Are you at an early stage in your academic career and need some help in perfecting your grant writing skills? Dr Martin Pickard is coming back to BU on 26th January to run a full day workshop.
 The day is designed for early career researchers with no, or very little, experience in preparing research applications. It covers the fundamental structure and arguments inherent within any research proposal and initially develops the principle ways to achieve this – whilst at the same time encouraging the necessary overarching approach.
The day is designed for early career researchers with no, or very little, experience in preparing research applications. It covers the fundamental structure and arguments inherent within any research proposal and initially develops the principle ways to achieve this – whilst at the same time encouraging the necessary overarching approach.
The workshop will take place on Talbot Campus and run from around 9.30am until 4-5pm. Lunch and refreshments will be provided. There are a limited number of spaces on the workshop so if you would like to come to the event please email Susan Dowdle to book a space as soon as possible.
Structure of the Day
Session 1: Introduction and general approach to the funding mechanisms
These sessions are individually tailored to the session theme. They evaluate and present key insights into the fundamental approach principles behind a successful grant application in the respective research area and develop the essential common elements of a successful bid.
Break – Coffee – Includes 10 minute assignment exercise
Session 2 – Theory and practice – optimising the approach
This builds from session 1 detailing the “in depth” structure of a successful bid, the need to present and optimise the supporting arguments and justifications required and how to achieve this.
Break – Lunch – including further assignment exercise
Session 3 – Building the case for funding – case studies and examples
Using the assignment exercises, and worked illustrations, this puts theory into practice covering most of the common pitfalls and provides the tips, tricks and techniques for optimising your proposal within minimum space.
Break – Coffee – including 10 minute assignment exercise
Session 4 – Theory into practice – interactive assignment analysis and workshop discussion
With analysis and reworking of both previous cases and current applications this primarily “Q & A” workshop session provides an important consolidation taking live examples through the optimisation process using the skills and techniques acquired throughout the day.


 Last month
Last month 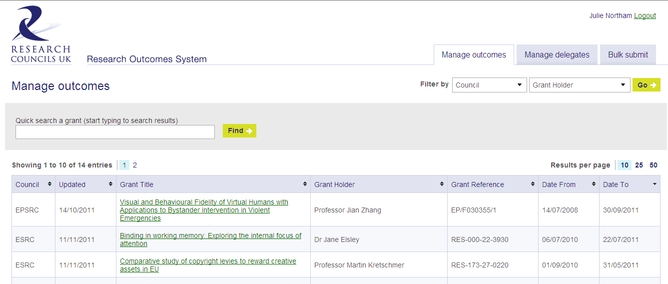

 Welcome to RCUK Demand Management week on the blog! Today’s focus is on the Arts and Humanities Research Council (
Welcome to RCUK Demand Management week on the blog! Today’s focus is on the Arts and Humanities Research Council ( Welcome to RCUK Demand Management week on the blog! Today’s focus is on the Natural Environment Research Council (
Welcome to RCUK Demand Management week on the blog! Today’s focus is on the Natural Environment Research Council ( Welcome to RCUK Demand Management week on the blog! Today’s focus is on the Economic and Social Research Council (
Welcome to RCUK Demand Management week on the blog! Today’s focus is on the Economic and Social Research Council (


 Welcome to RCUK Demand Management week on the blog! Today’s focus is on the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (
Welcome to RCUK Demand Management week on the blog! Today’s focus is on the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (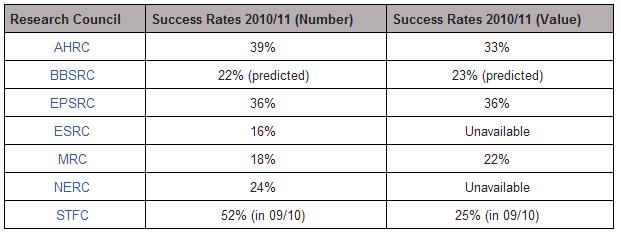
 What resources and processes has BU put in place to support Demand Management? – BU has established an
What resources and processes has BU put in place to support Demand Management? – BU has established an 










 Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh
Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh Exploring Embodied Research: Body Map Storytelling Workshop & Research Seminar
Exploring Embodied Research: Body Map Storytelling Workshop & Research Seminar Marking a Milestone: The Swash Channel Wreck Book Launch
Marking a Milestone: The Swash Channel Wreck Book Launch No access to BRIAN 5-6th February
No access to BRIAN 5-6th February ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease