Dr Henry Ngenyam Bang writes for The Conversation about his research into the environmental consequences of the Anglophone crisis in Cameroon…
The environment is the silent casualty in the Cameroon Anglophone crisis
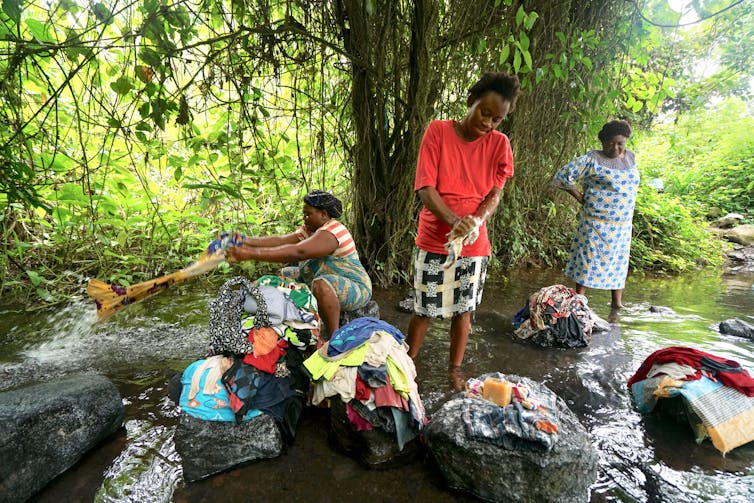

Photo by Giles Clarke/UNOCHA via Getty Images
Dr Henry Ngenyam Bang, Bournemouth University
Most analysis of Cameroon’s Anglophone crisis has been skewed towards the socioeconomic, cultural and political ramifications of the conflict.
But, based on my work on natural, environmental hazards and disaster management in Cameroon over the past two decades, I would argue that the environment in the Anglophone region is a silent casualty of the conflict. And it has largely been ignored.
Our recently published research on the crisis showed that over 900,000 people had been internally displaced. Eighty percent of the inhabitants of villages that were conflict hot spots had fled into adjacent forests. The research investigated the consequences of the Cameroon Anglophone crisis and determined it to be an acute complex emergency.
These developments are leaving huge environmental footprints and causing serious damage. This will get worse if the armed conflict escalates into a “complex disaster emergency”.
I have identified six environmental consequences of the Cameroon Anglophone crisis. These range from failures in environmental governance to increases in deforestation, unmet measures in Cameroon’s climate action plan, poor municipal waste management, the effects of scorched earth tactics and the impact of improvised explosive devices.
There is a need to address these environmental oversights and build them into resolving the crisis. This would prevent the environmental legacies of the armed conflict from haunting the region’s population after the crisis has ended.
The fallout for the environment
One of the effects of the fighting since 2016 was that it brought conservation activities to a halt in the country’s biodiversity hot spots in the Anglophone regions. Cameroon has around 14 national parks, 18 wildlife reserves, 12 forest reserves and three wildlife sanctuaries hosting rare and threatened species.
Before the crisis, many of these protected areas were still in a pristine condition because Cameroon had less tourism than other regions of Africa.
But the crisis has stalled several environmental projects.
For example, violence forced environmentalists and NGOS operating in the Tofala Hill Wildlife Sanctuary in Lebialem to flee. The Tofala Hill Wildlife Sanctuary is home to the critically endangered Cross River gorillas and other endangered wildlife like the African chimpanzee and elephant.
These gorillas are also under increased threat from militias such as the “Red Dragons” which have set up camps within the sanctuary (see Figure 1).
Likewise, efforts to protect the Mount Cameroon National Park, which hosts endangered primates, have been hampered. This poses a threat to the Nigerian-Cameroon chimpanzee, which already faces extinction.
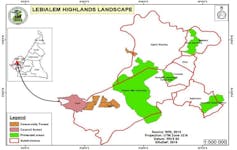
GSAC (2022)
Insecurity in areas hosting wildlife has led to a rise in uncontrolled illegal hunting. Poaching of endangered chimpanzees (see Figure 2) and elephants increased in the Tofala Hill Wildlife Sanctuary and the Takamanda and Korup National Parks after state rangers and eco-guards fled.

Photo by Julie Langford courtesy of the Limbe Wildlife Centre.
The rise in the number of internally displaced people has had a number of consequences.
Deforestation has risen as relocated communities have cut down trees to provide shelter and firewood.
They are also putting pressure on access to water. Toilet facilitates are inadequate in areas hosting large numbers of people. Drilling of wells, sometimes in unhygienic surroundings, and defecation in streams are also responsible for the poor water quality in the region.
The southwest region has recently experienced a cholera epidemic.
Thirdly, measures in Cameroon’s climate action plan have been halted by the crisis. The measures include providing fertilisers and improved seeds to farmers; installing renewable energy in rural areas; and restoring mangrove forests along the Limbe coast.
Fourthly, the crisis has worsened the problem of municipal waste management.
Separatists have threatened to burn the garbage collection company, HYSACAM. Some of its workers have been attacked. This has affected the collection of municipal waste in Bamenda and Buea, capitals of the Anglophone northwest and southwest regions.
Fifth, military forces are using scorched earth tactics that could create serious environmental harm. The military has destroyed houses, crops and livestock in several villages perceived to be strongholds of militia groups.
Likewise, militias have destroyed property owned by the state and that of civilians suspected to be colluding with security forces.
Satellite images from February and March 2021 confirm the destruction of multiple villages in the northwest region.
Lastly, the use of improvised explosive devices by militia groups against Cameroon’s military vehicles has been increasing and getting more sophisticated.
Explosive remnants and munitions can make the land uninhabitable, severely harm wildlife, and contaminate the soil and watercourses. Clearance of devices can also cause localised pollution, soil degradation and negative land use consequences.
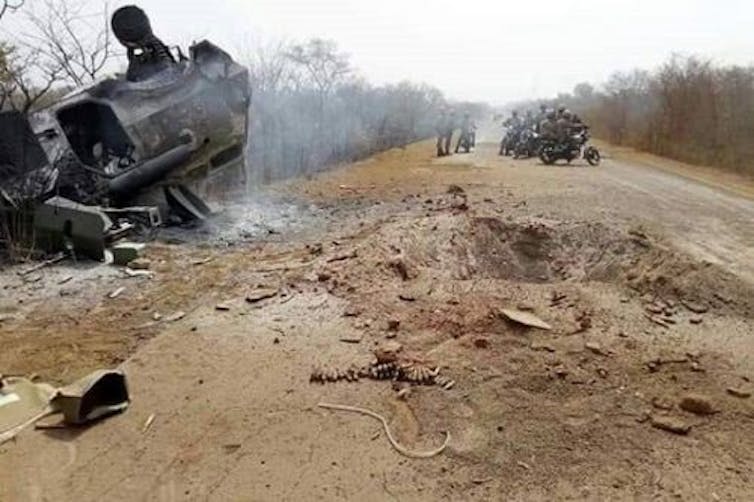

Photo courtesy of SBBC (2022).
Next steps
Contingency plans being put in place by the Cameroon government for a potential complex disaster emergency should consider the environmental aspects of the conflict.
First it’s necessary to empirically diagnose the environmental ramifications and how they can be resolved.
When seeking political solutions to the crisis, stakeholders should also incorporate measures to mitigate the environmental consequences.![]()
Dr Henry Ngenyam Bang, Disaster Management Scholar, Researcher and Educator, Bournemouth University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
 The last funding RDS Funding Development Briefings for the academic year will be on Wednesday, the 27th of July at 12 noon. These will restart again with a new programme in September.
The last funding RDS Funding Development Briefings for the academic year will be on Wednesday, the 27th of July at 12 noon. These will restart again with a new programme in September.










 Chiplun, a city in the Ratnagiri district in the state of Maharashtra. This is the hub for our collaboration and a key to providing more mental health support and well-being in the rural area within the region. This week during the Mental Health Awareness day in India – we tailored a camp that addressed some of the core issues the community face.
Chiplun, a city in the Ratnagiri district in the state of Maharashtra. This is the hub for our collaboration and a key to providing more mental health support and well-being in the rural area within the region. This week during the Mental Health Awareness day in India – we tailored a camp that addressed some of the core issues the community face. This event was supported by the Local team @Drs Shrutika and Sunil Kotkunde, our academic partners @S
This event was supported by the Local team @Drs Shrutika and Sunil Kotkunde, our academic partners @S














 Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University
Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU
Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU 3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease