Original article taken from the LSE Impact blog – http://blogs.lse.ac.uk/impactofsocialsciences/2016/03/04/academic-profile-services-many-mirrors-and-faces-for-a-single-ego/
Academic profiling services are a pervasive feature of scholarly life. Alberto Martín-Martín, Enrique Orduna-Malea and Emilio Delgado López-Cózar discuss the advantages and disadvantages of major profile platforms and look at the role of ego in how these services are built and used. Scholars validate these services by using them and should be aware that the portraits shown in these platforms depend to a great extent on the characteristics of the “mirrors” themselves.
The model of scientific communication has recently undergone a major transformation: the shift from the “Gutenberg galaxy” to the “Web galaxy”. Following in the footsteps of this shift, we are now also witnessing a turning point in the way science is evaluated. The “Gutenberg paradigm” limited research products to the printed world (books, journals, conference proceedings…) published by scholarly publishers. This model for scientific dissemination has been challenged since the end of the twentieth century by a plethora of new communication channels that allow scientific information to be (self-)published, indexed, searched, located, read, and discussed entirely on the public Web, one more example of the network society we live in.
In this new scenario, a set of new scientific tools are now providing a variety of metrics that measure all actions and interactions in which scientists take part in the digital space, making some hitherto overlooked aspects of the scientific enterprise emerge as objects of study. In the words of Jason Priem the First Revolution promoted the homogeneity of outputs (through academic journals, the main communication channel), and the Second Revolution promotes the diversity of outputs. We can draw a comparison between those revolutions and the changes that are taking place in the field of scientific evaluation: the First Revolution promoted the homogeneity of performance metrics (through the Impact Factor, the “gold standard” of scientific evaluation), and the Second Revolution promotes a diversity of metrics (h-index, altmetrics, usage metrics). The emergence of academic profiling services (most of them created in 2008) was a collateral consequence.
Because each of these tools focuses on fulfilling a different set of needs, caters to a specific audience (diverse communities), and provides a variety of different metrics, it stands to reason that they should reflect different sides of academic impact. Each platform becomes then a mirror reflecting the likeness of the communities that use it.
Recently, we set out to radiograph the discipline of Bibliometrics, not only trying to identify the core authors, documents, journals, and the most influential publishers in the field, but also comparing the diverse portraits shown by each platform, with special attention to the one offered by Google Scholar Citations. We collected data for a sample of 814 researchers who work mainly or incidentally in the field of Bibliometrics. These data can be browsed in the website Scholar Mirrors, and an analysis of the results can be found in this working paper.
During this exercise we isolated some of the main features of these academic profiling services (Google Scholar Citations, ResearchGate, Mendeley, and ResearcherID) in terms of their general advantages and disadvantages, which are summarized below in Table 1.
TABLE 1: COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT ACADEMIC PROFILING SERVICES
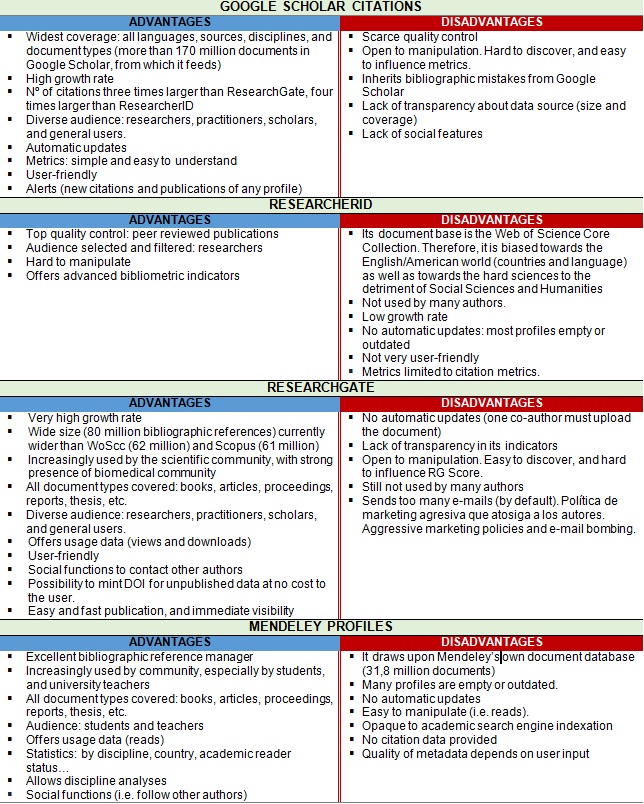
Each academic profile platform offered distinct and complementary data on the impact of scientific and academic activities as a consequence of their different user bases, document coverage, specific policies, and technical features. Not all platforms have a homogenous coverage of all scientific disciplines. Likewise, their user bases aren’t uniform either. Researchers should be aware that the bibliometric portraits shown in these platforms depend to a great extent on the individual characteristics of the “mirrors” themselves.
Google Scholar Citations profiles draw upon the vast coverage of Google Scholar (giving voice to all disciplines, languages, countries; academics and professionals) at the cost of a little accuracy (errors in parsing citations or authorship) and with an austere approach (few indicators, and little user interaction). Nonetheless, it offers the most advanced management system for versions and duplicates.
Regarding ResearchGate, the great amount of documents already uploaded by a growing user base (especially from the biomedicine community) supports the usefulness of some of its indicators (especially Views and Downloads, now combined into Reads). However, the lack of transparency compromises its reliability. Likewise, unannounced changes in some of its key features make this platform unpredictable at the moment.
Mendeley, despite being an excellent social reference manager, offers the most basic author profiling capabilities of all the platforms we analysed, although we should acknowledge the usefulness of the Reader metric. The term used to define this metric is, however, misleading, because it doesn’t accurately reflect the nature of the metric. Lastly, the fact that profiles aren’t automatically updated makes the system completely dependent on user activity. This fact strongly limits the use ofMendeley’s profile page for evaluating purposes.
ResearcherID does not offer automatic profile updates either. As a result, a great percentage of profiles have no public contributions listed in their profile (34.4% in our sample of bibliometricians, which should be the ones who are most aware of these tools). Moreover, we found errors in citation counts inherited from the Web of Science. A word of warning: the Web of Science also makes mistakes.
At any rate, the growth of academic profiling services is unstoppable, and practices like the aggressive marketing used by ResearchGate fuel the ego that dwells in every researcher through the systematic e-mail bombing directed to the Narcissus that lives inside of us. The potential positive effects are clear: new channels of information and new collaboration tools. However, this road might also lead us to look ourselves in the scholar mirror every day, and there lies the path to the Dark Side.
Paraphrasing Bill Clinton’s famous quote for the 1992 North American presidential campaign: “it’s the economy, stupid!” we could now state the following: it’s not the collaboration; it’s the ego, stupid! Ego moves Academia. These new platforms, whether they are integrated in other products or not, will be massively used by universities, research institutions, and national funding agencies to evaluate scholars, because scholars are validating them by using them massively. Hence, we should not conclude without warning about the dangers of blindly using any of these platforms for the assessment of individuals without verifying the veracity and exhaustiveness of the data.
This blog post is based on a working paper which can be found here. All the data obtained for each author profile and the results of the analysis can be found at Scholar Mirrors.
Note: This article gives the views of the author, and not the position of the LSE Impact blog, nor of the London School of Economics. Please review our Comments Policy if you have any concerns on posting a comment below.
About the Authors
Alberto Martín-Martín is a PhD Candidate in the field of bibliometrics and scientific communication at the Universidad de Granada (UGR).
Enrique Orduna-Malea works as a postdoctoral researcher at the Polytechnic University of Valencia (UPV).
Emilio Delgado López-Cózar is a Professor of Research Methods at the Universidad of Granada (UGR).
 HEFCE’s policy for open access states that all new peer-reviewed journal articles and papers from published conference proceedings (with ISSN) should be deposited in our institutional repository BURO (through BRIAN), in full text form. Full compliance with this policy is now crucial, as HEFCE’s requirements for the next REF include the condition that outputs can only be submitted to the REF if they are published as open access at the point of acceptance.
HEFCE’s policy for open access states that all new peer-reviewed journal articles and papers from published conference proceedings (with ISSN) should be deposited in our institutional repository BURO (through BRIAN), in full text form. Full compliance with this policy is now crucial, as HEFCE’s requirements for the next REF include the condition that outputs can only be submitted to the REF if they are published as open access at the point of acceptance. Our latest paper in the international journal BMC Pregnancy & Childbirth published late last month was highlighted yesterday in a
Our latest paper in the international journal BMC Pregnancy & Childbirth published late last month was highlighted yesterday in a  Our paper is great example of interdisciplinary research, as celebrated at the forthcoming Interdisciplinary Research Sector Day on June 21st (
Our paper is great example of interdisciplinary research, as celebrated at the forthcoming Interdisciplinary Research Sector Day on June 21st (


 This first week of March has been a good week for FHSS publications. On March 1st CMMPH Prof. Vanora Hundley published her collaborative paper ‘Do Cochrane summaries help student midwives understand the findings of Cochrane systematic reviews: the BRIEF randomised trial’.[1] With colleagues based across the UK and Ireland she surveyed over 800 midwifery students at nine universities. This results of the study can be found in the journal
This first week of March has been a good week for FHSS publications. On March 1st CMMPH Prof. Vanora Hundley published her collaborative paper ‘Do Cochrane summaries help student midwives understand the findings of Cochrane systematic reviews: the BRIEF randomised trial’.[1] With colleagues based across the UK and Ireland she surveyed over 800 midwifery students at nine universities. This results of the study can be found in the journal  The second FHSS publication is a chapter in a Kindle book on the Importance of public health in low- and middle- income countries, written by Dr. Puspa Raj Pant,CMMPH’s Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen, and BU Visiting Faculty Prof. Padam Simkhada.[2] Padam Simkhada is Professor of International Public Health and Associate Dean (Global Engagement) for the Faculty of Education, Health and Community at Liverpool John Moores University. The chapter is part of the Kindle book with the long title: Public Health for the Curious: Why Study Public Health? (A Decision-Making Guide to College Major, Research & Scholarships, and Career Success for the College Students and Their Parents) edited by Richard Lee Skolnik from Yale University, USA.
The second FHSS publication is a chapter in a Kindle book on the Importance of public health in low- and middle- income countries, written by Dr. Puspa Raj Pant,CMMPH’s Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen, and BU Visiting Faculty Prof. Padam Simkhada.[2] Padam Simkhada is Professor of International Public Health and Associate Dean (Global Engagement) for the Faculty of Education, Health and Community at Liverpool John Moores University. The chapter is part of the Kindle book with the long title: Public Health for the Curious: Why Study Public Health? (A Decision-Making Guide to College Major, Research & Scholarships, and Career Success for the College Students and Their Parents) edited by Richard Lee Skolnik from Yale University, USA.























 BU academics in the news in Nepal
BU academics in the news in Nepal New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease