
Polly, Sarah, Jastine and Irma at the end of project dinner
A year ago, Dr Helen Bolderston and I began our Fusion CCCP award, examining visual and social processes in autism and borderline personality disorder. We quickly appointed two part-time RAs who were current MSc students on the Developmental and Clinical Neuropsychology programme. Due to their excellent skill sets, obtained during the undergraduate degrees at BU and whilst working as voluntary and summer RAs, Sarah Wellaway and Jastine Antolin were the obvious candidates. We were assisted by Level 5 Psychology undergraduates Pollyanna Sapsford, together with Irma Konovalova who joined us in the summer.
The first part of this project required us to write scripts for and film 32 short movies. More than twenty BU students were our actors and we had a couple of fun evenings in a dark and wet November filming these scenes in Poole House and the old Retreat (amidst the noise of angle grinders whirring as work on the new Fusion Building was underway!) It turned out that Polly was a superb Director, so I happily let her take charge of the filming, and what a great job she made of it!
Given autism was the topic of Sarah’s MSc dissertation, she took the lead in organising the administrative side of the project which involved recruiting volunteers with autism from the local area. We made some fantastic connections with local organisations including Dorset Adult Asperger’s Support Group, Autism Wessex and the Cambian Wing College, with Sarah playing a huge role in making that happen. Together with our connections with the Autism Research Centre at the University of Cambridge and with Research Autism, we managed to recruit thirty participants with the condition (many of whom also took part in Sarah’s MSc experiment) and we are happy to report that almost all of them said they would love to come back and take part in future studies.
Polly and Irma’s final year dissertations are closely related to the Fusion project and will build on the insights they gained whilst working on this research over the last year.

Sarah, Jastine and I in a very hot and humid Barcelona!

The BPS Cognitive Section Conference: presenting our co-created and co-produced work
The autism branch of the study is almost complete and we hope to have the BPD side of the project wrapped up early in 2017. We presented our preliminary findings at the Festival of Learning this year and at the British Psychological Society Cognitive Section Annual Conference in Barcelona earlier this month. The Fusion award allowed not only me as presenter to attend the conference, but also Sarah and Jastine. It was a great way to end their time on the project as their contracts came to an end.
If anyone is in doubt about the benefits of involving students in their research, and in applying for Fusion funding, I can do no better than to let the students speak for themselves:
“My personal experience of being an RA for this project was invaluable. I have learnt a wealth of information and had first-hand experience in the organisation of a research project from beginning to end. The skills that I have acquired and developed during this time have been innumerable and I have also been given the opportunity to pass such skills to research apprentices. As part of this project I was also lucky enough to be able to attend the annual Cognitive Psychology Conference in Barcelona, which was not only an amazing experience but I also gained excellent tips from many professionals on delivering presentations as well as furthering my knowledge within fields that I had yet to learn about. And did I mention it was in BARCELONA!!” Sarah Wellaway
“It has been a huge privilege to be an RA and be part of a very motivated multidisciplinary team. This experience has expanded my knowledge and has provided me various research skills. It has also provided me opportunity to attend and take part in disseminating our research findings in a BPS conference abroad as well as exchanging ideas with academics who were experts in other psychological sub-fields. Overall, this experience has enabled me to attain personal and professional development, as it has increased my self-confidence and have provided me a set of abilities that will make me more employable in the future”. Jastine Antolin.
From my perspective as PI and an early career researcher, the last year has been incredible. We built a fantastic multidisciplinary team of academics, clinicians and students; we engaged external stakeholders like our participants with autism and the local support groups; we inspired a bunch of students by giving them invaluable experiences and skills for their future careers and on top of all that, conducted some cutting edge research in collaboration with one of the leading autism research centres in the world. It was hard work, but there is no doubt: it was certainly worth it!
Nicola Gregory, Lecturer in Psychology
 The study ‘Human rights and dignities: Experience of disabled women during pregnancy, childbirth and early parenting’ appeared under the heading ‘Maternity care failing disabled women, charity warns’ in the Journal of Family Health. The charity in question is Birthrights which funded the survey of women with physical or sensory impairment or long-term health conditions and their maternity care experiences. The research was conducted by midwifery researchers Jenny Hall, Jillian Ireland and Vanora Hundley at Bournemouth University and occupational therapist Bethan Collins, at the University of Liverpool.
The study ‘Human rights and dignities: Experience of disabled women during pregnancy, childbirth and early parenting’ appeared under the heading ‘Maternity care failing disabled women, charity warns’ in the Journal of Family Health. The charity in question is Birthrights which funded the survey of women with physical or sensory impairment or long-term health conditions and their maternity care experiences. The research was conducted by midwifery researchers Jenny Hall, Jillian Ireland and Vanora Hundley at Bournemouth University and occupational therapist Bethan Collins, at the University of Liverpool. Last month this important study had already been reported by the Royal College of Midwives (RCM) on their webpages (click here to read more). On the RCM website Louise Silverton Director for Midwifery at the RCM said: “It is deeply disappointing to hear that women with disabilities are not getting the maternity care they need and deserve. Although this is only a small survey, it does provide a very valuable insight into the realties of the care these women have received while pregnant. The RCM believes that maternity services should treat disabled women like every other woman, while ensuring that the care provided does not ignore or overreact to their specific wishes and aspirations.”
Last month this important study had already been reported by the Royal College of Midwives (RCM) on their webpages (click here to read more). On the RCM website Louise Silverton Director for Midwifery at the RCM said: “It is deeply disappointing to hear that women with disabilities are not getting the maternity care they need and deserve. Although this is only a small survey, it does provide a very valuable insight into the realties of the care these women have received while pregnant. The RCM believes that maternity services should treat disabled women like every other woman, while ensuring that the care provided does not ignore or overreact to their specific wishes and aspirations.”







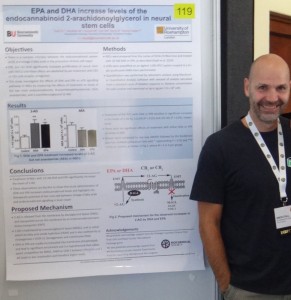







 We are often reminded that we should be paying attention to what we eat and making sure we exercise regularly. These recommendations are based on years of research into how diet and exercise can impact our health and well-being throughout the lifespan. However, it’s rare that these two crucial elements are studied together.
We are often reminded that we should be paying attention to what we eat and making sure we exercise regularly. These recommendations are based on years of research into how diet and exercise can impact our health and well-being throughout the lifespan. However, it’s rare that these two crucial elements are studied together.





 aths and many hundreds cases of injuries among Nepalese workers in these countries excluding India. For example, the Foreign Employment Promotion Board of Nepal recently reported that 1002 Nepalese migrant workers died in the 6 GCC countries and Malaysia in the last Nepalese calendar year, of which 357 (36%) were documented as cardiac related. However, in a quarter of deaths, the cause was unknown. Postmortem examination of migrant workers in many destination countries is not carried out and official records of the destination countries tend to record these deaths as being ‘from natural causes’. Information on underlying causes, such as heat stress on construction sites, is often not available.
aths and many hundreds cases of injuries among Nepalese workers in these countries excluding India. For example, the Foreign Employment Promotion Board of Nepal recently reported that 1002 Nepalese migrant workers died in the 6 GCC countries and Malaysia in the last Nepalese calendar year, of which 357 (36%) were documented as cardiac related. However, in a quarter of deaths, the cause was unknown. Postmortem examination of migrant workers in many destination countries is not carried out and official records of the destination countries tend to record these deaths as being ‘from natural causes’. Information on underlying causes, such as heat stress on construction sites, is often not available.


 Public Health England has launched a
Public Health England has launched a 











 Nursing Research REF Impact in Nepal
Nursing Research REF Impact in Nepal Fourth INRC Symposium: From Clinical Applications to Neuro-Inspired Computation
Fourth INRC Symposium: From Clinical Applications to Neuro-Inspired Computation ESRC Festival of Social Science 2025 – Reflecting back and looking ahead to 2026
ESRC Festival of Social Science 2025 – Reflecting back and looking ahead to 2026 3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Cookies – Tuesday 13 January 10-11am
3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Cookies – Tuesday 13 January 10-11am Dr. Chloe Casey on Sky News
Dr. Chloe Casey on Sky News ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease