 This week we published an editorial in the Journal of Biomedical Sciences on the question: “Is early diagnose for Vitamin A deficiency better than the current supplementation programme of Nepal?”
This week we published an editorial in the Journal of Biomedical Sciences on the question: “Is early diagnose for Vitamin A deficiency better than the current supplementation programme of Nepal?”
The editorial concludes that prevention is still better than cure, but instead of a mass Vitamin A supplementation in Nepal, we need a health promotion intervention aiming to increase the intake of relatively cheap vegetables and fruit (containing β carotene). In addition we need better surveillance and help to identify children with Vitamin A Deficiency and provide them with Vitamin A supplements. The primary focus should be on adopting sustainable food based approaches to combat vitamin A deficiency. In Public Health terms: rather than a blanket coverage of Vitamin A supplementation to whole population we should consider a targeted intervention aimed at those who need it most.
Reference:
Simkhada P, Sathian B, Adhikari S, van Teijlingen E, Roy B. (2015) Is early diagnose for Vitamin A deficiency better than the current supplementation programme of Nepal?. J Biomed Sci. 2(4):28-30.
http://www.nepjol.info/index.php/JBS/index
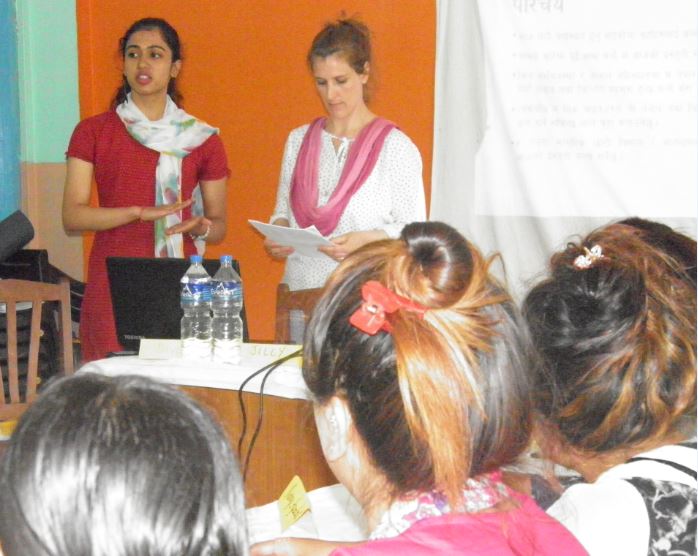
















 Andrew Harding and Colin Pritchard have recently had a paper published in the
Andrew Harding and Colin Pritchard have recently had a paper published in the  HSS PhD student Andrew Harding and fellow authors Jonathan Parker, Sarah Hean and Ann Hemingway have recently had a paper accepted for publication in Social Policy & Society, the sister publication to the Journal of Social Policy and run by the Social Policy Association.
HSS PhD student Andrew Harding and fellow authors Jonathan Parker, Sarah Hean and Ann Hemingway have recently had a paper accepted for publication in Social Policy & Society, the sister publication to the Journal of Social Policy and run by the Social Policy Association.












 No access to BRIAN 5-6th February
No access to BRIAN 5-6th February Missing Persons Indicator Project Recruitment
Missing Persons Indicator Project Recruitment Celebrating our Research: Postgraduate Research Showcase 2026
Celebrating our Research: Postgraduate Research Showcase 2026 Nursing Research REF Impact in Nepal
Nursing Research REF Impact in Nepal Fourth INRC Symposium: From Clinical Applications to Neuro-Inspired Computation
Fourth INRC Symposium: From Clinical Applications to Neuro-Inspired Computation ESRC Festival of Social Science 2025 – Reflecting back and looking ahead to 2026
ESRC Festival of Social Science 2025 – Reflecting back and looking ahead to 2026 ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease