World Alzheimer’s Day falls on 21 September each year and gives us an opportunity to focus on work going on across the world to understand and fight the disease. Over 850,000 people in the UK have some form of dementia, including Alzheimer’s, so research in this area is of importance to many of us.
Designing dementia friendly environments
Dr Jan Wiener, co-head of the Bournemouth University Dementia Institute (BUDI), is an Associate Professor in Psychology with a particular interest in navigation and wayfinding.
“Spatial awareness difficulties can be an early sign of dementia, which often manifests itself in people finding it hard to navigate around unfamiliar environments. This is a problem for people with dementia as many will move into a care home as the disease progresses, which can cause a lot of anxiety,” explains Dr Wiener.
“We want to develop a better understanding of what causes those difficulties with spatial awareness, starting with finding out how people navigate around different environments – what markers they use to help them – and what impedes them.”
“We have funding from the Economic & Social Research Council, which is enabling us to explore this area more fully. We’re using virtual environments and eye tracker technology to create familiar and unfamiliar buildings, which participants are then asked to navigate around.”
“The eye tracking technology enables us to see exactly where people are looking and which waypoints they’re likely to be using to help them get around. It helps us to develop a better understanding of whether people simply didn’t see a waypoint, such as a painting or a sign, or whether they saw it and didn’t know or remember what it meant.”
“Our research has very real implications for the design of care homes and other public places. Often the design and decoration of a care home is based on intuition and what staff feel works, although they may not know why. Our research is unique in that it’s providing an evidence base for building guidelines, based on what our tests show helps and hinders people to navigate different environments.”
Supporting nursing and care home staff to improve nutrition for people with dementia
Dr Jane Murphy, co-head of BUDI, is an Associate Professor in Nutrition who is currently leading a Burdett Trust funded project developing training tools for care staff to help improve nutrition in people with dementia.
“We know that as dementia progresses, it’s not uncommon for people to lose weight, which can lead to further physical and mental decline. This can be for all sorts of reasons – people may face physical difficulties with swallowing, might not be able to sense hunger or thirst or may not remember when they last ate or drank. For busy care home staff, managing this and knowing how best to support people they care for can be a real challenge, especially as everyone has different needs,” says Dr Murphy.
“We worked with local care homes in Dorset to find out how much people were eating and drinking and whether this was enough to meet the amount of energy they were using each day. Our results showed that around half of our participants weren’t eating or drinking enough to meet their daily energy needs. We also found that many people were spending a high proportion of their day sitting or sleeping, which may explain why some had small appetites.”
“This showed it can be really difficult to get nutrition right, especially when needs vary enormously between different people. Our next stage was to work with local care homes to draw out examples of best practice and strategies to help people with dementia to eat and drink well. Based on this, we’ve developed a training book and YouTube film, packed full of tips about nutrition and ideas for care home staff to try out. We chose to make them resources that can be used at any time, in recognition of how hard it can be to take time out to go on a training course.”
“We’ve been sharing these resources widely throughout the care sector and are now seeing the tools being used in care homes, as well as being incorporated into university training programmes. Most encouragingly, we’re beginning to hear stories of people with dementia who were at risk of or actually losing weight, beginning to reverse that trend, which shows us that the strategies we highlighted in our resources are making a real difference.”
How can ‘serious gaming’ help those with Alzheimer’s?
Ben Hicks, Lecturer in Health Psychology, has recently completed his PhD research which explored the use of technology clubs for older men with dementia in rural areas. Over the next couple of years he will be building on this work by carrying out research into the impact of ‘serious gaming’ on people with Alzheimer’s.
“My PhD focused on older men with dementia, living in rural areas of Dorset who are at risk of becoming very isolated,” explains Ben, “I introduced technology clubs, where they had a chance to try out Xbox games and the Wii Fit among others. It created a really social atmosphere and gave them a chance to learn new skills, dispelling the myth that people with dementia can’t learn anything new.”
“They proved very popular and thanks to funding from Dorset Partnership for Older People Project (POPP), the clubs have been able to carry on, even though my research has now finished. It’s great to have started something that’s going on to make a difference to people’s lives.”
“My new study will focus on the idea that ‘serious gaming’ can help people with dementia to improve their cognitive abilities. Whilst emerging research in this field demonstrates the potential of ‘Serious Games’ to support people living with dementia, more rigorous studies are required.”
“I’m going to be working with Alzheimer’s Valencia, a game development company and other organisations in Europe to explore which aspects of the games appeal and improve cognitive abilities. In the long run, we hope to develop guidance for other technology companies to help them to create similar games.”
For more information about BU’s dementia research, visit BUDI’s website.
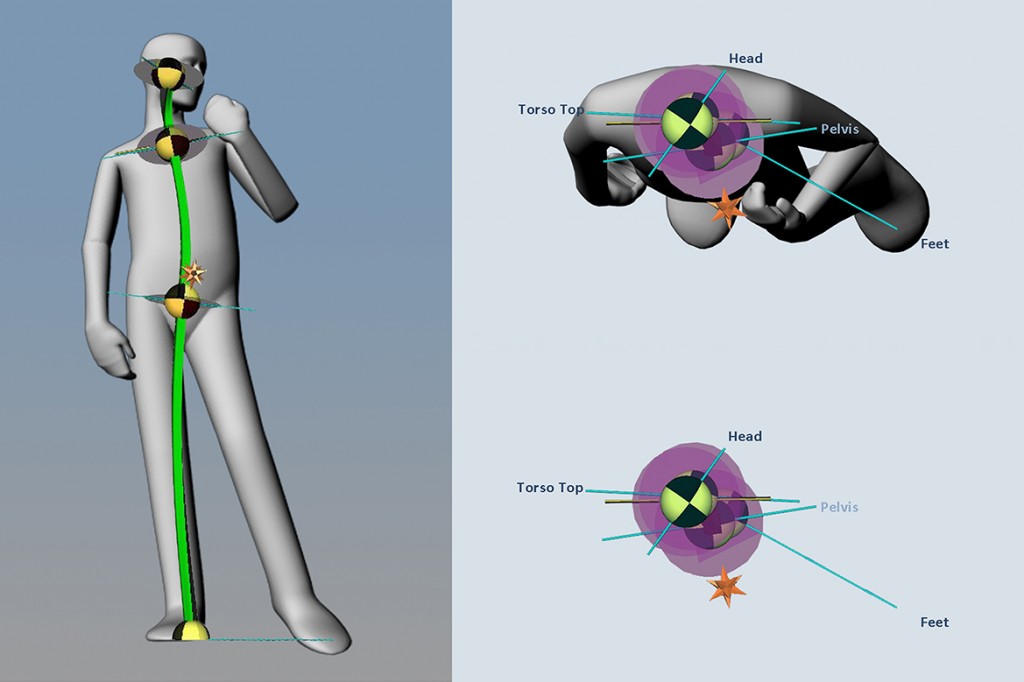













 We are often reminded that we should be paying attention to what we eat and making sure we exercise regularly. These recommendations are based on years of research into how diet and exercise can impact our health and well-being throughout the lifespan. However, it’s rare that these two crucial elements are studied together.
We are often reminded that we should be paying attention to what we eat and making sure we exercise regularly. These recommendations are based on years of research into how diet and exercise can impact our health and well-being throughout the lifespan. However, it’s rare that these two crucial elements are studied together.








 nd Leisure Education and Research) annual conference which took place in the historic town of Canterbury, between 13-16 September, on “Tourism, Lifestyles and Locations”.
nd Leisure Education and Research) annual conference which took place in the historic town of Canterbury, between 13-16 September, on “Tourism, Lifestyles and Locations”.

 Uber, Amazon, AirBnB, Netflix… The Internet has had many impacts to the economy. Not only to the consumer market, but widely across the service sector. There is a large amount of integration and automation to enable things like instant order confirmations. Work in these aspects of business processes is quite well established in the service sector.
Uber, Amazon, AirBnB, Netflix… The Internet has had many impacts to the economy. Not only to the consumer market, but widely across the service sector. There is a large amount of integration and automation to enable things like instant order confirmations. Work in these aspects of business processes is quite well established in the service sector.










 BU academics in the news in Nepal
BU academics in the news in Nepal New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease