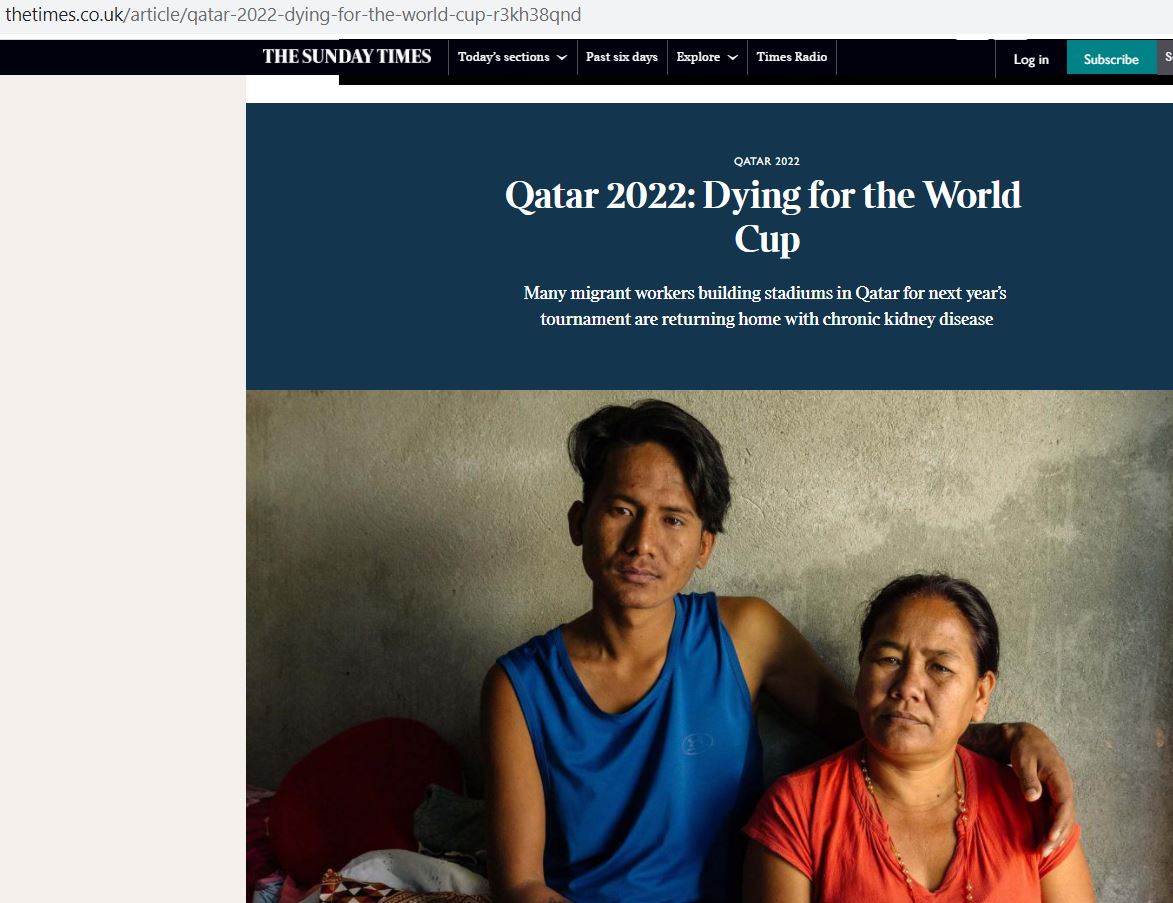
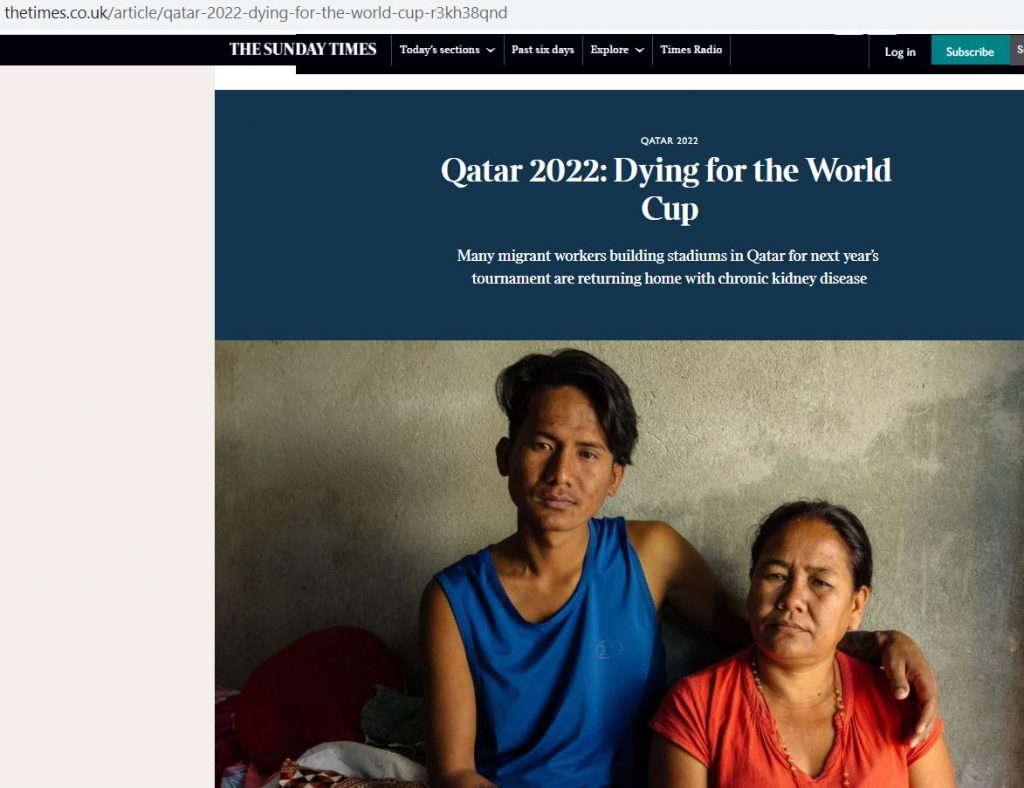
With the men’s FIFA football world cup starting on Sunday in Qatar it important to remember the human costs of those who build the infrastructure. The media coverage on the number of workers dying during the building of the football stadiums has highlighted the plight of foreign workers in the Middle East more generally. For example, BU’s researcher Dr. Nirmal Aryal was cited in The Sunday Times in an article with the title ‘Qatar 2022: Dying for the World Cup”, see the BU Research Blog published this time last year.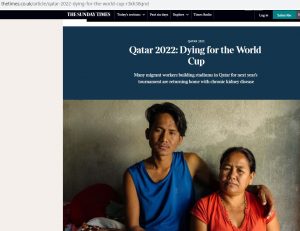
Here at BU we have conducted several studies into Nepali migrant workers, including those working in Qatar and elsewhere in the Middle East [1-13]. In the Middle East working conditions for foreign labourers are often Dirty, Dangerous and Difficult (commonly referred at as the 3Ds). Migrant workers often perform physically demanding work in a hot unprotected environment, suffer dehydration and/or exposure to chemical, excessive use of pain killers, and unhealthy lifestyle factors (such as restricted water intake and a high intake of alcohol/sugary drinks) which may precipitate them to acute kidney injuries and subsequent chronic kidney disease [1]. Dr. Regmi and colleagues in the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences are currently conducting a study into the kidney health of Nepalese migrant workers. This study is funded by the Colt Foundation.
From our work, we can say that in addition to the 3Ds, migrant workers are likely to experience a series of other challenges ranging from language and other cultural barriers, socio-economic problems and issues to do with their legal status, to a lack of health and safety training, difficulties in gaining access
to health services. If you have limited injury compensation in your line of work, a work injury attorney can answer commonly asked questions like “can employer make employee pay for accident?”

Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
CMMPH
References:
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., Sedhain, A., KC, R.K., Martinez Faller, E., Rijal, A., van Teijlingen, E. (2021). Kidney health risk of migrant workers: An issue we can no longer overlook. Health Prospect 21(1): 15-17.
- Aryal, N., Sedhain, A., Regmi, P., KC, R. K., van Teijlingen, E. (2021). Risk of kidney health among returnee Nepali migrant workers: A survey of nephrologists. Asian Journal of Medical Sciences 12(12), 126–132.
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., van Teijlingen, E., Trenoweth, S., Adhikary, P., Simkhada, P. (2020) The Impact of Spousal Migration on the Mental Health of Nepali Women: A Cross-Sectional Study, International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health 17(4), 1292; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph1704129
- Regmi, P., Aryal, N., van Teijlingen, E., Adhikary, P. (2020) Nepali migrant workers and the need for pre-departure training on mental health: a qualitative study, Journal of Immigrant & Minority Health 22, 973–981.
- Adhikary, P. van Teijlingen, E. (2020) Support networks in the Middle East & Malaysia: A qualitative study of Nepali returnee migrants’ experiences, International Journal of Occupational Safety & Health (IJOSH), 9(2): 31-35.
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., Faller, E.M,, van Teijlingen, E., Khoon, C.C., Pereira, A., Simkhada, P. (2019) ‘Sudden cardiac death and kidney health related problems among Nepali migrant workers in Malaysia’ Nepal Journal of Epidemiology 9(3): 755-758. https://www.nepjol.info/index.php/NJE/article/view/25805
- Adhikary P, van Teijlingen E., Keen S. (2019) Workplace accidents among Nepali male workers in the Middle East and Malaysia: A qualitative study, Journal of Immigrant & Minority Health 21(5): 1115–1122. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10903-018-0801-y
- Simkhada, P.P., van Teijlingen, E.R., Gurung, M., Wasti, S. (2018) A survey of health problems of Nepalese female migrants workers in the Middle-East & Malaysia, BMC International Health & Human Rights 18(4): 1-7. http://rdcu.be/E3Ro
- Adhikary P, Sheppard, Z., Keen S., van Teijlingen E. (2018) Health and well-being of Nepalese migrant workers abroad, International Journal of Migration, Health & Social Care 14(1): 96-105. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJMHSC-12-2015-0052
- Adhikary, P, Sheppard, Z., Keen, S., van Teijlingen, E. (2017) Risky work: accidents among Nepalese migrant workers in Malaysia, Qatar & Saudi Arabia, Health Prospect 16(2): 3-10.
- Simkhada, P.P., Regmi, P.R., van Teijlingen, E., Aryal, N. (2017) Identifying the gaps in Nepalese migrant workers’ health and well-being: A review of the literature, Journal of Travel Medicine 24 (4): 1-9.
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P., Adhikary, P., Bhatta, Y.K.D., Mann, S. (2016) Injury and Mortality in Young Nepalese Migrant Workers: A Call for Public Health Action. Asian-Pacific Journal of Public Health 28(8): 703-705.
- Adhikary P, Keen S and van Teijlingen E (2011). Health Issues among Nepalese migrant workers in the Middle East. Health Science Journal.5 (3):169-i75 DOI: 2-s2.0-79960420128.
 Rehabilitation research has long remained in the shadows of other health/medical disciplines, despite its immense potential to reshape patient outcomes and community health. The Rehabilitation Research Symposium Series in Qatar is a significant initiative aligned with global and national frameworks such as the WHO’s (World Health Organization) Rehabilitation 2030 and Qatar’s National Vision 2030.
Rehabilitation research has long remained in the shadows of other health/medical disciplines, despite its immense potential to reshape patient outcomes and community health. The Rehabilitation Research Symposium Series in Qatar is a significant initiative aligned with global and national frameworks such as the WHO’s (World Health Organization) Rehabilitation 2030 and Qatar’s National Vision 2030.








































 Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week
Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian
Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian NIHR-funded research launches website
NIHR-funded research launches website MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease