
Original post by Mafalda Picarra, JISC – https://scholarlycommunications.jiscinvolve.org/wp/2016/07/06/the-springer-compact-offset-model-update-on-progress/
In this blog post, Jisc Collections provides an update on how the Springer Compact agreement is progressing in the UK.
In March 2015, Jisc Collections announced that it had reached an agreement with Springer for an offset model to contain the costs of publication and subscription access for UK institutions. Six months have passed since the agreement launched in January 2016, with an additional 368 articles published free of charge in the pilot phase between October and December 2015.
The Springer Compact agreement is a flipped model which enables researchers from 91 participating UK institutions to publish their articles immediately as open access in ~1,600 Springer journals as well as to access all content published in ~2,500 Springer journals. In this flipped model, rather than paying a subscription fee and an unknown number of APC charges, the institution pays a set fee for unlimited APCs based on their 2014 APC expenditure with Springer and a top up fee to cover access to all the subscription content – thus containing the total cost of ownership.
This model moves away from the traditional historical print spend model aiming to reduce costand administration barriers to hybrid open access publishing and to increase open access. All UK articles published in eligible Springer Open Choice hybrid journals are made immediately open access upon publication and are automatically compliant with funder requirements.
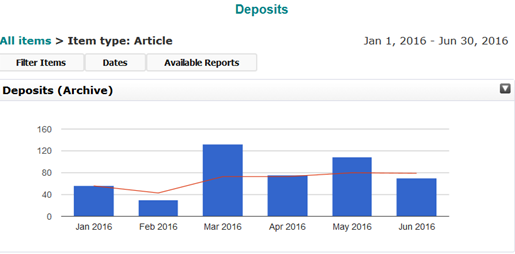
Since January, 1259 articles have been published by authors from 92% of UK institutions participating in the agreement (Figure 1). In only five months (January to May), 86% of UK institutions have already published open access articles equivalent to or in excess of their total 2014 APC spend. This means that researchers from these institutions are publishing more OA articles than they did in 2014 but the cost to the institutions is capped. If we look at the pro-rata (Jan-May) of the total fee paid to Springer for this year (2014 APC spend and subscription top up fee), 23% of these institutions have already published open access articles to value of the total combined fee.
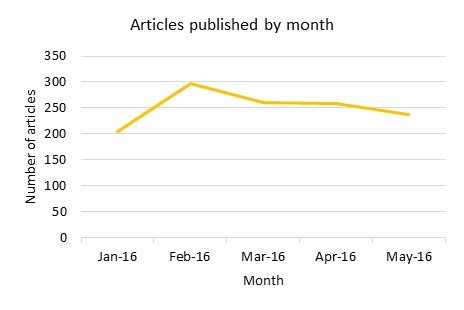
Figure 1 Articles published by month.
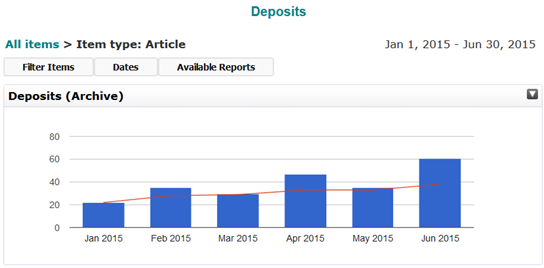
In addition, the number of articles published on open access through Springer’s hybrid journals has increased by 25% in the first five months of the agreement when compared to the total number of articles published in 2015 (Figure 2).
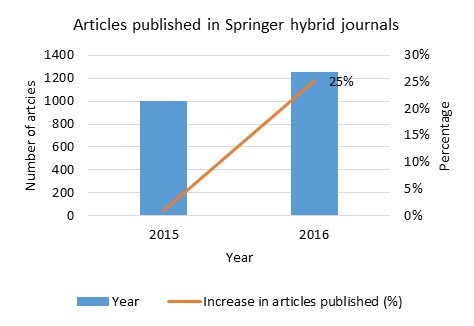 Figure 2 Articles published by UK authors in Springer hybrid journals in 2015 (subject to APC payment) and 2016 (under the Springer Compact deal).
Figure 2 Articles published by UK authors in Springer hybrid journals in 2015 (subject to APC payment) and 2016 (under the Springer Compact deal).The subject areas where more articles have been published include Medicine (22%), Biomedical and Life Sciences (18%), Education (9%), Earth and Environmental Science (7%), Chemistry and Materials Science (6.6%), Engineering (6.5%), and Mathematics and Statistics (5.8%) (Figure 3).
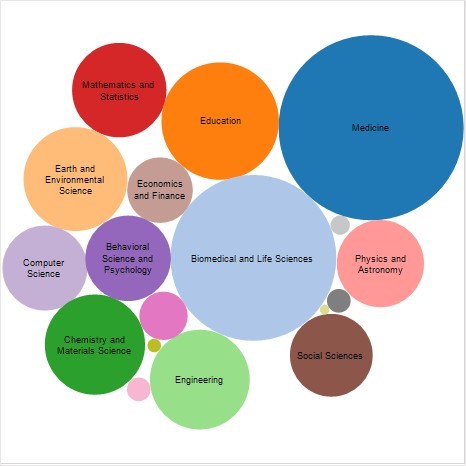
Figure 3 Articles published by subject.
Examples of journals with the highest number of publications include Diabetologia (26 articles), Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology (22 articles), Synthese (19 articles), Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders (17 articles), Psychopharmacology (17 articles), and The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology (17 articles) (Figure 4).
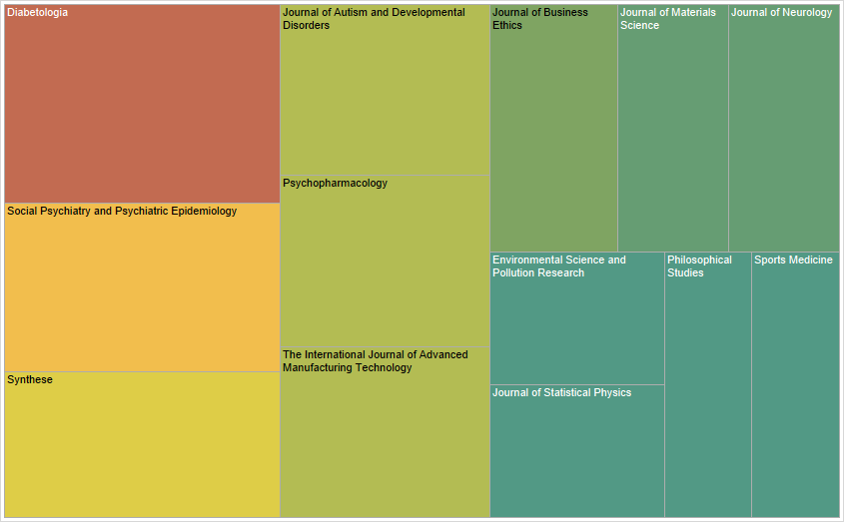
Figure 4 Journals with the highest number of publications.
The feedback received from libraries at Jisc’s offsetting workshops[1] suggests that this is a workable and efficient model that other publishers could adopt. The administration has been easier for institutions, for instance, by rationalising the eligibility, approval and payment processes which consequently saves staff time. Institutions have reported that it is relatively easy to determine eligibility and that there is no need for authors to consider different application processes or funding routes. This model is also seen as beneficial for institutions given the fact that there are no fixed limits on the number of articles that authors can publish and authors are not required to use a code or a voucher to pay for APCs.
The Springer Compact agreement also helps researchers to comply with funders and institutions open access mandates. It does so by enabling compliance with the key requirements stated in various research funders open access policies: articles are made immediately available on open access (no embargo periods apply), articles are made openly available under CC BY licences, and a copy of the final peer-reviewed manuscripts will be deposited in repositories via Jisc’s Publications Router.
Paul Ayris, Director of UCL Library Services, said: “The Springer Compact deal is an excellent new model that enables UK authors to achieve Gold open access at no additional cost. As well as the significant financial benefits, it simplifies administration for authors and institutions, and streamlines the process of complying with funders’ open access policies. UCL wholeheartedly supports this model, and hopes to see other publishers following suit.”
Veronika Spinka, Open Access Manager, Springer Nature, added: “Springer Compact is a workable model that reduces the manual effort and workload for authors and institutions. Workflows provide a high-quality service level to accommodate all parties. Based on customer feedback, we continue to make our processes more efficient and reliable so that OA publishing becomes as easy as possible.”
By working with Springer and UK institutions to implement this model we continue to identify a number of areas where further improvements could be made. Some of these are about ensuring consistency in reporting (for example, by ensuring that research funders such as RCUK are acknowledged in the articles), others are about communications with authors and continuing to simplify the administration. We will continue to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of this agreement over the year and to share findings and recommendations for best practice with institutions and publishers. We also hope that other publishers will be encouraged by our initial evaluation of the Springer Compact model and consider exploring similar flipped models.
Information on the articles published on open access can be consulted on the OpenAPC initiative website.
For more information on how you can make use of this agreement BU has with Springer, please refer to this blog post : http://blogs.bournemouth.ac.uk/research/2016/04/11/you-can-now-publish-open-access-for-free-with-springer-open-choice-journals/
[1] Jisc has been running a series of workshops on ‘Getting the most from open access offsetting deals’ to inform staff in higher education institutions about our negotiated deals to help reduce the costs of publishing open access articles. These workshops have been attended by more than 40 participants from higher education institutions. The next workshop will be held on 25 July 2016 (https://www.jisc.ac.uk/events/getting-the-most-from-open-access-offsetting-deals-25-jul-2016).



 As we know Nigel Farage, the now internationally infamous politician who led the UKIP juggernaut for Brexit is keen to see an ‘Independence Day from the EU’ established in the British calendar once (or if) the button on Article 50 is pushed.
As we know Nigel Farage, the now internationally infamous politician who led the UKIP juggernaut for Brexit is keen to see an ‘Independence Day from the EU’ established in the British calendar once (or if) the button on Article 50 is pushed.


 Andrew Harding and Colin Pritchard have recently had a paper published in the
Andrew Harding and Colin Pritchard have recently had a paper published in the 







 The
The  Workshop
Workshop The research councils are replacing their electronic grants submission service, Je-S, in 2017. More information about this project can be found here
The research councils are replacing their electronic grants submission service, Je-S, in 2017. More information about this project can be found here  HSS PhD student Andrew Harding and fellow authors Jonathan Parker, Sarah Hean and Ann Hemingway have recently had a paper accepted for publication in Social Policy & Society, the sister publication to the Journal of Social Policy and run by the Social Policy Association.
HSS PhD student Andrew Harding and fellow authors Jonathan Parker, Sarah Hean and Ann Hemingway have recently had a paper accepted for publication in Social Policy & Society, the sister publication to the Journal of Social Policy and run by the Social Policy Association.










 BU paper among top 20 most cited papers
BU paper among top 20 most cited papers Nepal migrant workers returning from India
Nepal migrant workers returning from India New BU midwifery publication
New BU midwifery publication MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease