 My name is Anjana Regmi Paudyal, and I am a PhD student in the Faculty of Health, Environment and Medical Sciences (HEMS), Bournemouth University (BU). My doctoral research focuses on modern slavery, particularly the opportunities and barriers to survivors reintegrating into their families and communities. I was honoured to take part in the Turing Scheme traineeship and other international academic activities in Nepal, which became a truly transformative experience both personally and professionally. The Turing Scheme lasted four weeks and was hosted by the Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences (MMIHS) in Kathmandu.
My name is Anjana Regmi Paudyal, and I am a PhD student in the Faculty of Health, Environment and Medical Sciences (HEMS), Bournemouth University (BU). My doctoral research focuses on modern slavery, particularly the opportunities and barriers to survivors reintegrating into their families and communities. I was honoured to take part in the Turing Scheme traineeship and other international academic activities in Nepal, which became a truly transformative experience both personally and professionally. The Turing Scheme lasted four weeks and was hosted by the Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences (MMIHS) in Kathmandu.
 My traineeship was arranged through Bournemouth University in partnership with MMIHS in Kathmanduand it was supported by my BU supervisors Dr. Orlanda Harvey and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen. I chose this placement because MMIHS has a strong research culture and offers opportunities to collaborate with students, faculty, and NGOs working in migration and modern slavery.
My traineeship was arranged through Bournemouth University in partnership with MMIHS in Kathmanduand it was supported by my BU supervisors Dr. Orlanda Harvey and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen. I chose this placement because MMIHS has a strong research culture and offers opportunities to collaborate with students, faculty, and NGOs working in migration and modern slavery.
From the very beginning, I felt warmly welcomed by academics and students, which helped me settle in quickly. The first week was spent getting to know the university, its values, and its research culture. I particularly enjoyed informal discussions with first- and second-year MSc students, where we shared ideas and experiences across different academic settings.
By the second week, the focus shifted towards intensive academic engagement. I participated in a  research workshop on grant applications, systematic reviews, and qualitative research methods led by expert guest speakers. These sessions sharpened my skills in data analysis and literature reviews, giving me fresh insights into areas highly relevant to my own PhD. Alongside this, I began engaging with NGOs (Non-Governmental Organisations) working in the field of migration and modern slavery. I met with Ms. Manju Gurung, Director of POURAKHI Nepal, an organisation that supports female returnee migrants and survivors of trafficking. I also gathered policy documents and insights from Green Tara Nepal (GTN) and the Nepal Development Society (NeDS), both of which have significant experience in migration health. These connections will help to shape my upcoming PhD fieldwork.
research workshop on grant applications, systematic reviews, and qualitative research methods led by expert guest speakers. These sessions sharpened my skills in data analysis and literature reviews, giving me fresh insights into areas highly relevant to my own PhD. Alongside this, I began engaging with NGOs (Non-Governmental Organisations) working in the field of migration and modern slavery. I met with Ms. Manju Gurung, Director of POURAKHI Nepal, an organisation that supports female returnee migrants and survivors of trafficking. I also gathered policy documents and insights from Green Tara Nepal (GTN) and the Nepal Development Society (NeDS), both of which have significant experience in migration health. These connections will help to shape my upcoming PhD fieldwork.
During the third week, it was my turn to share. I presented my PhD project, and my approach, using photo elicitation, is relatively new in Nepalese research, therefore, it sparked great curiosity among students and faculty. The discussions that followed were highly rewarding, especially around ethical considerations and practical challenges. I was struck by the students’ engagement, particularly the second-year MSc cohort, who found the sessions useful for their own research journeys.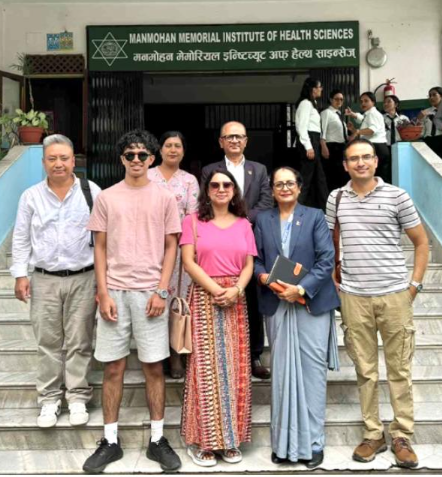
As my time in Nepal came to an end, I reflected on the differences between teaching and learning styles in the UK and Nepal. I spoke with students about the UK system, where independent study and varied assessment methods are emphasised, which was particularly valuable for those considering postgraduate studies abroad. Beyond academia, I was fortunate to experience cultural festivals within and beyond Kathmandu Valley, which deepened my appreciation of Nepal’s vibrant traditions and community spirit.
 I was fortunate to witness the “Gaijatra Festival” in Bhaktapur, Nepal. Gai Jatra is a Newari Hindu festival that honours deceased loved ones by parading decorated cows or children dressed as cows through the streets. The belief is that cows guide souls to the afterlife. Celebrated around the August full moon, the festival features music, dance, humor, and satire to provide comfort to grieving families and encourage them to embrace life despite their loss.
I was fortunate to witness the “Gaijatra Festival” in Bhaktapur, Nepal. Gai Jatra is a Newari Hindu festival that honours deceased loved ones by parading decorated cows or children dressed as cows through the streets. The belief is that cows guide souls to the afterlife. Celebrated around the August full moon, the festival features music, dance, humor, and satire to provide comfort to grieving families and encourage them to embrace life despite their loss.
Looking back, this traineeship not only enhanced my academic and research skills but also strengthened my confidence in working across cultures and linking theory with practice. It confirmed my motivation to pursue a global research career and taught me the importance of being open, flexible, and curious. My greatest achievement was being able to present and discuss my methodology with such an engaged audience, while also building long-term connections with NGOs and academic partners.
I would wholeheartedly recommend the Turing Scheme to other students. It is challenging but deeply rewarding, offering the chance to grow personally, academically, and professionally while contributing meaningfully to international collaborations. The environment at MMIHS was  welcoming, though more structured compared to the UK. Students showed huge interest in UK teaching and assessment styles. Most academic sessions were in English, but some conversations were in Nepali, which helped me practice my language skills and build rapport.
welcoming, though more structured compared to the UK. Students showed huge interest in UK teaching and assessment styles. Most academic sessions were in English, but some conversations were in Nepali, which helped me practice my language skills and build rapport.
If you get the opportunity: Say yes to goin abroad on the Turing Scheme. It challenges you, but the growth and insights are worth it. I am much more confident working with diverse groups, whether in academic or NGO settings. Presenting my PhD methodology in Nepal and receiving recognition and engagement from students and academics. Academic presentation, intercultural dialogue, trauma-informed sensitivity, networking with NGOs, and collaborative learning. Absolutely. The Turing Scheme was transformative for both my personal and professional development.
 Congratulations to Jonathan Parker, Ivan Gray, Andrew Morris and Sally Lee, the editors of the fourth edition of Newly-Qualified Social Workers: A Practice Guide to the Assessed and Supported Year in Employment [1]. This new edition has eleven chapters. Apart from the various chapters produced or co-produced by the editors, this 2026 text also include a chapter by two further Bournemouth University academics, including Dr. Richard Williams and Dr. Louise Oliver. The latter contributed ‘Chapter 7: Research and NQSW: Developing yourself as a research minded and critically reflective practitioner’.
Congratulations to Jonathan Parker, Ivan Gray, Andrew Morris and Sally Lee, the editors of the fourth edition of Newly-Qualified Social Workers: A Practice Guide to the Assessed and Supported Year in Employment [1]. This new edition has eleven chapters. Apart from the various chapters produced or co-produced by the editors, this 2026 text also include a chapter by two further Bournemouth University academics, including Dr. Richard Williams and Dr. Louise Oliver. The latter contributed ‘Chapter 7: Research and NQSW: Developing yourself as a research minded and critically reflective practitioner’.











































 REF Code of Practice consultation is open!
REF Code of Practice consultation is open! BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project
BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University
Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease