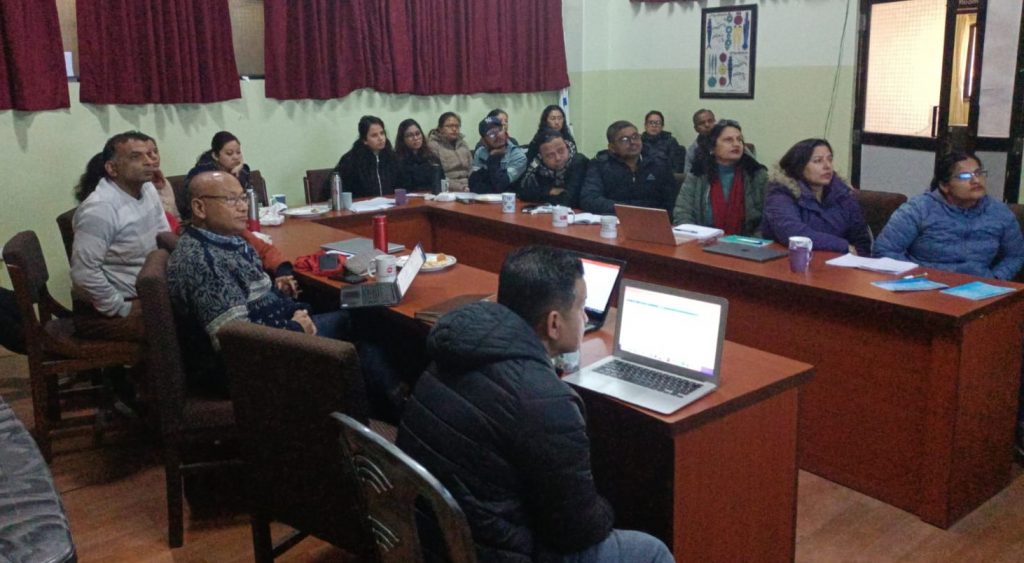
 This week our collaborators on the Sonamoni project traveled from Bangladesh and Uganda to Dorset for a set of research planning meetings. The visitors represented CIPRB (The Centre for Injury Prevention and Research, Bangladesh) and DWB (Design without Borders). They were hosted by colleagues from Bournemouth University, the RNLI (Royal National Lifeboat Institute) and from the University of Southampton. Since Monday we managed to have an intensive week of design workshops, reviewing and incorporating local-community prioritised interventions for child drowning prevention (aged <2years) in Bangladesh. I say ‘we managed’, but I have been at home all week with COVID-19. The past few days I was beginning to feel quite well again, so I was unpleasantly surprised that I was still positive when I tested yesterday, and even more so this morning. Consequently, missing the whole week working with our visiting collaborators.
This week our collaborators on the Sonamoni project traveled from Bangladesh and Uganda to Dorset for a set of research planning meetings. The visitors represented CIPRB (The Centre for Injury Prevention and Research, Bangladesh) and DWB (Design without Borders). They were hosted by colleagues from Bournemouth University, the RNLI (Royal National Lifeboat Institute) and from the University of Southampton. Since Monday we managed to have an intensive week of design workshops, reviewing and incorporating local-community prioritised interventions for child drowning prevention (aged <2years) in Bangladesh. I say ‘we managed’, but I have been at home all week with COVID-19. The past few days I was beginning to feel quite well again, so I was unpleasantly surprised that I was still positive when I tested yesterday, and even more so this morning. Consequently, missing the whole week working with our visiting collaborators.
The Sonamoni project recently presented its own video recording on YouTube,which you can watch here!
Sonamoni is a public health project is funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) through its Research and Innovation for Global Health Transformation programme. For more information, visit the NIHR website.

Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH)






 Today we received notice that our paper ‘The impacts of decentralisation on health systems: a systematic review of reviews’ has been accepted by the international journal BMJ Global Health. [1] This review of reviews was produced as part of the Nepal Federal Health System Project, examining the consequences for the health system of Nepal’s move to a federal government structure. This is a joint project (2020-2024) led by the University of Sheffield and in collaboration with Bournemouth University, the University of Huddersfield,
Today we received notice that our paper ‘The impacts of decentralisation on health systems: a systematic review of reviews’ has been accepted by the international journal BMJ Global Health. [1] This review of reviews was produced as part of the Nepal Federal Health System Project, examining the consequences for the health system of Nepal’s move to a federal government structure. This is a joint project (2020-2024) led by the University of Sheffield and in collaboration with Bournemouth University, the University of Huddersfield, 


































 BU attendance at third annual GCPHR meeting in June
BU attendance at third annual GCPHR meeting in June Interactive Tangible and Intangible Heritage Applications – BU student work featured in new book chapter
Interactive Tangible and Intangible Heritage Applications – BU student work featured in new book chapter Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week
Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease