We’re excited to launch our series of free events online and in-person, as part of the ESRC Festival of Social Science 2022.

What can research tell us about our society? We’ll be holding events for the public featuring discussions on how young people can build an entrepreneurial mindset and discover how play and gamification can reduce anxiety in children around medical appointments. Find out more about our fascinating programme of events.
The ESRC Festival of Social Science 2022
Which one of us is human?
Saturday 22 October
Bournemouth Library, Bournemouth
Imagine a future where robots and humans looked identical: how would you know who is human? Join this interactive event to identify the ‘robot’ from live performers. Discuss your tactics and explore the mystery behind the experience.
How to become a young entrepreneur
Tuesday 25-Thursday 27 October
The Old School House, Boscombe
Not everyone wants to be an entrepreneur, but entrepreneurial skills can not only help young people to start their own businesses, but they can also help boost their employability. Join this event to find out how young people can build an entrepreneurial mindset.
Tuesday 8 November
Online
Medical monsters: reducing medical anxiety through play and gamification
Saturday 12 November
Bournemouth Gateway Building, Bournemouth
Anxiety around medical appointments and admissions can affect people in different ways, from causing distress and worry to preventing people seeking the medical help they need. Join this interactive session to explore how play and gamification strategies can reduce patient anxiety in children. Featuring specially designed sessions of Jenga, LEGO® SERIOUS PLAY® and virtual reality experiences.
Closed-group activities as part of the Festival of Social Science
Some activities are organised with partner organisations or particular groups and are not open for general registration.
Are drones the future of delivery?
If predictions about the future of deliveries are correct, we might start seeing a lot more drones in our skies. But how do you feel about this? How much do you actually know about drones and how they will be used?
Join us to learn more and play a custom-designed board game, to explore how we’ll make decisions about drones in our future.
Youth in nature: escaping to the outdoors
Social science evidence suggests nature exposure benefits mental and physical health, yet teenagers have low rates of access to nature and levels of nature connectedness. Research shows youth nature engagement requires a sense of purpose; therefore, this event invites young people to experience activities centred on ‘being’ or ‘doing’ in outdoor space.
Don’t get scammed online
Being scammed online is often seen as a problem for older people, but young people can fall victim to scams too. This workshop helps young people think about their online experience and learn how to avoid being scammed.
If you have any questions about these events, or if you would like to know how you can get involved in one of our Public Engagement with Research events, please email the public engagement team.

 Apply now
Apply now

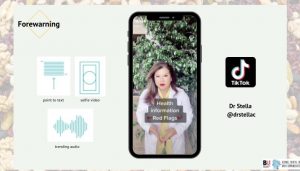
 To help guide people through the process of creating social media stories for information and health literacy, Professor Feigenbaum designed the
To help guide people through the process of creating social media stories for information and health literacy, Professor Feigenbaum designed the 





 Apply for £500-£5,000 to fund your public engagement activity or event
Apply for £500-£5,000 to fund your public engagement activity or event










 Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University
Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU
Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU 3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease