 What are bibliometrics?
What are bibliometrics?
Bibliometrics are a set of methods used to study or measure text and information. Citation analysis and content analysis are the most commonly used bibliometric methods. Bibliometric methods can help you explore the academic impact of a field, a set of researchers or a particular journal paper.
What is citation analysis?
Citation analysis looks at where a document has been referenced by others since it was originally published – this information can be used when searching for materials and in analysing their merit. Undertaking citation analysis on yourself is useful for assessing your own research performance. Specialist databases such as Web of Science and Scopus provide various tools for doing this analysis.
Searching for citation information on the Web of ScienceSM
 Web of ScienceSM is hosted by Thomson Reuters and consists of various databases containing information gathered from thousands of scholarly journals, books, book series, reports, conference proceedings, and more:
Web of ScienceSM is hosted by Thomson Reuters and consists of various databases containing information gathered from thousands of scholarly journals, books, book series, reports, conference proceedings, and more:
- Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-Expanded)
- Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI)
- Arts & Humanities Citation Index (A&HCI)
- Index Chemicus (IC)
- Current Chemical Reactions (CCR-Expanded)
- Book Citations Index – coming soon!
These databases enable you to perform a variety of tasks, such as search published literature, undertake citation analysis, track new research within a particular field, and identify chemical compounds and reactions. Data is available from around 1990, and even earlier in some cases.
By producing a Web of ScienceSM Citation Report for yourself (or for others), you can find out who is citing your work and how it is being used in other people’s publications so that you can get a feel for the overall citation activity around your outputs. Search for an author’s name and then click on ‘Create Citation Report’ from the results page.
Producing this report will give you information such as the number of items published in each year, the number of citations to those items for each year, the average number of citations per item, and your h-index based on this information. Click here for web tutorials on how to use the Web of ScienceSM.
Searching for citation information on Scopus
Scopus, part of Elsevier’s SciVerse facility, was launched in November 2004 and is an abstract and citation database containing around 19,500 titles from more than 5,000 publishers. Scopus enables researchers to track, analyse and visualise research, and has broad coverage of the scientific, technical, medical and social sciences fields and, more recently, the arts and humanities. Data is currently largely available from 1996 but it does go back further than this in some cases. For more information about Scopus, click here.
By searching for yourself (or others) on the Scopus database using the author search facility, you can use the ‘View Citation Overview’ function to get a feel for the citations activity around your outputs. The information is presented and can be analysed in a number of ways, including pie charts, graphs and tables, and shows the breakdown of citation activity over a number of years and your h-index based on this data. Various tutorials on using Scopus can be accessed here.
Scopus and the Research Excellence Framework (REF):  HEFCE has announced that Elsevier have been chosen as the provider of citation data services to the REF sub-panels that have chosen to make use of citation information as part of the assessment process. Using the Scopus database, HEFCE will provide the relevant sub-panels with raw citation data (i.e. not normalised) accompanied by contextual information, which will assist those panel members in making decisions about the outputs part of the REF submissions.
HEFCE has announced that Elsevier have been chosen as the provider of citation data services to the REF sub-panels that have chosen to make use of citation information as part of the assessment process. Using the Scopus database, HEFCE will provide the relevant sub-panels with raw citation data (i.e. not normalised) accompanied by contextual information, which will assist those panel members in making decisions about the outputs part of the REF submissions.
What is the h-index?
The h-index was conceived by Professor Jorge Hirsch in 2005 within the field of physics and is fast becoming one of the most widely used metrics for research evaluation. It is also becoming increasingly used as a measure of research activity and academic prominence across various subject areas.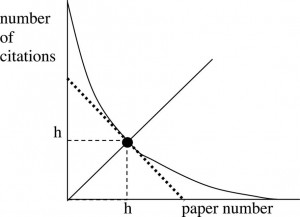
The benefit of the h-index over other citation measures is that it is not influenced by a few highly cited papers and it ignores any papers that remain uncited. It is calculated based on the number of papers by a particular author that receive h or more citations. Therefore, an h-index of 15 means that a person has at least 15 papers that have been cited 15 times or more. Fortunately, the Web of Science and Scopus both automatically calculate the h-index as part of their citation analysis functions so there is no need to work it out manually.
If you’d like to know more about the h-index, the original research document can be accessed from the Cornell University Library webpage.
What are journal impact factors?
Journal Impact Factors are published annually on the Web of Knowledge and provide a way of ranking journals based on the citation performance of articles published by those journals from the previous two years. For more information about how impact factors are calculated and how they can be used, see my previous blog post.
Other methods of ranking journals also exist, such as the ABS Academic Journal Quality Guide and the ERA journal ranking list. Journal rankings can be useful when choosing which journal to publish in, for example.
 BU will be hosting a half day Research Excellence Framework (REF) event, supported by the REF team, on 22 February 2012 to which all staff are invited to attend.
BU will be hosting a half day Research Excellence Framework (REF) event, supported by the REF team, on 22 February 2012 to which all staff are invited to attend.

 I work at the University on a part-time basis. Can I still be submitted to the REF? – As above, the REF recognises part-time working as a clearly defined circumstance which can result in a researcher being unable to produce four outputs during the REF assessment period. It is likely this will be dealt with on a pro-rata basis, e.g. a researcher who has been on a 0.5 FTE contract throughout the REF period is likely to be required to submit 2 outputs. Further details will be included in the BU REF Code of Practice.
I work at the University on a part-time basis. Can I still be submitted to the REF? – As above, the REF recognises part-time working as a clearly defined circumstance which can result in a researcher being unable to produce four outputs during the REF assessment period. It is likely this will be dealt with on a pro-rata basis, e.g. a researcher who has been on a 0.5 FTE contract throughout the REF period is likely to be required to submit 2 outputs. Further details will be included in the BU REF Code of Practice. This first exercise was considered to be a ‘light touch’ review as the external reviewers were not asked to look in detail at each output but to provide general comments about an individual’s research profile and an overview assessment of the UOA as a whole.
This first exercise was considered to be a ‘light touch’ review as the external reviewers were not asked to look in detail at each output but to provide general comments about an individual’s research profile and an overview assessment of the UOA as a whole.

 Bibliometrics pilot – HEFCE ran a pilot exercise in the construction of bibliometric indicators of research quality in 2008-09, using
Bibliometrics pilot – HEFCE ran a pilot exercise in the construction of bibliometric indicators of research quality in 2008-09, using  The REF will assess research excellence through a process of expert review, informed by indicators where appropriate. It will be based on HEIs submitting evidence of their research activity and outcomes, to be assessed by expert panels.
The REF will assess research excellence through a process of expert review, informed by indicators where appropriate. It will be based on HEIs submitting evidence of their research activity and outcomes, to be assessed by expert panels. What are bibliometrics?
What are bibliometrics? Web of ScienceSM is hosted by Thomson Reuters and consists of various databases containing information gathered from thousands of scholarly journals, books, book series, reports, conference proceedings, and more:
Web of ScienceSM is hosted by Thomson Reuters and consists of various databases containing information gathered from thousands of scholarly journals, books, book series, reports, conference proceedings, and more:

 Why do I need to think about the impact of my research?
Why do I need to think about the impact of my research?


 Although a major contributor to life at BU, the study of Tourism is often wrongly maligned as being a niche subject on the periphery of more established areas of study such as Business & Management and Geography. Well, in the UK alone over 100 institutions offer HE courses at undergraduate level including “top tier” universities such as Exeter, Surrey, Strathclyde and Stirling with many more competing for students and staff across Europe and beyond with major concentrations of activity in North America, the Middle East, South East Asia and Australia and New Zealand where tourism is not only a significant area of academic interest but also of valuable income, foreign exchange earnings and employment.
Although a major contributor to life at BU, the study of Tourism is often wrongly maligned as being a niche subject on the periphery of more established areas of study such as Business & Management and Geography. Well, in the UK alone over 100 institutions offer HE courses at undergraduate level including “top tier” universities such as Exeter, Surrey, Strathclyde and Stirling with many more competing for students and staff across Europe and beyond with major concentrations of activity in North America, the Middle East, South East Asia and Australia and New Zealand where tourism is not only a significant area of academic interest but also of valuable income, foreign exchange earnings and employment.











 Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian
Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian NIHR-funded research launches website
NIHR-funded research launches website Academics write for newspaper in Nepal
Academics write for newspaper in Nepal New paper published on disability in women & girls
New paper published on disability in women & girls Global Consortium for Public Health Research 2025
Global Consortium for Public Health Research 2025 MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease