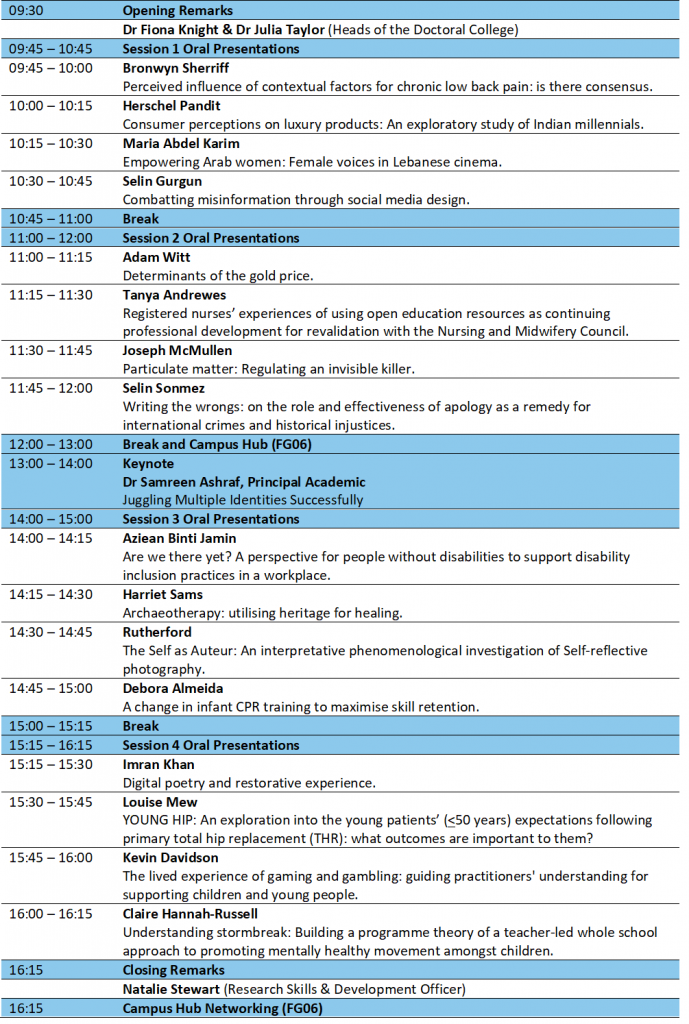
The 13th Annual Postgraduate Research Conference, hosted by the Doctoral College.
Rabeea Maqsood (PhD, FHSS) with this poster entitled: The association between Combat Related Traumatic Injury and Heart Rate Variability in the UK Armed Forces Personnel and Veterans- a quantitative secondary data analysis of the ADVANCE study.
Click the poster below to enlarge.
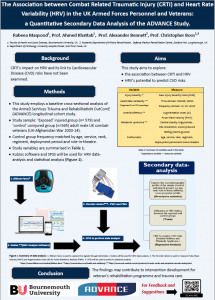
CRTI’s impact on HRV and its link to Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) risk have not been examined. This study aims to explore: the association between CRTI and HRV, and HRV’s potential to predict CVD risk. This study employs a baseline cross-sectional analysis of the ArmeD SerVices TrAuma and RehabilitatioN OutComE (ADVANCE) longitudinal cohort study, consisting of 579 adult male UK combat-veterans (UK-Afghanistan War 2003-14) with CRTI; frequency-matched to 565 uninjured men by age, service, rank, regiment, deployment period and role-in-theatre. Measures include single-lead ECG based HRV (RMSSD, SDNN, LF, HF, LF/HF-5-min ECG recordings), arterial stiffness (augmentation index, pulse wave velocity), injury-severity (NISS scores), and metabolic syndrome. Kubios software and SPSS will be used for HRV data-analysis and descriptive tests, respectively. CRTI’s influence on HRV and its relationship to CVD risk will be examined using T-tests and correlation. The findings may contribute to intervention development for veteran’s rehabilitation programme and trauma care.
You can view the full poster exhibition and pre-recorded presentations on the conference webpage.
If this research has inspired you and you’d like to explore applying for a research degree please visit the postgraduate research web pages or contact the Doctoral College dedicated admissions team.























 Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop
Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching
UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives
SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives BRIAN upgrade and new look
BRIAN upgrade and new look Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh
Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease