 BU academics from the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences had a strong presence at the International Confederation of Midwives (ICM) in Canada this lunch time. They presented four separate academic posters today at the ICM conference in Toronto. First, Dr. Alison Taylor presented her poster ‘Mothers need to talk, midwives need to listen: Insights from breastfeeding mother’s video diaries’. Secondly, Sara Stride and Dr. Sue Way presented their poster on ‘UUPP Study: Updating the Understanding of Perineal Practice at the time of birth across the United Kingdom’.
BU academics from the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences had a strong presence at the International Confederation of Midwives (ICM) in Canada this lunch time. They presented four separate academic posters today at the ICM conference in Toronto. First, Dr. Alison Taylor presented her poster ‘Mothers need to talk, midwives need to listen: Insights from breastfeeding mother’s video diaries’. Secondly, Sara Stride and Dr. Sue Way presented their poster on ‘UUPP Study: Updating the Understanding of Perineal Practice at the time of birth across the United Kingdom’.
 Prof. Vanora Hundley, Dr. Ann Luce (BU Faculty of Media & Communication), Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen and two students, Sofie Edlund and Sian Ridden also presented their poster on ‘Changing the narrative around birth: midwives’ views of working with the media’.
Prof. Vanora Hundley, Dr. Ann Luce (BU Faculty of Media & Communication), Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen and two students, Sofie Edlund and Sian Ridden also presented their poster on ‘Changing the narrative around birth: midwives’ views of working with the media’. 
 And, last but not least, Prof. Vanora Hundley and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen also contributed to a poster produced by Dr. Andrew Symon and colleagues from across the UK: ‘Midwifery-led antenatal care models: Mapping a systematic review to an evidence-based quality framework to identify key components and characteristics of care’.
And, last but not least, Prof. Vanora Hundley and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen also contributed to a poster produced by Dr. Andrew Symon and colleagues from across the UK: ‘Midwifery-led antenatal care models: Mapping a systematic review to an evidence-based quality framework to identify key components and characteristics of care’.
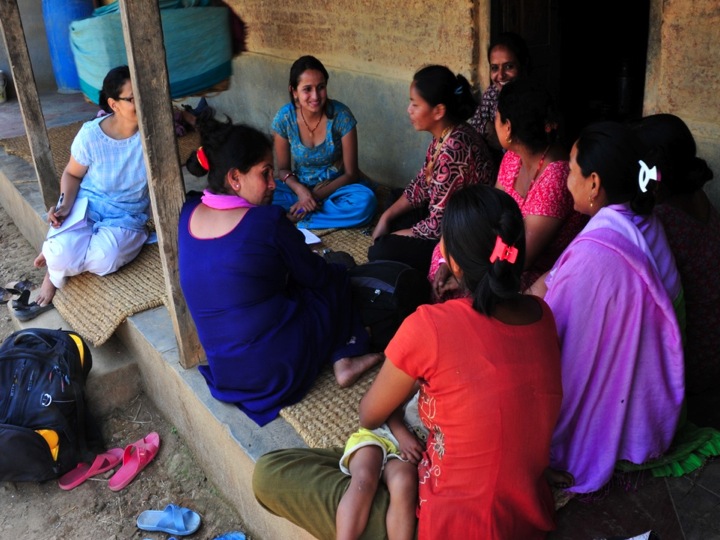















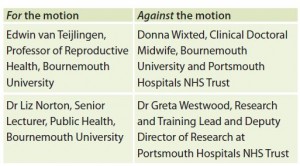

 The study
The study 





















 Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop
Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching
UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives
SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives BRIAN upgrade and new look
BRIAN upgrade and new look Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh
Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease