 ‘Staying Home Connecting Care’ is a British Academy funded research project exploring care provided to people at home during the Covid-19 pandemic. As society locked down, people with age-related frailties, disabilities, and certain health conditions needed to shield at home. Many relied on the support of family carers, home care workers and volunteer-run schemes to supply them with the care, companionship and essential supplies of food and medicines to stay safe and well at home.
‘Staying Home Connecting Care’ is a British Academy funded research project exploring care provided to people at home during the Covid-19 pandemic. As society locked down, people with age-related frailties, disabilities, and certain health conditions needed to shield at home. Many relied on the support of family carers, home care workers and volunteer-run schemes to supply them with the care, companionship and essential supplies of food and medicines to stay safe and well at home.
Over the past year we have been interviewing care workers, volunteers and carers from across Bournemouth, Christchurch, Poole (BCP) and Dorset, about their experiences of providing such care and support to people in their homes during the pandemic.
We recently organised an online workshop, ‘Care and Support at home in the time of Covid’. The aim of this free event was to share the interim findings of the study with a public audience, and invite feedback, reflection and discussion.
The highlight of the event was the roundtable discussion in which six speakers took part, each with extensive experience of home care work, voluntary and community pandemic activities and/or care of vulnerable adults. The round table speakers were:
Sue Warr from Prama life, Jon Sloper from Help and Kindness, Rosie Thompson from Gillingham Community Kindness, Sarah Ward from the Covid-19 Poole Community Support Group, Pam Henderson from Bournemouth University’s PIER Partnership and Andrew Davis from Right at Home and Dorset Home Care Providers’ Association.
Each round table participant spoke in fascinating and poignant detail about their activities during the pandemic. They reflected on how the ‘Staying Home’ research findings resonated with their own insights and experiences, and shared their perspectives on the priorities for future research and policy.
Several themes recurred throughout the course of the round table discussion. The dynamism and resourcefulness of the voluntary and community sector response to the pandemic was evident from many of the talks, which detailed how people in communities across BCP and Dorset rapidly and creatively devised practical schemes for getting help and support to people at home. The innovative use of telephone and web-based technologies to build new infrastructures to connect people was also a key area of discussion.
Speakers highlighted important shifts over the course of the pandemic. As one remarked, it is easy to forget the public uncertainty about how coronavirus was transmitted in the early days, when an effective vaccine seemed a distant prospect. This made close-contact caring for adults vulnerable to Covid-19 acutely stressful and challenging for carers and care workers.
Over time, as needs of people at home for basic supplies of food and medicines eased from summer 2020, other needs became apparent, not least many people’s poor mental health and loneliness. The isolation and loss of services had a profound impact on (family) carers. The pandemic has stretched to breaking point the fragile support networks on which many carers continue to depend. The phase of clapping for care workers and carers is over, but for some, the challenges to daily existence posed by the pandemic are more acute than ever.
Speakers highlighted several important questions for future research and policy. How can the hugely positive innovations within the voluntary organisations and communities be best supported and transformed as society reopens? How can that project be harnessed to the transformation of the social care system to make it fairer and fit for purpose, with appropriate levels of public investment? How can the rights and needs of people who still need to shield, and their carers, be protected, as wider society reopens?
Evaluation
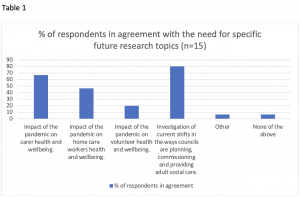
20-25 people attended the event, and, 15 of them anonymously completed the evaluation survey at the end of the workshop. All agreed that the presentation of interim findings was clear, accessible, interesting and informative, and that the roundtable furthered their understanding of care during Covid-19. All except one agreed that research on social care needs to take account of unwaged forms of support, such as that provided by carers and volunteers, as well as that provided by workers within social care services. One commented “This is a really important need as I don’t think people realise the scope of unpaid care that is happening”, whilst another remarked, “I feel the total focus is always around residential care, and other areas…including homecare and voluntary, get forgotten”.
Survey respondents highlighted several areas for further research.
The event was recorded and a link to it can be found here.
Dr Rosie Read, Principal Investigator
Erica Ferris, Research Assistant
Faculty of Health and Social Sciences
Bournemouth University
Email for correspondence: rread@bournemouth.ac.uk

 Chiplun, a city in the Ratnagiri district in the state of Maharashtra. This is the hub for our collaboration and a key to providing more mental health support and well-being in the rural area within the region. This week during the Mental Health Awareness day in India – we tailored a camp that addressed some of the core issues the community face.
Chiplun, a city in the Ratnagiri district in the state of Maharashtra. This is the hub for our collaboration and a key to providing more mental health support and well-being in the rural area within the region. This week during the Mental Health Awareness day in India – we tailored a camp that addressed some of the core issues the community face. This event was supported by the Local team @Drs Shrutika and Sunil Kotkunde, our academic partners @S
This event was supported by the Local team @Drs Shrutika and Sunil Kotkunde, our academic partners @S





 The Science, Health, and Data Communications Research Group invites you to our Autumn-Winter 2021 research series. These talks are open to the public, and encompass topics on representations of women scientists in the media, health inequalities and COVID-19, how comics are used for health messages, and how politics drives decisions around health and science.
The Science, Health, and Data Communications Research Group invites you to our Autumn-Winter 2021 research series. These talks are open to the public, and encompass topics on representations of women scientists in the media, health inequalities and COVID-19, how comics are used for health messages, and how politics drives decisions around health and science.




























 New Nepal scoping review on maternal & neonatal health
New Nepal scoping review on maternal & neonatal health Fourth INRC Symposium: From Clinical Applications to Neuro-Inspired Computation
Fourth INRC Symposium: From Clinical Applications to Neuro-Inspired Computation Writing policy briefs
Writing policy briefs Upholding Excellence: The Concordat to Support Research Integrity
Upholding Excellence: The Concordat to Support Research Integrity ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease