Has anyone else been shouting at the radio last week and over the weekend, or muttering aloud while reading social media posts? Or is that just me? There has been nowhere to hide from negative and badly informed stories about students, universities and the virus this week. Then you add in the news that lorries will need permits to enter Kent in January and things start to feel a bit bleak. So to cheer you all up for the weekend we have the usual wide and varied selection of policy news. If it carries on like this we might need to start including recipes or knitting patterns to lighten the mood (we’re not knitters, BTW).
Another delay to the big #HEpolicy announcements?
With the Autumn budget scrapped we start to wonder what will happen to the Comprehensive Spending Review and the associated announcements on the Review of Post-18 Education and Funding, and the Augar report that informed it. And the other things we are waiting for, which may or may not be linked, i.e. the response to the Pearce report on the TEF and a subsequent OfS plan for the TEF going forwards. The link being that the outcome on fees may be a link to “quality” which may link to the ambition for the TEF as an indicator. The BBC article we linked to above says that the CSR will still proceed but last year’s review was downgraded to a one year update. This year’s was meant to be a 4 year review but may go the same way. In which case, we may be heading for another delay on big changes to fees and funding.
That would be consistent with other things – we reported last week that Nicola Dandridge had said that the OfS admissions review would stay on pause until we had got through this year’s recruitment cycle, with continued uncertainty about the timing of A levels and other assessments next year and the potential for other disruption.
The OfS have also not rushed to radical change on the NSS, despite the government’s request for a “root and branch review” by the end of the year. They announced this week that the review will take place in two stages. The first stage will
- Assess the bureaucratic burden the NSS places on providers and how this could be reduced.
- Explore the unintended consequences of the NSS for provider behaviour and how these could be prevented, including whether the NSS drives the lowering of academic standards and grade inflation.
- Examine the appropriate level at which the NSS could continue to provide reliable data on the student perspective on their subject, provider and the wider system, and what could be done without depending on a universal annual sample.
- Examine the extent to which data from the NSS should be made public, including the implications of Freedom of Information (FoI) legislation.
- Ensure the OfS has the data it needs to regulate quality effectively.
- Ensure the NSS will stand the test of time, and can be adapted and refined periodically to prevent gaming.
- Ensure the UK wide role of the survey is considered in any recommendations.
The second stage of the review will look more widely at the role of the NSS, including which questions should be asked to support regulation and student information across all four countries of the UK. OfS intend to consult students, providers and employers in their review.
The contract for the 2021 NSS has already been awarded, and the OfS intend to continue with the survey next Spring, however, providers will not be required to promote it. Also: given the significance of the review, the board agreed on a number of measures to amend the 2021 NSS. First, any decision on what to publish from the NSS and at what level should await the outcome of the review to ensure that the 2021 published results were aligned with the new direction of travel resulting from the review.
There is a Wonkhe blog questioning the assumptions and Government concerns over the NSS, and another by David Kernohan which asks really good questions.
Research news
Research Professional had a lot to say this week:
- How likely it is that the Government’s R&D budget promises can be realised
- Several universities are unofficially jostling to host ARPA
- UKRI have asked for more funds to deliver the place based levelling up agenda
- An article speculating whether UKRI may fall to the Government’s cull during their consideration of the making the research system more efficient
They also covered the Industrial Strategy Council’s report highlighting strikingly uneven distributions across the UK of research and innovation funding. Meanwhile over on Wonkhe a new blog asks whether focussing state R&D spend at regions which are not currently research-intensive is a levelling-up solution and provides examples from the UK and overseas. And the Royal Society explore the contribution of public and non-profit research organisations to the research and innovation landscape.
UKRI
New UKRI Chief Executive Professor Dame Ottoline Leyser spoke this week: Science and Society, 20 years on: legacy and lessons for a post-Covid world at an online event marking the 20 year anniversary of this report. The report was credited with triggering a policy and institutional shift towards public engagement, dialogue and deliberation. Dame Ottoline spoke of the lasting significance of the Science and Society report and emphasised the continued importance of public engagement in research and innovation:
- We have made good progress. But despite efforts to engage the public in research there remains a significant gap between those who feel able to make informed choices, to question, challenge and influence research and innovation, and those who feel disconnected, underrepresented and disenfranchised…For this group, science is something that is done to you, not something in which you have a voice.
- In the next 20 years, we need to make the next step in the evolution of the place of science in society…science IN society. Science needs to be a normal part of cultural life…An expanded research and innovation concept that includes all the participants, not just the researchers and innovators, can build science capital, connecting a much wider range of people with the system, making it familiar and part of their world.
- This approach would build the research and innovation system out into society, at the same time as continued development of public engagement to include much more embedded co-creation would bring a wider range of voices in to the system.
Science Minister, Amanda Solloway, also spoke at the event. The UKRI press release for the event is here.
Commons Science & Technology Committee : Wonkhe report on this week’s session of the Science and Technology Committee:
- Giving evidence to the House of Commons Science and Technology Committee, William Bonvillian of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Peter Highnam of the US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) set out the working model of DARPA, including potential avenues for the commercialisation of research and innovation, and spoke to the challenges of replicating DARPA’s success outside of the defence context. Regina Dugan of Wellcome Leap suggested that the life sciences could be a potential focus of a fledgling agency, while Antoine Petit of French National Centre for Scientific Research spoke on the relationship between researchers and government in the French system. You can watch the entire session here; or ask us for a more comprehensive summary (Ref: D24/09-10:05)
PhDs: Oxford University was recognised by the media this year as making inroads into improving the diversity of the undergraduate students it admitted. The Telegraph report on a pilot approach they are testing to address diversity within PhD admissions. Oxford intend to take into account a student’s socio-economic background as well as their academic credentials.
PQs
- The proportion of transport-technology research innovation grants awarded to (a) female entrepreneurs (b) companies led by women (7.4% awarded to teams led by women); and the proportion awarded to disabled entrepreneurs (not known – no disability data collected).
- Any obligation & timescale that organisations in receipt of R&D tax breaks are required to publish their research within; and preventing duplication
Admissions
In 2020/21 enrolments were expected to drop as Britain hit the lowest point of the population demographic dip for young people. However, nationally admissions numbers have been good (for home, international and disadvantaged access) suggesting that the limitations of Covid have not hampered recruitment as much as feared (although enrolment may be a different story). The UCAS clearing analysis statistical releases are available here.
Wonkhe highlight a record 515,650 students with a confirmed place, up 4% from last year, and an 8% increase in the numbers of disadvantaged students. There has been a 12% increase in numbers of students accepted into higher tariff institutions, attributed partly to an increase in overseas applicants, and partly to the effect of the late adjustment of centre assessed grades. The Guardian, i News, and Tes have the story. The UCAS press release gives more information here.
UCAS Chief Executive Clare Marchant said:
- This has been one of the most momentous of undergraduate admissions cycles in living memory. The dust certainly hasn’t settled – our end of cycle reporting in the winter will provide the definitive account of the year.
- Predictions that the lower and medium tariff providers could have their numbers decimated haven’t come to pass… While there has been little (medium tariff) or no growth (lower tariff) in overall acceptances for the two other groups, they have not fallen off a cliff edge for these groups as a whole; though recruitment in the weeks following A level results day didn’t benefit them to the extent in previous years as students used their raised grades to move (back) to higher tariff
- Courses that will educate the next generation of frontline workers have been incredibly popular. The inspiring and welcoming healthcare sector is currently due to have a record 34,190 new nursing students, a huge increase of more than a fifth on last year. Demand for teaching courses has also risen during the pandemic. These courses are particularly popular with mature applicants, and previous UCAS research has shown the link between these subjects and periods when the economy and job market is in decline.
- … the demand for UK HE is still palpable, testament to all those who work in the sector.
Read more from Clare here.
Labour Party “conference”
Parliament has not broken for party conference recess this year. Labour opted to run four days of virtual contact for party members including the popular fringe events which normally discuss a wide range of matters significant within the policy sphere.
HE Fees: Earlier in the week Research Professional reported there wouldn’t be an announcement on Labour’s fee policy: Playbook understands that following discussions on that topic last week (covered in last Monday’s edition), progress was made—but not enough for Labour to nail its colours to the mast on university matters. The smart money is on an official policy line in mid-to-late October.
Too many graduates?
Tuesday saw an event led by Policy Exchange (who describe themselves as a centre-right think tank): Too Many Graduates, Too Few Workers: How should higher education adapt to a shrinking knowledge economy? Dods ‘attended’ the event and have summarised the discussion here; it is worth a read with the party divisions clear behind the thoughts expressed.
Wonkhe also suggest indicators of Labour’s emerging HE attitude were present at the event:
- there were hints of a developing Labour policy that seemed keen to improve technical routes within and around universities, and on providers being even more closely linked to ideas of place and space. And: Shadow Minister for Further and Higher Education Emma Hardy enumerated her benefits of higher education – soft power, individual aspirations, and public good.
There’s a good (and slightly humorous) Wonkhe blog on the event and it expands more on the Labour education hints:
- The ideas in the earlier policy of higher level education without leaving your locality, and the support for higher technical education, appears to suggest a developing policy position that takes the best of the NES thinking and marries it with some of the more sensible parts of Augar.
Introducing…
We are pleased to introduce Roshana Wickremasinghe, Policy Adviser for SUBU! Roshana has been with SUBU since February. Previously she taught secondary level English in Poole as part of the Teach First Leadership Development Programme. She has an MA in Transformational Leadership in Education, and hopes to undertake a PhD examining the impact of government policy on public perception of HE.
Do look out for Roshana’s contributions to this week’s policy update and more from her on the student perspective in future editions.
Student Matters – SUBU guest blog
Roshana covers the new student fees parliamentary petition and an Advance HE report on student transition.
Petition: In addition to the popular petition that gained 352,658 signatures over the summer, another petition asking for a partial tuition fee refund has appeared with 191,000+ signatures. Rather than a total refund, the petition is calling for a partial refund due to the implementation of online teaching. The government’s response to the previous petition was that universities should review complaints issued by students receiving poor quality learning, with vague wording not directly addressing the issue. With many universities in America already reversing any plans for in person teaching despite historic promises, it will be interesting to see how this will impact consumer rights in the UK system if our universities make similar U-turns.
Transition: AdvanceHE have published a report on the 20/21 transition process back to university for new and returning students. The document explores how universities can support students by managing expectation, awareness of student concerns, addressing digital poverty, supporting wellbeing and supporting academic study. The report comes in response to the increased concerns of students during this typically stressful time of year (money, socialising, campus safety measures and timely advice). Whilst the report does not reach any ‘stand out’ conclusions, it does stress the need for clear and personalised communications to students during the full transition process.
Student Unions
The Adam Smith institute published: State of the Unions: How to restore free association and expression, combat extremism and make student unions effective critiquing the student union model of today.
Roshana summarises the briefing paper: The highly critical report proposes that student unions currently cost taxpayers £165 million per annum, with an average spend of £75 per student per year. The report goes on to state that unions undermine freedom of association and expression through compulsory membership, lack democratic legitimacy, limit free speech and pursue a narrow political agenda (the list is much longer than this). Despite the almost humorous tone of the report, criticising SUs for banning sombreros and clapping, it has been well received in government by figures such as Sajid Javid and a foreword written by the Chair of the House of Commons Education Committee.
On the day of issue both Wonkhe and Research Professional dismissed the report.
RP: The report…is nothing if not provocative…It is available online if you wish to read more. However, if you want a nuanced take on what is undeniably a legitimate area of interest then you needn’t bother. Much of the report will already be familiar to Playbook readers. It turns out that when trying to give cast-iron examples of where students’ unions, which host many thousands of events every year, have a problem with “cancel culture”, it’s the same old tired examples that get dragged up. Nonetheless, the paper certainly provokes debate, if you like that sort of thing.
Wonkhe: When the Department for Education published its proposed restructuring regime for higher education providers back in July, many were surprised to find that expenditure on students’ unions – and in particular their sabbatical officers and “niche activism” – had been identified for scrutiny. There didn’t seem to be any anchoring evidence for the assertion that funding for such things was “disproportionate” and “not focused on serving the needs of the wider student population”, but now, courtesy of the Adam Smith Institute, some background has emerged…[It] contains a long list of culture war stories about students, and some inaccurate and misleading figures on expenditure and voter turnout, but very little on student welfare, student voice, or the good work that students’ unions have been doing to support students during the pandemic. It proposes that students’ unions be split up, with the National Union of Students required to collect individual subscriptions from students. Of course Wonkhe have a blog on it too: Do students’ unions waste money?; and one for data buffs.
The report is easy to dismiss. However, the Chair of the Education Select Committee, Robert Halfon, a particularly influential parliamentary figure, stated the suggestion of a split model was “intriguing”. He continued:
- By making the political part of student unions voluntary, ordinary students would no longer be required to finance political activities of which they did not approve… money could be focussed on those functions that students do appreciate, such as decent social and recreational facilities, better student sports, and more effective academic representation.
Research Professional report that Halfon stated:
- student unions had to choose whether to represent members or become “bastions of obsessive political campaigning. Across our universities and colleges, far too often, freedom of expression and intellectual curiosity on campus are being deeply eroded because of minority political activism.”
The same RP article mentions NUS’ immediate refutation of the briefing paper (poorly researched, outright misinformation, OfS concluded no evidence of free speech being systematically suppressed), alongside the Adam Smith Institute’s response which maintained the integrity of their report and findings.
HEPI have a story New polling shows students’ support for the Labour Party has grown under Keir Starmer and students have become more politicised since the start of 2020
Students & Covid
The flurry of commentary and blogging surrounding Covid and the influx of students to their university area continued this week. Here is a selection mostly from Wonkhe:
- Not enough whack for the moles: The press seems to frame students in lockdown as some kind of mild inconvenience, but…if students are in lockdown without enough money to cover essentials, away from support networks and unable to work or return home, what happens next?… universities are going to want to do all they can in the coming days to avoid misery for those that follow the rules, and misery for those that don’t. (Wonkhe)
- What data is useful for responding to C-19 risks? There is very little useful “real time” data on student activity or the presence or absence of a Covid-19 outbreak… But we can track cases which may have an impact on students, staff, and local communities, at a high resolution but with a time lag – using public data. (Wonkhe)
- Keeping student data safe through Covid (Wonkhe)- University staff and students must be aware of what happens to their data; this means processes must be completely clear and transparent. Institutions should also bear in mind that the only acceptable circumstance for health or track and trace data to be shared in the case of Covid-19 is if a public health body, for example Public Health England (PHE), requests it. It is therefore essential that processes are in place to avoid mixing or aggregating it with other data that might be shared elsewhere by mistake.
- We know that online fraud and scamming ramped up during lockdown. In recent weeks this has given way to greater numbers of cyber attacks. This Wonkhe blog anticipates the university sector is particularly vulnerable and makes recommendations of how to prepare.
- Wonkhe examine the SAGE minutes here, and state: what we have is more evidence that lazy or in some cases dangerous assumptions about student behaviour have clouded the advice given to DfE which has then re-emerged as advice to universities.
- iNews features a student’s reflections on his return to university: We no longer have that lively ebullient feeling we once had. The sense of collectiveness is simply absent…. Not being able to go out and live the student life is peculiar, but I know it is best for our safety. My peers and I are fearful of contracting the disease, but we also fear our education will be significantly impacted too. The messaging from the Government is also incredibly confusing. Reopening institutions will inevitably result in people interacting through lecture theatres, seminar rooms and public transport. I’m worried this could cause an astonishing escalation of Covid-19 cases across the country and lead to more blame being put on the shoulders of young people.
- The health secretary, Matt Hancock, was quick to shift the accountability to young people. This blame game is profoundly unfair.
- Similar themes on lacking the sense of belonging, which we know is so important to students, is raised in this Wonkhe blog, and it also reminds about commuter students.
- On Wednesday the PM confirmed that schools, colleges and universities should remain open despite: the recent rise in coronavirus cases. There was mention of students in the C-19 debate on Tuesday:
- Boris Johnson – The most important thing is that the students who are now back at university in large numbers should, like everybody else, follow the guidelines. It is also important that, where there are outbreaks in universities, students should not be going home to infect their older relatives.
- The above touches on one of this week’s major themes that rose in the publics’ consciousness: fear that students may infect relatives when they return home at vacation times (with Christmas being particularly celebrated) alongside fear students won’t be allowed home for Christmas. iNews cover it here: Ministers have yet to draw up plans to prevent students from spreading coronavirus, but will be desperate to avoid telling students to celebrate Christmas away from their families. And Wonkhe reiterate that SAGE did not say students cannot return home at Christmas and debate whether the concept of ‘household’ will allow students to pop home at the weekends.
- Finally Wonkhe tell us that Advance HE has released“Safe for Staff”, a report into the equality implications of reopening university campuses.
PQs
- What research is being done on younger students spreading covid-19 into the wider community. (Focuses on schools/colleges.)
- Still no answer to what additional support will be provided to universities in areas where there is no campus or local walk in covid-19 testing centres.
- What discussions the Government has had with universities about the steps taken to prevent new outbreaks of C-19 when students return home.
- Steps to ensure foreign students are quarantined upon entry to the UK & oversight of the process
Career Satisfaction
HESA have published: Higher Education outcomes: How career satisfaction among graduates varies by ethnicity. Wonkhe cover the report and – yes, you guessed it – they do have a blog dissecting it further:
- A new report from HESA finds that UK domiciled Black mature graduates were less likely to report career satisfaction than their peers.
- An analysis of Longitudinal Destination of Leavers from Higher Education (LDLHE) data dating back to 2013 found a nine per cent difference in career satisfaction between Black graduates aged above 26 and their White peers. For younger graduates the gap was around 2.6 per cent, in both cases after controlling for personal and study characteristics.
- These findings also highlight the lack of a current career satisfaction measure for graduates – there’s no measure in the new Graduate Outcomes survey, though it is suggested that HESA are looking at addressing this.
Graduate Career Recruitment
The Association of Graduate Careers Advisory Services (AGCAS) has published: Evaluating the effectiveness of employer engagement (shorter summary report here). It explores the range of careers or employability-related interactions taking place at universities between students and employers through surveys with AGCAS members and 8 interviews with graduate recruiters. Key findings:
- The careers fair is not dead. In face-to-face interactions, careers fairs are still seen as one of the most effective employer engagement activities for both universities and employers.
- Employer-led skills sessions/presentations were the most commonly offered activity, and rated one of the most effective activities according to employers.
- Work-based learning such as placements, and embedded curricula activity are considered most effective by universities, despite the majority of employer engagement activities being extra-curricular.
- From a university perspective, generic advertising services are considered to be the least effective employer engagement activity
- Before March 2020, a minority (only 21%) of careers-related employer engagement was delivered virtually and only 30% was embedded. Virtual was also not considered to be as effective as face-to-face delivery.
- To measure effectiveness, universities tend to focus on experiential feedback, while employers look for quantitative numbers of hires or applicants and return on investment.
- Employers want to know that the information they are sharing will reach students, so they are often keen to speak to student-facing staff as well as employer engagement professionals/their account manager.
- The majority of careers services have specialist employer engagement teams with some form of employer engagement strategy, and most use an account management model to personalise the service they offer employers.
The final page considered graduate recruitment activities in the post pandemic world:
- The pandemic has had a severe and signification impact on students, graduates and the wider population and it is unlikely that things will ever fully return to normal. Whilst appreciating the damage caused by the crisis, it is also important to acknowledge where it has influenced positive changes. For employer engagement, we may see the use and effectiveness of online activities increase dramatically. The flexibility resulting from increased remote working may see employers targeting a wider range of universities more sustainably. Students who struggled to afford the costs of travel to interviews and assessment centres may find their access to opportunities improved.
AGCAS plan more ‘short pulse surveys’ to understand how C-19 has changed employer engagement moving forward into the future from now onwards.
HEPI have a relevant blog: Isolation Generation – looking ahead to the sector’s unique recruitment challenge which highlights that this year’s Year 13s have an almighty catch up to achieve on top of contemplating their next steps. The article paints this year group as an even bigger challenge than the lockdown-exam-cancellation generation because of the lack of face to face contact that can be delivered. Excerpt:
- Almost 90% of next year’s applicants are already in the advanced research stages of their application but only 27% have already chosen their final five higher education courses.
- We might have expected that number to be higher, but with 59% reporting that they do not have enough information to make their decisions, it is clear there is an immediate need for more targeted information and advice. As pre-applicants undertake their research, they are casting their net beyond friends and family to find new opinions. There is obvious growth in virtual Open Days and virtual school events, but university websites are now seen as more important by 57% of all students. UCAS, too, by more than 40%.
- At the other end are parents and the recommendations from friends, which are comparatively less influential. Only 1% of pre-applicants told us their parents were now more influential when making their choices and just 9% said the same about friends. Applicants are now placing their trust directly with first parties. For the higher education sector, it means more scrutiny of their messaging, but also more demand.
- Next year’s applicants are very aware of what is coming for the economy.
- More than half of all Year 12s said since the lockdown they now assign more importance to ‘high graduate employment rates’. A fifth, think the same for placement years. This year’s applicants are looking for recession-proof degrees more than ever, and the onus is on universities and colleges to convince them of their own efficacy.
Today’s students are Gen Z and the sector should base their assumptions on the fact that they are the most agile and digitally-focussed customers they have come across. They want the answer to everything in their pocket – and they expect it now.
PQs
- Does the Government intend to mandate universities to publish their C-19 risk assessments.
- Providing support to university students unable to provide a guarantor to secure their accommodation; the number of students unable to provide a guarantor
- What additional funds will be made available for universities for deep cleaning after cases of C-19
- Whether NUS representatives will be invited to join the taskforce on university capacity
- Any plans for a new immigration route to allow international students to undertake a work or study based placement of between 6 & 12 months.
Inquiries and Consultations
Click here to view the updated inquiries and consultation tracker. Email us on policy@bournemouth.ac.uk if you’d like to contribute to any of the current consultations.
Other news
Social Sciences: HEPI blog: For employers, the Social Sciences stand up to the STEM obsession
OfS Board: David Palfreyman and Simon Levine will continue as non-executive board members on the OfS board for a three year period.
Student skills survey: Wonkhe are running a survey about student skills following their Secret Life of Students conference last week. They are working to understand current thinking on the skills students should be acquiring during their time at university. There’s no national consensus on what these skills should be, or even what they’re called – we’ve heard soft skills, life skills, employability skills, transferable skills – but employers want students to be able to demonstrate them. We know that whatever you call them, it doesn’t make sense to think about “skills” as distinct from subject knowledge, so we’re asking academics and those in academic-adjacent roles such as education developers, careers advisors, education technologists, and librarians to share your views about the state of student skills in 2020 via this short survey. As an incentive, once you complete the survey, you will be offered the chance to enter your name into a draw to win £100 in Amazon vouchers and a £100 donation to the charity of your choice.
Different times: The Guardian states universities are expecting unprecedented demand for student hardship funds as the part time job market collapsed under Covid. It also covered concerns that online learning will lead to higher drop out rates as students struggle to adjust to digital study and curtailed socialisation. Monitoring engagement online is also a concern. The article ends with a comment from Jacqueline Stevenson at Leeds: for some students, taking a break from their course will be the best thing, rather than a catastrophe. “Dropping out can be a pejorative term and is caught up with the idea of failure. But if someone makes a sensible decision to leave, and may come back later to finish their course, that should be celebrated. A student can carry that feeling of failure with them for a very long time.”
Study UK: The British Council’s ‘Study UK’ event (including 65 UK universities) will promote the benefits of studying in the UK to UG & PG prospective students across Europe during October and November. 13,000 students from Europe are expected to join the education events. This event aims to give students direct contact with UK universities, which the students cited as the most influential source for making their study abroad decisions. Maddalaine Ansell, Director of Education at the British Council said: ‘
- Our research shows that European students view the UK as the most attractive overseas study destination for teaching quality and employability. However, misconceptions about the application process, fees and requirements – particularly after the UK’s withdrawal from the EU – may be discouraging some from applying. Study UK Europe: Gateway to the UK aims to address this through a unique mix of information sessions and one-to-one conversations with higher education institutions. We will enable UK universities to reach European students directly – and to provide them with the information they need to start what we hope will be a life changing UK study journey.’
Subscribe!
To subscribe to the weekly policy update simply email policy@bournemouth.ac.uk.
Did you know? You can catch up on previous versions of the policy update on BU’s intranet pages here. Some links require access to a BU account – BU staff not able to click through to an external link should contact eresourceshelp@bournemouth.ac.uk for further assistance.
JANE FORSTER | SARAH CARTER
Policy Advisor Policy & Public Affairs Officer
Follow: @PolicyBU on Twitter | policy@bournemouth.ac.uk

 Back in April I started my new post as Senior Lecturer in Sport and Sustainability – one of six appointments made under BU’s Academic Targeted Research Scheme. The Scheme has been designed to attract and recruit talented individuals to conduct research in specific, targeted areas which align with BU 2025.
Back in April I started my new post as Senior Lecturer in Sport and Sustainability – one of six appointments made under BU’s Academic Targeted Research Scheme. The Scheme has been designed to attract and recruit talented individuals to conduct research in specific, targeted areas which align with BU 2025. I published the
I published the  NERC introduced
NERC introduced  SAIL (Staying Active and Independent for Longer) has been a three year EU funded project that utilised a social innovation approach to developed 10 pilots that aimed to support active aging. Four pilots were developed in the Netherlands, 2 in France, 2 in Belgium and 2 within the UK. The role Bournemouth University Team (Prof Ann Hemingway, Prof Adele Ladkin and Dr Holly Crossen-White) was to undertake an evaluation of the pilots and develop a feasibility study regarding the use of social innovation.
SAIL (Staying Active and Independent for Longer) has been a three year EU funded project that utilised a social innovation approach to developed 10 pilots that aimed to support active aging. Four pilots were developed in the Netherlands, 2 in France, 2 in Belgium and 2 within the UK. The role Bournemouth University Team (Prof Ann Hemingway, Prof Adele Ladkin and Dr Holly Crossen-White) was to undertake an evaluation of the pilots and develop a feasibility study regarding the use of social innovation.



 On 17th September 2020 students from DePaul University, USA; SSLA, India, and Bournemouth University engaged in an online dialogue exploring the effects of the current pandemic and their understanding of Psychology.
On 17th September 2020 students from DePaul University, USA; SSLA, India, and Bournemouth University engaged in an online dialogue exploring the effects of the current pandemic and their understanding of Psychology.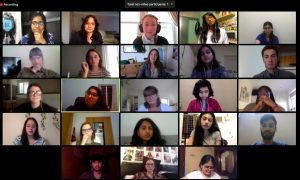


 The procedures for late submissions of external research and knowledge exchange applications has been updated in line with strategic guidance from UET to ensure that quality applications are submitted and adhere to BU’s financial regulations. The updated procedure can be found on the
The procedures for late submissions of external research and knowledge exchange applications has been updated in line with strategic guidance from UET to ensure that quality applications are submitted and adhere to BU’s financial regulations. The updated procedure can be found on the 











 Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh
Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh Exploring Embodied Research: Body Map Storytelling Workshop & Research Seminar
Exploring Embodied Research: Body Map Storytelling Workshop & Research Seminar Marking a Milestone: The Swash Channel Wreck Book Launch
Marking a Milestone: The Swash Channel Wreck Book Launch No access to BRIAN 5-6th February
No access to BRIAN 5-6th February ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease