 This week the editor of the journal Journal of Education & Research informed us that our paper ‘Reflections on variations in PhD viva regulations: “And the options are….”’ has been accepted for publication [1]. This paper grew out of a discussion between the six authors about the apparent differences between the outcomes of the PhD viva at different universities. We have all acted as internal or external examiners for a PhD viva and had noted inconsistencies between universities, either in the regulations or in the interpretation of their PhD regulations. The authors are based at three different universities, on two different continents and, between them, have examined PhD theses submitted to universities based in at least ten different countries. Three authors are based in BU’s Faculty of Health & Social Sciences (Prof. Vanora Hundley, Dr. Pramod Regmi & Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen), two authors are based in the School of Human & Health Sciences at the University of Huddersfield (Prof. Padam Simkhada & Dr. Bibha Simkhada and both are Visiting Faculty at BU), and one author is based in the Institute for Global Health in the School of Public Health & Health Sciences at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, USA (Prof. Krishna C. Poudel).
This week the editor of the journal Journal of Education & Research informed us that our paper ‘Reflections on variations in PhD viva regulations: “And the options are….”’ has been accepted for publication [1]. This paper grew out of a discussion between the six authors about the apparent differences between the outcomes of the PhD viva at different universities. We have all acted as internal or external examiners for a PhD viva and had noted inconsistencies between universities, either in the regulations or in the interpretation of their PhD regulations. The authors are based at three different universities, on two different continents and, between them, have examined PhD theses submitted to universities based in at least ten different countries. Three authors are based in BU’s Faculty of Health & Social Sciences (Prof. Vanora Hundley, Dr. Pramod Regmi & Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen), two authors are based in the School of Human & Health Sciences at the University of Huddersfield (Prof. Padam Simkhada & Dr. Bibha Simkhada and both are Visiting Faculty at BU), and one author is based in the Institute for Global Health in the School of Public Health & Health Sciences at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, USA (Prof. Krishna C. Poudel).
This paper outlines the range of outcomes of a PhD examination. It also includes four short case studies, each reflecting on a particular aspect /differences we experienced as examinees or as examiners. The authors aim to alert PhD candidates and examiners to study the examination rules set by the awarding university, as the details of the PhD examination outcome, and hence the options available to both examiners and the students, may differ more than one might expect. This is the latest CMMPH education publication around aspects of the PhD [2-5].
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health (CMMPH)
References:
- van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, B., Regmi, P., Simkhada, P., Hundley, V., Poudel, K.C. (2022) Reflections on variations in PhD viva regulations: “And the options are….”, Journal of Education and Research (accepted).
- Way, S, Hundley, V., van Teijlingen, E, Walton, G., Westwood, G. (2016) Dr Know. Midwives 19: 66-7.
- Wasti, S.P. Regmi, P.R., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E., Hundley, V. (2022) Writing a PhD Proposal, In: Wasti, S.P., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P.P., Hundely, V. & Shreeh, K. (Eds.) Academic Writing and Publishing in Health & Social Sciences, Kathmandu, Nepal: Himal Books: 176-183.
- Hundley, V., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2022) Converting your Master’s or Doctoral Thesis into an Academic Paper for Publication, In: Wasti, S.P., et al. (Eds.) Academic Writing and Publishing in Health & Social Sciences, Kathmandu, Nepal: Himal Books: 184-189.
- Regmi, P., Poobalan, A., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2021) PhD supervision in Public Health, Health Prospect: Journal of Public Health 20(1):1-4. https://www.nepjol.info/index.php/HPROSPECT/article/view/32735/28111
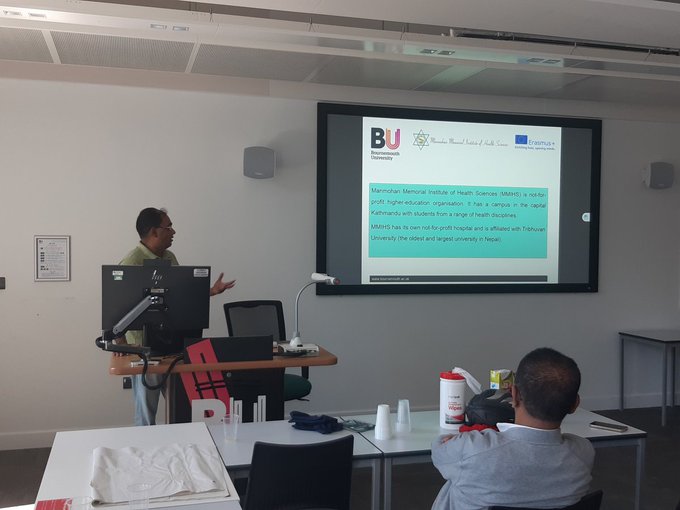
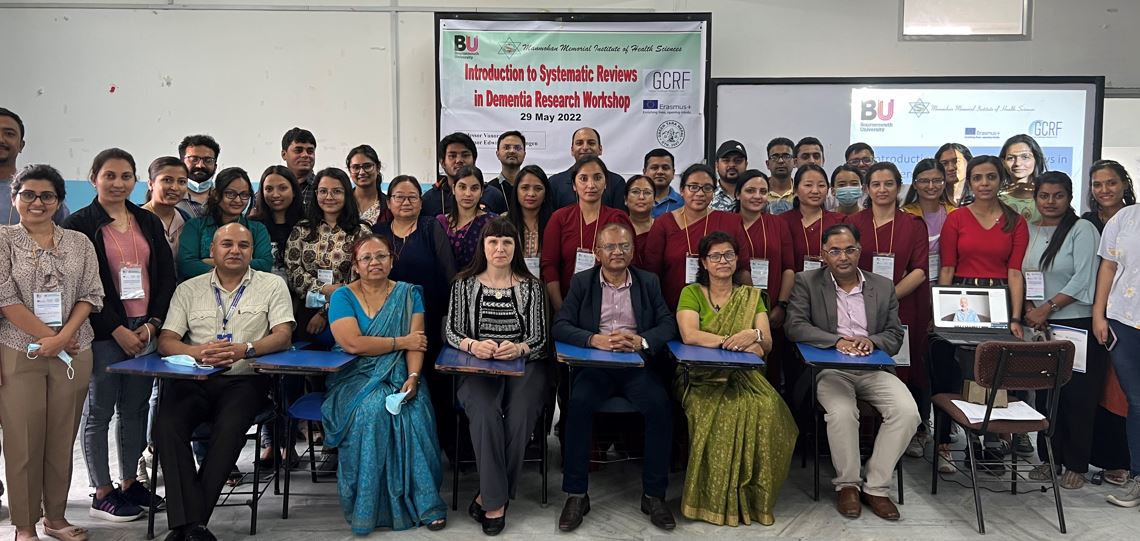
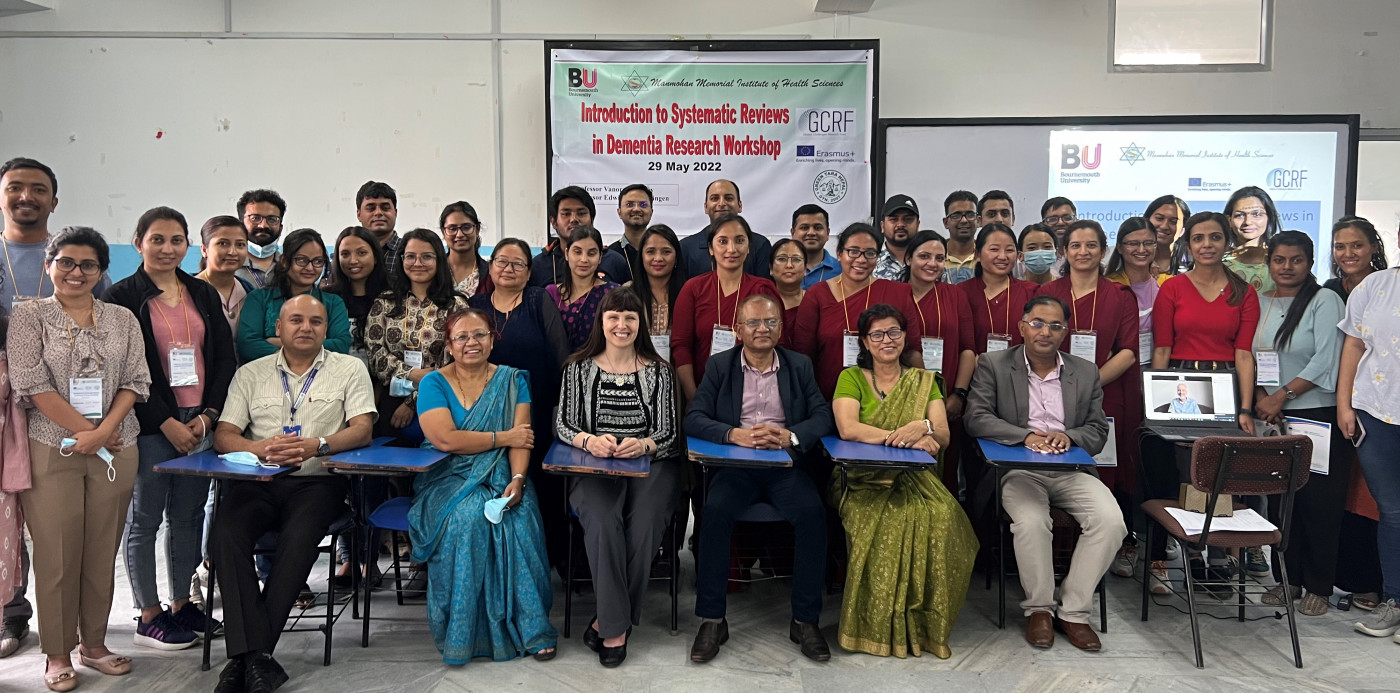




















































 Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration
Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration 3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March
Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward?
Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward? ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease