An internationally significant and ground-breaking paper has appeared in the journal Nature, led by Dr Phil Riris of the Institute for the Modelling of Socio-Environmental Transitions.
The work investigates 30,000 years of population resilience, with contributions from collaborating scholars from 14 institutions in 7 countries. The paper marks a watershed in our understanding of how people in the past adapted to, and overcame, disturbances. It is available in open access.
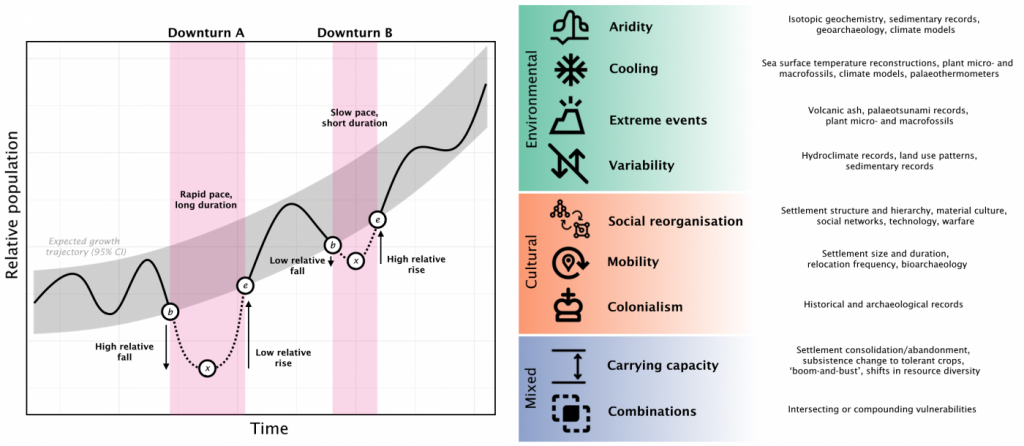
Left: A sketch of an archaeological population time series with downturns and metrics obtained during the analysis. Right: Example types and groups of disturbances noted in the literature.
The key finding of the paper is that land use – the kinds of subsistence practices, mobility regimes, and extent of infrastructure investments – enhanced both how often a population experienced downturns and their ability to recover from them. In particular, agricultural and agropastoral societies in prehistory were especially likely to suffer demographic busts. However, they also displayed an improved ability over time to “bounce back”.
This result has wide-ranging implications for the development of sustainable land use practices, as traditional lifeways may have intrinsic rates of failure “baked into” their function and operation. The paper speculates that, similar to resilient ecosystems or ecological communities, such localised, small-scale, or short-term failures in human socio-environmental systems may contribute to building improved long-term resilience for the system as a whole.

Artistic impression of some of the types of disturbances experienced by ancient societies.
Importantly, these patterns only reveal themselves in the macro-scale comparison of independent case studies, and take multiple decades or even centuries to unfold. Archaeology is the only field able to tackle these timescales systematically, and underscores the value and contribution of the historical sciences to resilience-building and sustainability challenges in the present.
URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07354-8
The research was funded by the Arts and Humanities Research Council (AH/X002217/1).














 The annual Family Science Day in Dorchester on Sunday, 17th March 2024, was a vibrant celebration of the British National Science Week. This free event aims at making science accessible and engaging for families, providing a platform for learning and discovery in a fun and interactive way. With an attendance of 800 enthusiastic visitors, the event showcased 20 hands-on science stalls. BU was represented by staff, undergraduate and postgraduate students, and postdoctoral researchers. Contributors included Demetra Andreou (Fish Through Time), Amanda Korstjens (Voices in the Jungle), and Genoveva Esteban (Hidden World of Microbes), alongside Kirthana Pillay (postdoctoral researcher) and undergraduate students Dan Stevens and Jacob Tate from the Department of Life and Environmental Sciences. Xun He (Head of MINE Research Cluster, Psychology) and Fred Charles (Head of Department for Creative Technology) led a stall on Measuring Social Behaviour with VR & Brainwaves, with assistance from PhD student Damla Kuleli, research assistant Charlie Lloyd-Buckingham, and BU alumnus Rianna Green. BU Student Ambassador Lily Bater provided exceptional support throughout the day.
The annual Family Science Day in Dorchester on Sunday, 17th March 2024, was a vibrant celebration of the British National Science Week. This free event aims at making science accessible and engaging for families, providing a platform for learning and discovery in a fun and interactive way. With an attendance of 800 enthusiastic visitors, the event showcased 20 hands-on science stalls. BU was represented by staff, undergraduate and postgraduate students, and postdoctoral researchers. Contributors included Demetra Andreou (Fish Through Time), Amanda Korstjens (Voices in the Jungle), and Genoveva Esteban (Hidden World of Microbes), alongside Kirthana Pillay (postdoctoral researcher) and undergraduate students Dan Stevens and Jacob Tate from the Department of Life and Environmental Sciences. Xun He (Head of MINE Research Cluster, Psychology) and Fred Charles (Head of Department for Creative Technology) led a stall on Measuring Social Behaviour with VR & Brainwaves, with assistance from PhD student Damla Kuleli, research assistant Charlie Lloyd-Buckingham, and BU alumnus Rianna Green. BU Student Ambassador Lily Bater provided exceptional support throughout the day.



 Summary: This paper used the Delphi method to provide expert consensus on items to be included in a contracture risk assessment tool (ORACLE). The items were related to factors associated with joint contractures, appropriate preventive care interventions, and potentially relevant contextual factors associated with care home settings. The promise of a risk assessment tool that includes these items has the capacity to reduce the risk of contracture development or progression and to trigger timely and appropriate referrals to help prevent further loss of function and independence.
Summary: This paper used the Delphi method to provide expert consensus on items to be included in a contracture risk assessment tool (ORACLE). The items were related to factors associated with joint contractures, appropriate preventive care interventions, and potentially relevant contextual factors associated with care home settings. The promise of a risk assessment tool that includes these items has the capacity to reduce the risk of contracture development or progression and to trigger timely and appropriate referrals to help prevent further loss of function and independence.
 BRIAN (Bournemouth Research Information And Networking) is BU’s publication management system.
BRIAN (Bournemouth Research Information And Networking) is BU’s publication management system.















 Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration
Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration 3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March
Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward?
Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward? ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease