these different perspectives.
What about afterwards? Do I need to go away and do loads of work?
Well… that depends! The interactive day will result in some novel research ideas. Some of these may be progressed immediately; others might need more time to develop. You may find common ground with other attendees which you choose to take forward in other ways, such as writing a paper or applying for research funding. Your Research Facilitator will be on hand to support you as you develop bids for funding.
What if my topic area is really specific, and doesn’t really relate to food?
Your contribution will be very welcome! One of the main benefits of this type of event is to bring together individuals with a range of backgrounds and specialisms who are able to see things just that bit differently to one another.
So, is this just networking?
Definitely not! It is a facilitated session with the primary intention of developing innovative research ideas, which also enables the development of networks. It gives you the opportunity to explore research ideas which you may develop over time, together with the chance to find common ground with academics from across BU and beyond.
How do I book onto this event?
To take part in this exciting opportunity, BU staff should complete the Food Security Application Form and return this to RKEDevFramework by Friday 13th October. As places are limited, this will be assessed to ensure good mix of attendees with different perspectives. Places will be confirmed w/c 16th October 2017.
By applying, you agree to attend for the full duration of the event on 25th October 2017 (c. 9:30 – 16:00). This event will be held on BU’s Talbot Campus.
If you have any queries prior to submitting your application, please contact Lisa Gale-Andrews, RKEO Research Facilitator.
This event is part of the Research Knowledge Exchange Development Framework.
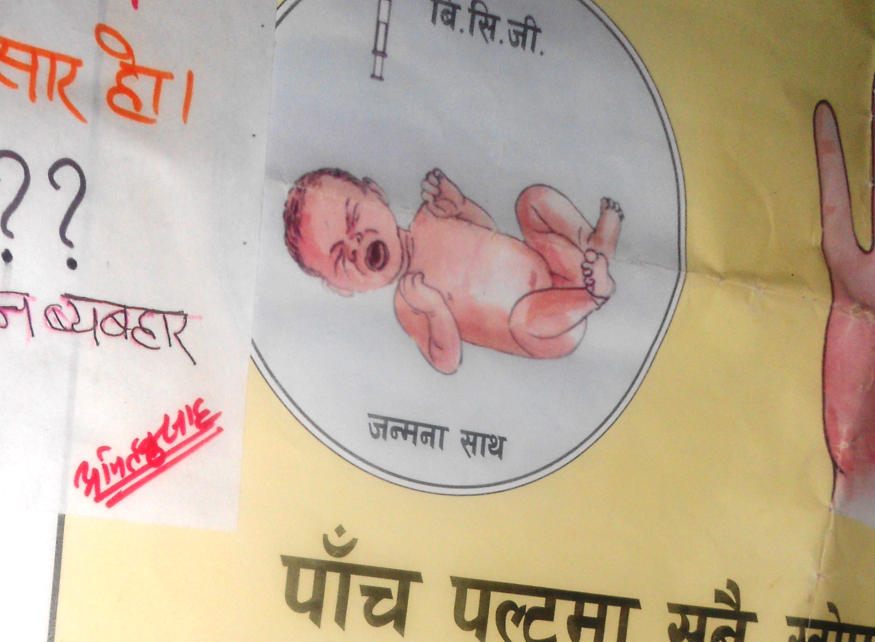 Today the journal BMC Health Services Research accepted our scientific paper ‘The contribution of female community health volunteers (FCHVs) to maternity care in Nepal: a qualitative study’ [1]. FCHVs who form an integral part of community-based primary healthcare system of Nepal. Some 50,000 FCHVs working across the country distribute temporary contraception or refer for other methods of family planning in formal healthcare centres.
Today the journal BMC Health Services Research accepted our scientific paper ‘The contribution of female community health volunteers (FCHVs) to maternity care in Nepal: a qualitative study’ [1]. FCHVs who form an integral part of community-based primary healthcare system of Nepal. Some 50,000 FCHVs working across the country distribute temporary contraception or refer for other methods of family planning in formal healthcare centres.


 The UK’s seven research councils have
The UK’s seven research councils have  It is estimated that 23% of the UK population is affected by mental health problems at some point each year. In spite of recent progress, more research is needed to better understand how to prevent, diagnose and treat mental illness. Only about a quarter of people with a mental health problem are deemed to receive ongoing treatment, leaving the majority grappling with mental health issues seeking help or information on their own, and depending on the informal support of family, friends or colleagues.
It is estimated that 23% of the UK population is affected by mental health problems at some point each year. In spite of recent progress, more research is needed to better understand how to prevent, diagnose and treat mental illness. Only about a quarter of people with a mental health problem are deemed to receive ongoing treatment, leaving the majority grappling with mental health issues seeking help or information on their own, and depending on the informal support of family, friends or colleagues.






 Our
Our 














 3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March
Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward?
Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward? BU academics in the news in Nepal
BU academics in the news in Nepal ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease