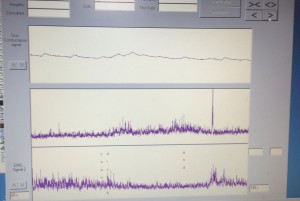
We were very fortunate to receive Fusion funding for our collaboration between colleagues and students in Health and Social Sciences, Sports Science, and a variety of external practice partners. Essentially the funding will enable us to obtain psychophysiological recording equipment to be used to measure emotional responses in a wide variety of learning and training settings. Below is a screenshot of a typical recording from this kind of equipment.
Huge progress has been made over the last couple of decades in our understanding of emotion and feelings. A compelling conclusion from this enormous body of work is the primacy of emotion in how we operate in the world. Darwin knew this, as did Freud, but many still cling to the notion of the achievements of homo sapiens (“wise man”!) as founded on cognition and rational thinking. For them, feelings are a vestigial remnant of our evolutionary past, not dissimilar to the appendix – no longer having any purpose, and also potentially a threat to our well being.
Affective neuroscience completely opposes this so-called rational approach: emotions and feelings guided our survival in our evolutionary past, but the big news is that they still do! Accumulations of theory and research from fields such as affective neuroscience, positive psychology, and health psychology support this simple but crucial switch in emphasis. Some everyday practice reveals the primacy of emotion, for example emotionally skilled doctors tend to bring about better health outcomes for their patients, children are taught to pay attention to their ‘uh oh’ signs (involuntary emotional responses of sweaty palms and heart beating faster) to keep them safe. So emotions are not the redundant and fickle “appendix” of our behavioural systems, but in fact are their driving force.
Despite an array of pragmatic findings about the way emotions and feelings work, this largely ‘pure’ body of neuroscience has not been directly applied to any particular field of practice. This project aims to correct that omission. The applications of affective science to how we learn and change our behaviour are potentially enormous, as the physiological emotional measures offer a straightforward ‘window’ into the person’s emotional responses.
The Fusion funding enables us to build on one of the applications, through running a study developing a previous pilot. This will be based on a form of training using natural horsemanship that has been demonstrated to be very successful in behaviour change for young offenders and young people who do not engage with school. This is an example of what it looks like (thanks to TheHorseCourse for the picture):

The equipment, and experience gained through carrying out the initial study, will also allow for projects with other practice partners to go ahead, for example, work with people with acquired brain injuries, and children with profound learning disabilities. If any of this interests you, please get in touch with Sid Carter or Emma Kavanagh, and we’d be glad to tell you more.



















 uth Asian and broader Black & Minority Ethnic (BME) communities in the UK.
uth Asian and broader Black & Minority Ethnic (BME) communities in the UK.










 REF Code of Practice consultation is open!
REF Code of Practice consultation is open! BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project
BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University
Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease