
This autumn BU put on a diverse range of events as part of the annual ESRC Festival of Social Science, which saw 387 events held nationwide. The Festival, which celebrates the research of social scientists, focused on a theme of ‘lifelong wellbeing’ in 2023.
BU contributed to the Festival for the 12th year in a row, attracting more than 340 attendees to eight very different events, ranging from an evening celebration of ska music in Dorset, complete with band, to an online webinar aimed at debunking the misconceptions that exist about Long-COVID. For the first time, BU partnered with the University of Southampton, running two joint events.
The Festival is designed to promote and increase awareness of social science and ESRC-funded research, enable social scientists to engage with non-academics and increase awareness of the contributions the social sciences make to the wellbeing and economy of UK society.
 Our festival programme kicked off with ‘Life through my lens: Tackling weight and unemployment’, a drop-in, interactive exhibition in Poole’s Dolphin Centre.
Our festival programme kicked off with ‘Life through my lens: Tackling weight and unemployment’, a drop-in, interactive exhibition in Poole’s Dolphin Centre.
Dr Sophia Amenyah and Professor Lee-Ann Fenge led the day-long event, which showcased photos and stories from participants in the ASPIRE project.
This project explores how to reduce unemployment and obesity at the same time by supporting people to make healthier lifestyle choices.
 Curious shoppers were able to pop in and view the exhibition and could choose their own images to illustrate what health and wellbeing meant to them and add comments to a collage.
Curious shoppers were able to pop in and view the exhibition and could choose their own images to illustrate what health and wellbeing meant to them and add comments to a collage.
Many passers-by spent time chatting to the researchers and volunteers from Healthwatch, the independent champion for people who use health and social care services 
“It was really interesting to reflect upon modern and traditional approaches to healthcare” Feedback from attendee
 BU researchers and cyber security undergraduates teamed up with cyber technology organisation CyNam to deliver ‘CyGamBIT – using play to stay safe online’ for pupils from Years 12 and 13.
BU researchers and cyber security undergraduates teamed up with cyber technology organisation CyNam to deliver ‘CyGamBIT – using play to stay safe online’ for pupils from Years 12 and 13.
BU Professor of Forensic Security Vasilis Katos welcomed students from four different schools, who got to play CyGamBIT, a game designed to engage young people with current and emerging online threats to enable them to stay safe online. 
Members of BU’s CyGamBit team, including Dr Jane Henriksen-Bulmer, Emily Rosenorn-Lanng and Stevie Corbin-Clarke were on hand to answer questions about the game and students also heard from BU undergraduates about the cyber security courses on offer at the university.

“I knew the pupils would get far more out of this than me just talking to them about it” Feedback from Mark Mortell, Head of Computer Science, Parkstone Grammar School
“Great event, top work!” Feedback from school attendee
The next event in our series, ‘UK drowning: Turning the Tide’, took place at the RNLI College on Poole quayside, which looked at how to stay safe when swimming in open water.
Dr Sam Hills, whose research looks at the risk factors associated with drowning, led an interactive session with colleagues from BU and Dr Martin Barford from Leeds Trinity University for a packed room of wild-swimming enthusiasts and others interested in drowning prevention. Dr Jill Nash from BU discussed her ongoing research project exploring the influence of emotions on RNLI communications and their link to behaviour change.

Attendees had a go at line-throwing, with the help of RNLI volunteers, tested their physiological response to cold water (one arm only immersed!) and tried out an immersive virtual reality experience.
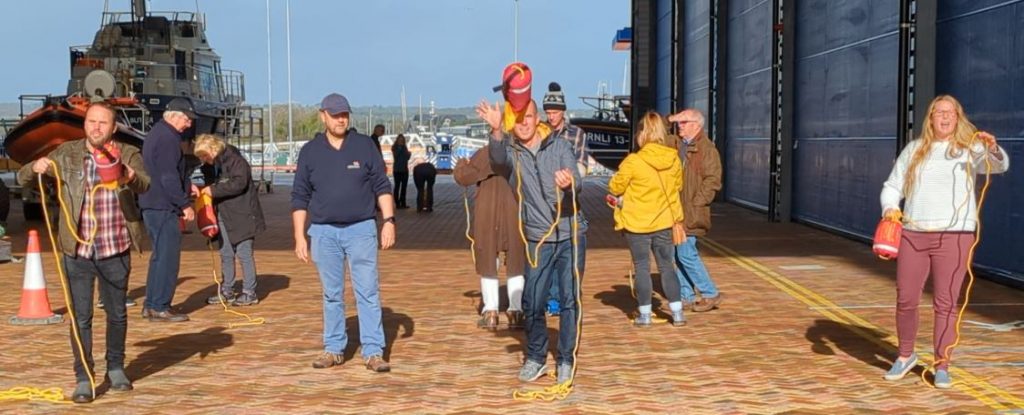


“Love how interactive it was. Very informative and I’m interested in following this research in future” Feedback from attendee
Our following event was a real departure from previous years – ‘Two-tone towns: A social History of Ska in Dorset’ combined talks from Dr Ian Gwinn and Dr Tabitha Baker with video interviews and a roof-raising set from local ska band The Guns of Navarone!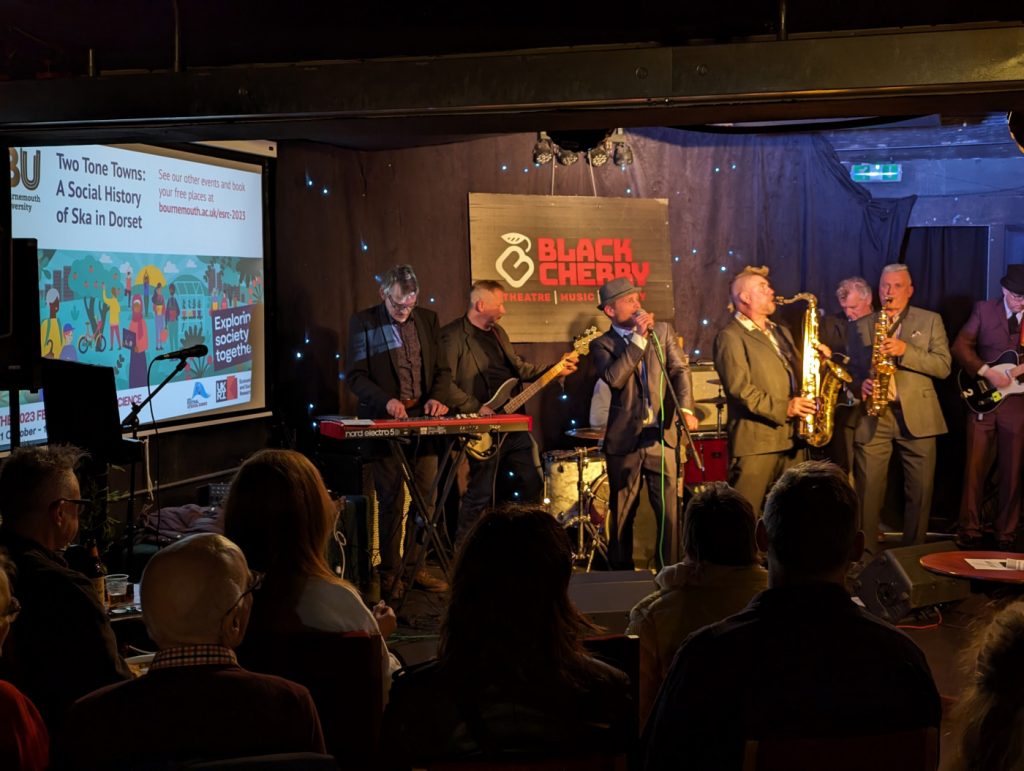 

Taking place at our Café Scientifique venue, the Black Cherry Café in Boscombe, attendees learned about the social significance of ska music in rural areas such as Dorset and got to dance to some classic tunes from The Specials and Madness. 
Louise Boston-Mammah from research partner DEED, a local organisation which aims to support teachers and students’ understanding of global issues and cultural diversity, commented: “What moved me the most about this event was the passion of those who were part of the local Ska scene and how they found a voice through this event”.
“This was a really interesting and enjoyable event. A great combination of learning about local history and musical performance by a great band” Feedback from attendee
Two of our events this year were jointly run with researchers from the University of Southampton: ‘Sharing the Coast’ and ‘Sharing the Forest’. Both explored the idea of the ‘right to roam’, whether Bournemouth’s coastline or the New Forest’s woods and heathland.
 At the clifftop Branksome Dene Room, BU’s Dr Andrea Jarman introduced the coast event with a look at the complex legal situation regarding access to beaches, using Swanage as an example.
At the clifftop Branksome Dene Room, BU’s Dr Andrea Jarman introduced the coast event with a look at the complex legal situation regarding access to beaches, using Swanage as an example.
Local campaigner Steve Elsworth spoke passionately about successfully fighting to restore access to Castle Cove Beach in Weymouth and Professor Rick Stafford provided a perspective on the non-human species that share the coastline. 
“Fantastic event. Very welcoming and informative” Feedback from attendee
“Three really great and diverse discussions and presentations” Feedback from attendee
 The second event took place at Lyndhurst Community Centre, in the heart of the New Forest. University of Southampton’s Dr Sarah Nield gave an overview of the laws, rights and obligations governing the Forest.
The second event took place at Lyndhurst Community Centre, in the heart of the New Forest. University of Southampton’s Dr Sarah Nield gave an overview of the laws, rights and obligations governing the Forest.
 She was joined by representatives from Forestry England, the New Forest National Park Authority and the Campaign for National Parks among others, who all contributed to a lively and engaging discussion.
She was joined by representatives from Forestry England, the New Forest National Park Authority and the Campaign for National Parks among others, who all contributed to a lively and engaging discussion.
Attendees also took part in three interactive quizzes that tested their knowledge on the area’s biodiversity, recreational use and the laws surrounding communing.
“It was really helpful to hear diverse views” Feedback from attendee
“Learnt lots about the forest as someone who uses it often” Feedback from attendee
A team of researchers led by Professor Debbie Holley delivered ‘The magic of play: enhancing wellbeing during medical interventions’ at Bournemouth Gateway Building, an event aimed at healthcare professionals.
The workshop explored how magic and play therapy can support wellbeing during hospitalisation and medical appointments. 
Participants took part in interactive activities, using knitted toy characters, LEGO® SERIOUS PLAY® and virtual reality, to discover how they can help promote distraction from pain and anxiety.

“It was interesting to learn about how to use play to build a rapport with children” Feedback from attendee
The final event in our Festival series, ‘Long-COVID: Myths, misconceptions and lives experiences’, took place online, to ensure those most likely to be interested could safely and easily attend.
More than 120 people joined the live session, led by BU researchers Dr Emma Portch and Dr Rachel Moseley, with University of Brighton colleague Dr Liam Wignall. They were joined in discussion by Dr Charles Shepherd of The ME Association and Claire Higham of Long Covid Advocacy.
Long-COVID is estimated to affect 1.9 million people in the UK, but research has found low public awareness of the condition, with many feeling that medical professionals do not take it seriously.
As well as exploring the truth behind some of the myths around Long-COVID, Emma and Rachel shared the latest research findings and participants heard about the experiences of those living with the condition.

“Absolutely excellent presentation on a really important topic” Feedback from attendee
“Thank you for acknowledging and doing research on Long Covid. In Canada, we struggle to be heard” Feedback from attendee
The ESRC changed the rules in 2023 around which institutions could take part in the Festival, which meant BU could no longer be a standalone contributor. It is thanks to our collaboration with the University of Southampton that we were able to take part this year and deliver such a broad range of events.
Event organisers applied via a competitive internal process in July, and were selected by a panel comprising researchers and Professional Services staff. They were supported in bringing their engaging, creative projects to life by Adam Morris (formerly Engagement Officer, now Impact Advisor) and Beverley Allen (Events and Communications Coordinator).
If you would like to take part in a future ESRC Festival of Social Science, it is a great time to start thinking about what you could propose. Start by taking a look at the call for the 2023 festival to get an idea of what we’re looking for in applications for 2024.
The open call for next year’s festival will go out May/June 2024.
If you would like to start discussing your ideas, please get in touch with the public engagement with research team at publicengagement@bournemouth.ac.uk.

 Pillar 1 asserts that comprehending the scale of global mass graves is paramount to understanding the nature of the problem. Consequently, pillar 1 will result in an open-source map of mass grave sites and ancillary outputs that have the potential to strengthen protection, forensic investigation, justice efforts, commemoration and remembrance for the benefits of survivors.
Pillar 1 asserts that comprehending the scale of global mass graves is paramount to understanding the nature of the problem. Consequently, pillar 1 will result in an open-source map of mass grave sites and ancillary outputs that have the potential to strengthen protection, forensic investigation, justice efforts, commemoration and remembrance for the benefits of survivors.
 Bournemouth Protocol on Mass Grave Protection and Investigation land and sea migratory routes and to what extent they might contain mass graves and hence warrant protection through a concerted human rights framework and policy.
Bournemouth Protocol on Mass Grave Protection and Investigation land and sea migratory routes and to what extent they might contain mass graves and hence warrant protection through a concerted human rights framework and policy.






 Explore how working with the media can help to raise the profile of your work and research and lead to impact.
Explore how working with the media can help to raise the profile of your work and research and lead to impact.

 Our festival programme kicked off with
Our festival programme kicked off with  Curious shoppers were able to pop in and view the exhibition and could choose their own images to illustrate what health and wellbeing meant to them and add comments to a collage.
Curious shoppers were able to pop in and view the exhibition and could choose their own images to illustrate what health and wellbeing meant to them and add comments to a collage.
 BU researchers and cyber security undergraduates teamed up with cyber technology organisation CyNam to deliver
BU researchers and cyber security undergraduates teamed up with cyber technology organisation CyNam to deliver 







 At the clifftop Branksome Dene Room, BU’s
At the clifftop Branksome Dene Room, BU’s 
 The second event took place at
The second event took place at  She was joined by representatives from
She was joined by representatives from 






 This is a reminder that the European Research Executive Agency invites those interested in applying for the next call to join the
This is a reminder that the European Research Executive Agency invites those interested in applying for the next call to join the 










 Fourth INRC Symposium: From Clinical Applications to Neuro-Inspired Computation
Fourth INRC Symposium: From Clinical Applications to Neuro-Inspired Computation Writing policy briefs
Writing policy briefs Upholding Excellence: The Concordat to Support Research Integrity
Upholding Excellence: The Concordat to Support Research Integrity Today’s Documentation Will Serve Tomorrow’s Justice
Today’s Documentation Will Serve Tomorrow’s Justice ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease