
What can I say? Achieving the funding with the British Academy, and embarking on the research has been one of my highlights of my academic career! The project has just completed, but I’d like to tell you a little bit more how it all happened, what it means to me, and offer some light-hearted moments, if I may.
First off – My journey to achieving funding was not an easy route. Looking at my data, I achieved success with the British Academy after a number of unsuccessful applications (over thirteen years) with the ESRC, the AHRC, Leverhulme, the Nominet trust, and a few with the British Academy as well. Well actually, It took seven failed bids with the British Academy, before success. Persistence, inevitably is a key facet, and it may not be as simple as, ‘ill respond to the feedback, and next time I will be successful’. As we know feedback can be highly subjective, and whilst you might get an idea of what you should have done better, there are no guarantees, or necessarily templates to follow. For example I have looked a good range of successful bids, and whilst you might get an idea of what might need to be presented, sometimes that can be misleading. You have your own voice, style and mode of narrative delivery, and you should not forsake that in seeking success. You need to sell your ideas, as much as yourself. I should know more about that, as prior to my academic career, I worked as a sales executive for quite a few years, and I have learned that its all about personal credibility, a product that offers good value for money, availability and endurance.
Writing funding bids, is a bit like working in the sales industry. You do need to get the order, but you have to be continually selling. Its about the process of continually selling, as much as the destination of the order.
So maybe learn from my experiences, which I am going to try and work through in this short blog.
There is no magical recipe to achieve external funding, but I think the most significant is ‘Don’t Give up’ in the immortal words of Peter Gabriel and Kate Bush Success can never be guaranteed, but you need to treat it like a process rather than a destination that is essential for you to arrive at.
Over the years that I have submitted bids, it’s been upsetting waiting for the deadline to pass, checking emails to see if you are going to get that magical acceptance message, and many times receiving the sad news, that ‘this time your bid was not successful, and you should not be deterred from trying again’. This seems like the end of a journey, but I would argue – for whatever reason you think you have been turned down, you should treat it like a new beginning, a chance to rework – rethink – ‘get back on your feet’ and ‘dust off your clothes’. As Kelly Clarkson says ‘What Doesn’t kill You Makes You Stronger’. OK that can seem a bit trite, because it can be devastating feeling rejected, and sometimes you don’t recover, and I think this is the essence of what we need to confront, in our research endeavors. It’s great to feel emboldened by a new sense of animation, where you start again, and you clearly see what you now need to do, but it’s not that easy. For example you should be wary not to Climb Every Mountain – you do need to be selective, and maybe you have missed an easier route, to where you want to go.
As I have learned over the many years of not being successful with external funding, there are three key elements that we need to consider:
- Your ability and identity – as a researcher or a personality.
- Your desire – what does this mean to you and what are you really going to achieve.
- The means – what are the pathways, the obstacles and the contexts that we need to work through to get where we want to.
For me most of my previous unsuccessful funding bids were ‘theoretical’, mostly I was thinking though how ideas can change though research. My ability, my desire and the means were too focused on my experiences of research, rather than what’s out there in the ‘real world’. The big shift for me was to conceive that research should be about process, impact and participants, rather than necessarily theories, debates and destinations.
So let’s take my research ideas as an example. Over the years I have researched LGBT identity in the media. I have produced a number of publications, presented at international conferences, and established an academic professional identity. This is certainly useful – to be perceived as an appropriate person to do funded research, but you need to demonstrate that you may be aware of what’s happening in the wider world, and what needs to be looked at.
LGBT studies is highly significant, but it can’t be just theoretical. How many times have I attended conferences and witnessed excellent conference papers with stellar academic foundations, often demonstrating the latest theories, mostly in the past focusing on gender performative theory, and more recently looking at affect theory. I am astounded by the academic rigor of these papers, and clearly the presenters have excellent experience in textual analysis, but mainly these texts are demonstrating academic potential.
While writing for funded research needs theoretical foundations, and sometimes developing a theory model may be a highly significant outcome, to make impact in the bid you need to articulate real world contexts, that may be messy, slippery and incomplete, but may offer a view or insight into something that we are missing.
In my research area the experiences of LGBTQ asylum claimants came to my attention though researching documentaries. Rather than focusing on representation, or even performance, I started thinking about experience. What were the experiences of LGBTQ asylum claimants in the UK? I had seen documentaries about the experiences of LGBTQ refugees in Europe, such as Exiled: Europe’s Gay Refugees at the same time I had seen the phenomenal documentary Our Journey to Europe which whist does not feature openly gay or queer refugees does frame the use of mobile technology. I then produced a paper called Queer Youth Refugees and The Pursuit of the Happy Object: documentary, technology and vulnerability, published in the book Youth Sexuality and Citizenship. Later I worked with Ieuan Franklin on a paper for Richard Berger who was curating a special issue on youth and refugees for the journal Interactions: Studies in Communication & Culture. Our paper was titled ‘Undocuqueer’ movement and DREAMers: activist online space and the affective queer body, which focused on the Undocuqueer Movement in the United States, where undocumented queer youth are struggling for rights.
This experience of new research that linked real world experiences of LGBTQ asylum claimants, made me think more about real world contexts. I wanted to find out what was happening to LGBTQ asylum claimants in the UK. With myself as lead investigator and Ieuan Franklin as co-investigator, we produced the funding application for the British Academy, consulting with Alan Mercel Sanca of LGB&T Equality Network Dorset who had some links with NGOs that supported LGBTQ asylum claimants. So working with a practice oriented stakeholder was incredibly useful, and led me to theorize who might be regional participants in the project. That said since we started the project, many of the participants changed, and in fact we ended up with a very different range of stakeholders. Also because of Covid-19 our project ended up being fundamentally different. We had planned to visit a number of regional NGOs, but it all ended up being done on Zoom. In many ways this was a benefit, as we were able to reach a far wider range of contacts. Added to this over the course of the project we established links with the regional NGOs and formed a prototype network across the UK, and I am pleased to report many of the participants are now supporting us in developing a follow on bid with the Nuffield Foundation.
Having now completed the British Academy project, I feel quite differently about funding applications. As principal investigator, you need to consider who is the best person to do the research, and though hiring our fabulous post-doctoral research assistant Mengia Tschalaer on the British Academy Project, I quickly learned what a pleasure it is to hire someone who is passionate about the subject area, and can be a great asset. At many points Mengia was driving the research as much as Ieuan or I. What a wonderful team member. So:
Point One – maybe you are not doing all the research, and hiring motivated others makes perfect sense.
Point Two – (which is a corollary of point one) – don’t make it all about you, look for needs in society, not necessarily just ways of looking.
Point Three – don’t be afraid to fail in bidding, research is a process not a destination. Even failed bids can lead to great outcomes for you.
On that note one of my failed applications to the British Academy was a proposal for book on the AIDS activist Pedro Zamora. Although this was never funded externally, and it was researched in my own research time with support from the Fusion Fund, this is one of my favourite achievements. Notably when I launched the book at GLBT Historical Society in San Francisco, it felt like a defining moment, especially when I was interviewed in the Bay Area Reporter.
So don’t think of funding applications as destinations that you must reach, but treat each application as a process based journey, where you will develop your ideas, which will be useful, whatever happens.
Writing funding applications is inherently personal, you spend considerable time working on the application, not really knowing if you are going to be successful, but you try.
And in the immortal words of the ethereal Sandy Denny of Fairport Convention, lets always give it ‘One More Chance’
 Congratulations to Anjana Paudyal, PhD student in the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences (FHSS), on the first publication from her PhD work. Anjana’s PhD research focuses on human trafficking in Nepal. Human trafficking is a form of modern slavery and it is a common crime aggravated by poverty, political instability, illiteracy, unemployment, as well as climate change. Despite being a global problem, modern slavery is understudied and poorly understood. Victims of modern slavery are exploited and can experience significant physical, psychological, or sexual, and reproductive health problems. Until recently, there has been little research, especially in low-income countries such as Nepal, around the need and opportunities for health promotion and education in this vulnerable group.
Congratulations to Anjana Paudyal, PhD student in the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences (FHSS), on the first publication from her PhD work. Anjana’s PhD research focuses on human trafficking in Nepal. Human trafficking is a form of modern slavery and it is a common crime aggravated by poverty, political instability, illiteracy, unemployment, as well as climate change. Despite being a global problem, modern slavery is understudied and poorly understood. Victims of modern slavery are exploited and can experience significant physical, psychological, or sexual, and reproductive health problems. Until recently, there has been little research, especially in low-income countries such as Nepal, around the need and opportunities for health promotion and education in this vulnerable group.












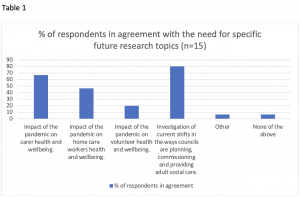
 Covid-19 lockdowns and social distancing have socially and spatially reorganised the reproductive labour entailed in supporting, maintaining and sustaining people in everyday life. The closure of schools, day centres, shops and non-essential services, alongside prohibitions on household mixing, have meant that caring work has been much more spatially concentrated and contained within households than in normal times. For reasons of health, age or physical frailty, a large number of adults have come to depend more than usual on others to support and care for them at home.
Covid-19 lockdowns and social distancing have socially and spatially reorganised the reproductive labour entailed in supporting, maintaining and sustaining people in everyday life. The closure of schools, day centres, shops and non-essential services, alongside prohibitions on household mixing, have meant that caring work has been much more spatially concentrated and contained within households than in normal times. For reasons of health, age or physical frailty, a large number of adults have come to depend more than usual on others to support and care for them at home. gland ) Project Output (supporting mental health and wellbeing in India)
gland ) Project Output (supporting mental health and wellbeing in India) 







 On 17th September 2020 students from DePaul University, USA; SSLA, India, and Bournemouth University engaged in an online dialogue exploring the effects of the current pandemic and their understanding of Psychology.
On 17th September 2020 students from DePaul University, USA; SSLA, India, and Bournemouth University engaged in an online dialogue exploring the effects of the current pandemic and their understanding of Psychology.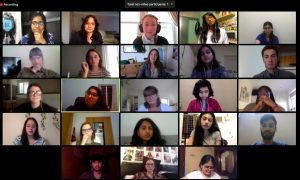
 In March, POST launched the Covid-19 outbreak expert database
In March, POST launched the Covid-19 outbreak expert database










 Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian
Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian NIHR-funded research launches website
NIHR-funded research launches website Academics write for newspaper in Nepal
Academics write for newspaper in Nepal New paper published on disability in women & girls
New paper published on disability in women & girls Global Consortium for Public Health Research 2025
Global Consortium for Public Health Research 2025 MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease