 Yesterday we received the postcards to advertise our Festival of Social Sciences (FoSS) ‘Sonamoni’ event which will be held in the beautiful RNLI building on West Quay Road in Poole on Saturday 8th November. This public event focusing on drowning prevention in Bangladesh is free and can be booked online, click here! The FoSS is a UK-wide festival every autumn. It is funded by the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC) to promote social science research with the general public. The FoSS comprises events ranging from exhibitions, lectures and panel debates through to performances, guided walks and workshops. We would like to thank the ESRC for its support for its support, which includes producing the postcards, and the coffee and teas to be served at the RNLI on Saturday November 8th.
Yesterday we received the postcards to advertise our Festival of Social Sciences (FoSS) ‘Sonamoni’ event which will be held in the beautiful RNLI building on West Quay Road in Poole on Saturday 8th November. This public event focusing on drowning prevention in Bangladesh is free and can be booked online, click here! The FoSS is a UK-wide festival every autumn. It is funded by the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC) to promote social science research with the general public. The FoSS comprises events ranging from exhibitions, lectures and panel debates through to performances, guided walks and workshops. We would like to thank the ESRC for its support for its support, which includes producing the postcards, and the coffee and teas to be served at the RNLI on Saturday November 8th.
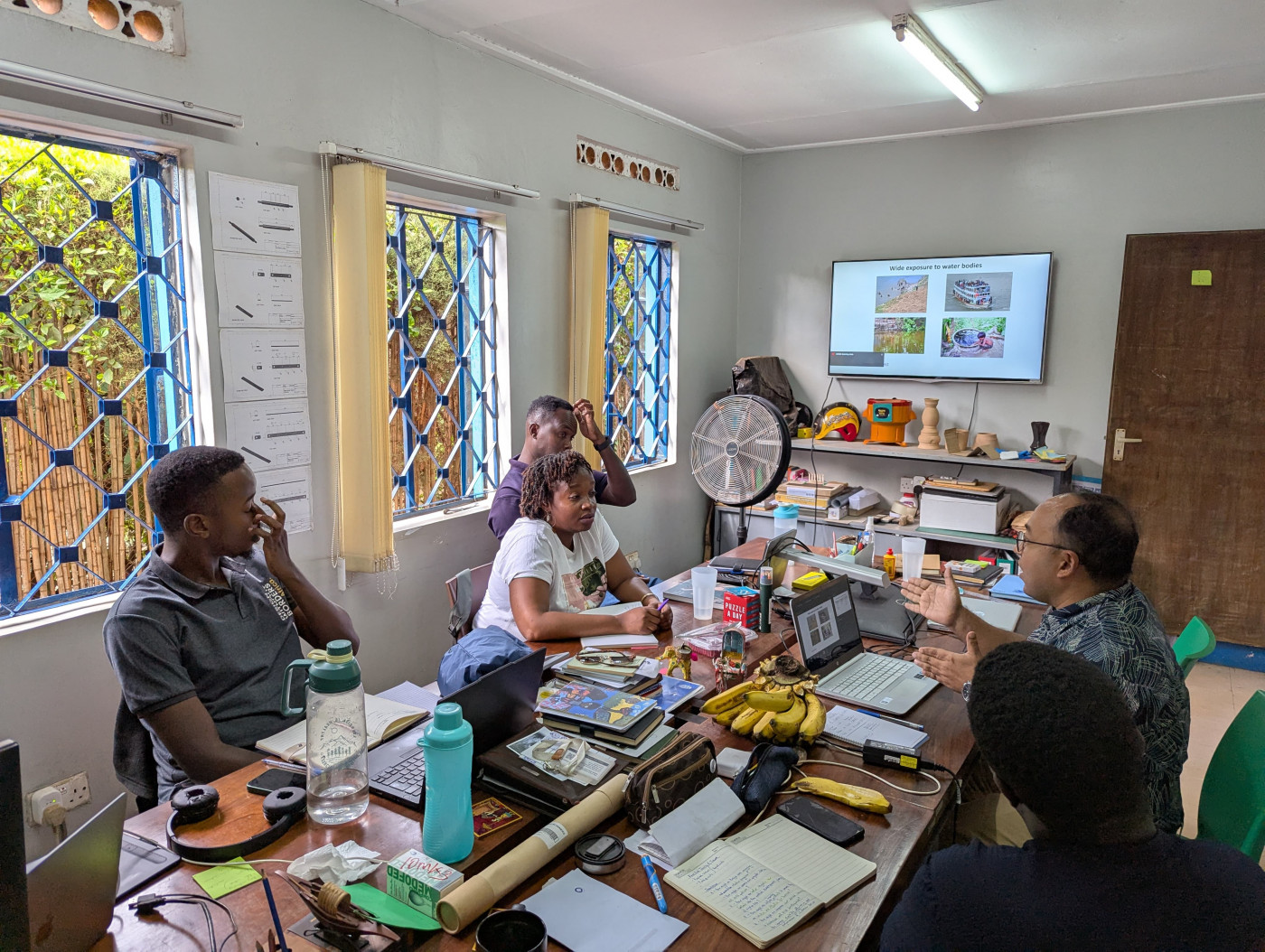
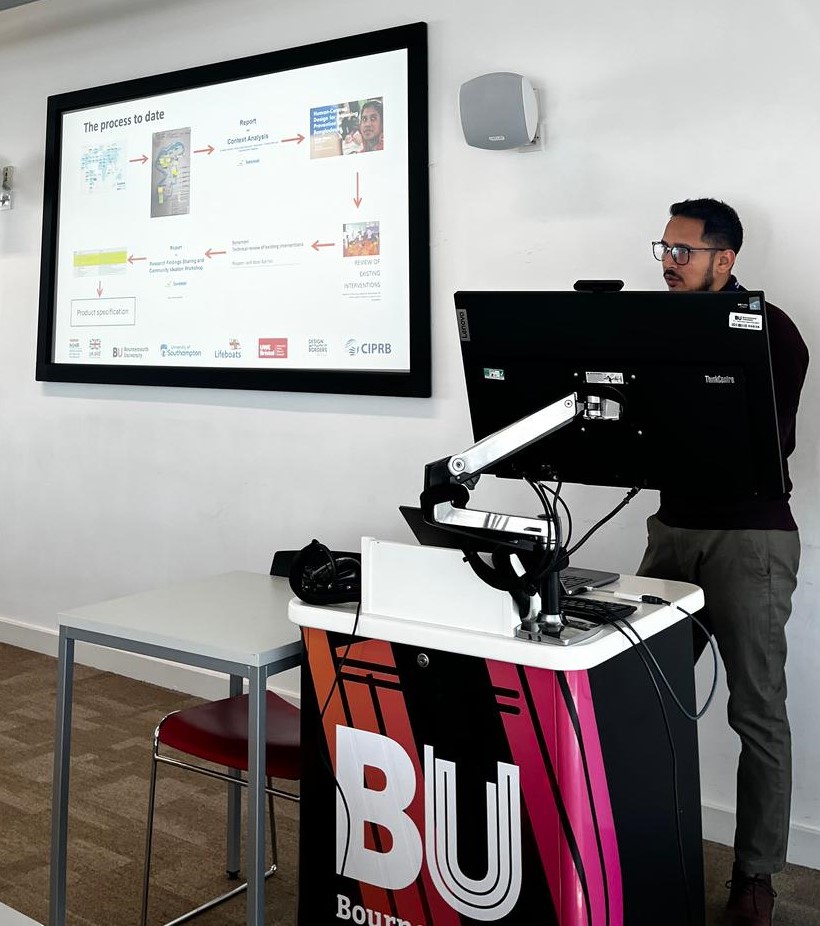
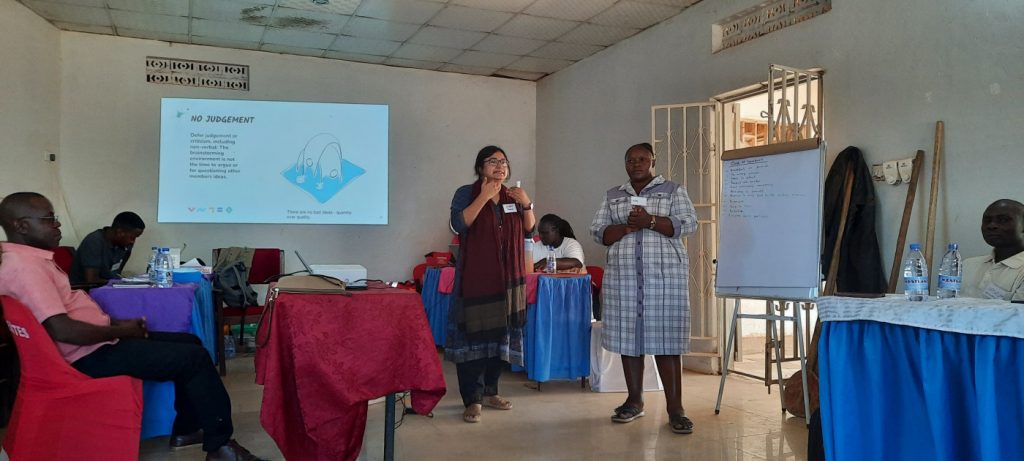
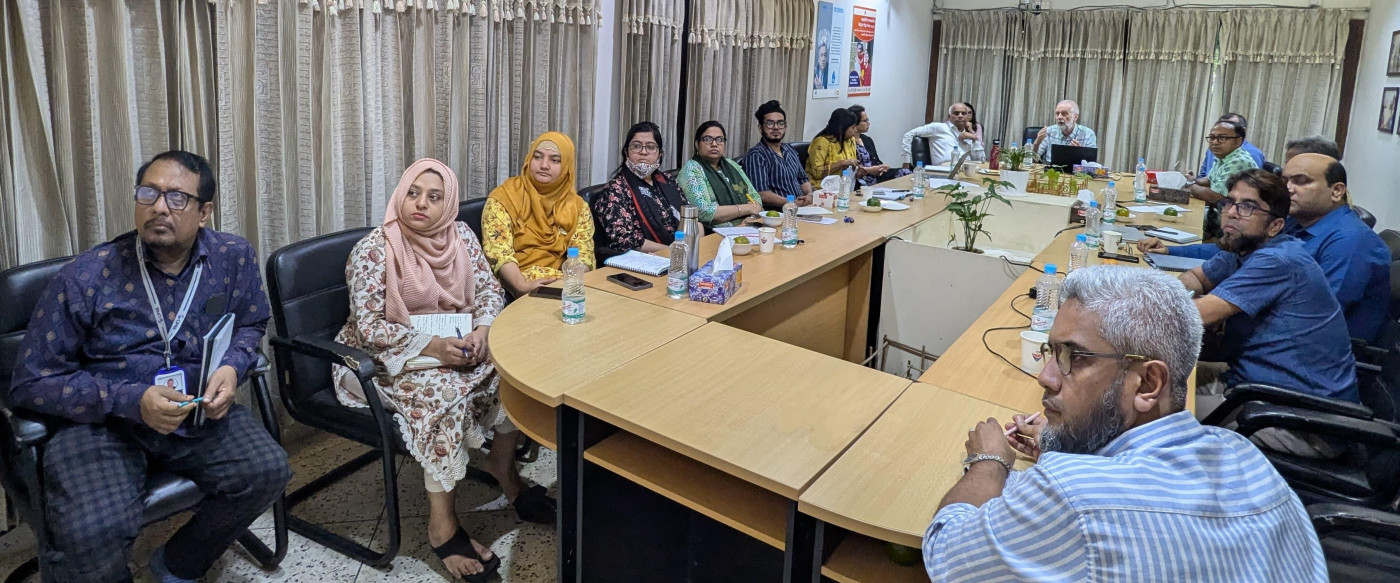
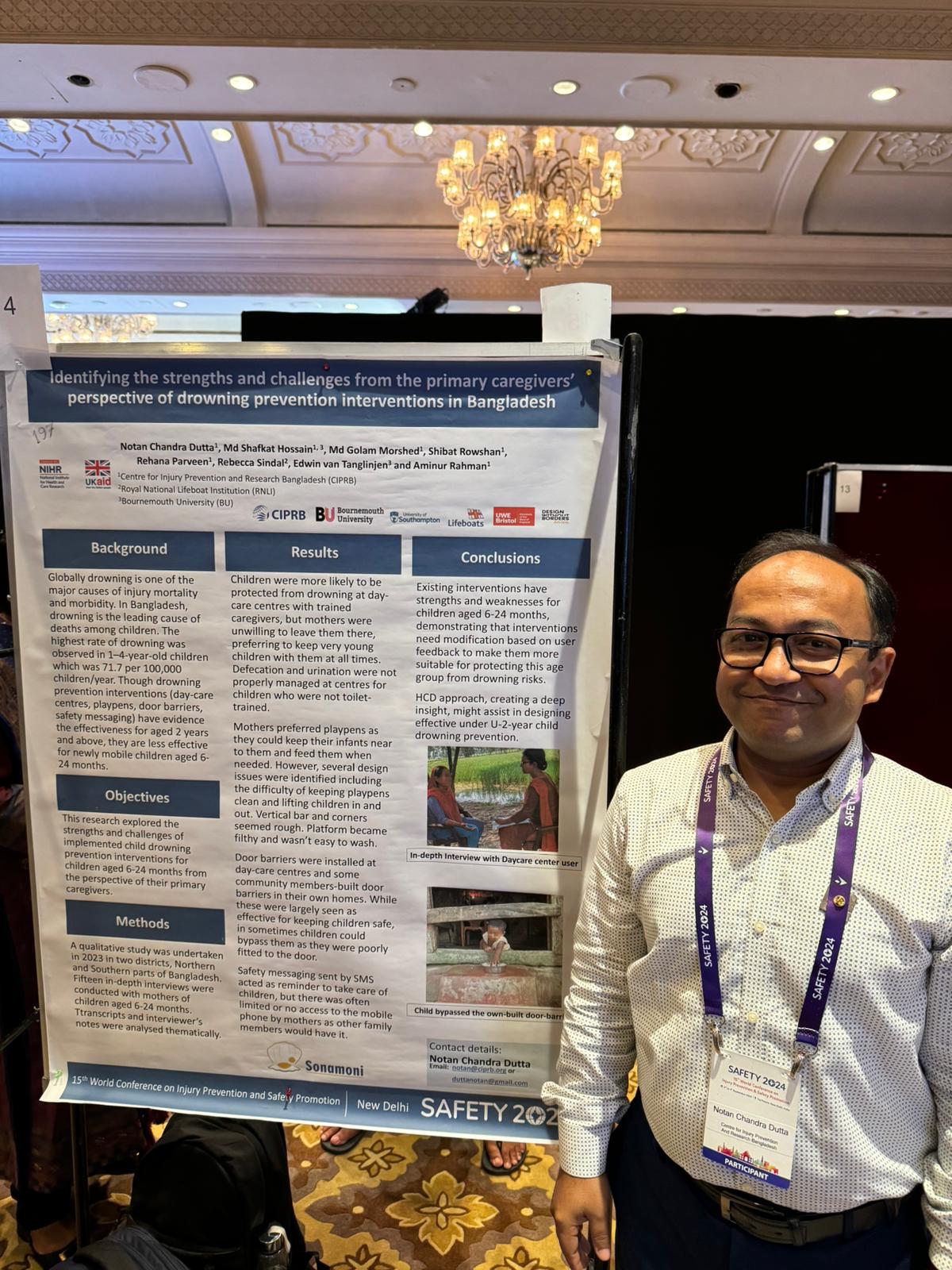
 The Sonamoni Project is dedicated to reducing drowning deaths among newly mobile children (under 2 years) by working closely with rural communities in Bangladesh. Using human-centred design (HCD) techniques, the project is identifying solutions, developing prototypes, and assessing their effectiveness. This exciting project is funded by the UK National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) using UK aid from the UK government to support the improvement of global health through high-quality research.
The Sonamoni Project is dedicated to reducing drowning deaths among newly mobile children (under 2 years) by working closely with rural communities in Bangladesh. Using human-centred design (HCD) techniques, the project is identifying solutions, developing prototypes, and assessing their effectiveness. This exciting project is funded by the UK National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) using UK aid from the UK government to support the improvement of global health through high-quality research.
Sonamoni is coordinated by Bournemouth University in collaboration with our partners: the University of the West of England (Bristol), the University of Southampton, and the Royal National Lifeboat Institution (RNLI), Design Without Border (DWB) in Uganda and the Centre for Injury Prevention and Research, Bangladesh (CIPRB).































 REF Code of Practice consultation is open!
REF Code of Practice consultation is open! BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project
BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University
Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease