
Ada Lovelace
Tuesday 12th October is Ada Lovelace Day: an international celebration of women’s achievements in science, technology, engineering and maths (STEM). Often referred to as the ‘first computer programmer’, Ada Lovelace (1815-1852) inspired Alan Turing’s work on the first modern computers in the 1940s. Find out more about her here.
All week we are profiling a selection of the women who work in STEM disciplines at BU, in areas as varied as games technology, sport psychology, electronics and clinical nutrition. Today we feature Dr Rebecca Neal and Dr Amanda Wilding.

Dr Rebecca Neal
Dr Rebecca Neal, Senior Lecturer in Exercise Physiology and Programme Leader for the Sport and Exercise Science degree programme. Rebecca teaches physiology and research methods units across the Department of Rehabilitation and Sport Sciences and the Department of Sport and Events Management. She has conducted research in the Extreme Environments Laboratory at the University of Portsmouth in the areas of exercise and environmental physiology and sports performance for the English Institute of Sport, British Triathlon, GlaxoSmithKline and the Ministry of Defence.
Susan Dewhurst, Head of Department and Principal Academic in Exercise Physiology, who nominated her, says: “Rebecca is an early career researcher excelling in the traditionally male-dominated field of sport and exercise science. Her work in the field of extreme environmental physiology is published in prestigious physiology journals and she has been the recipient of external and internal grants to advance her work. [She] contributes greatly to transferring her research findings to the end user, through public engagement events, magazine articles and podcasts aimed at raising the awareness of the issues and needs of individuals exercising in extreme environments.”
What does Ada Lovelace mean to you?
“The vision that Ada Lovelace had, to create and use a computer that would produce an answer that has not been pre-programmed, is fundamental to research in STEM. I’ve been interested in understanding how the body works since trying to develop athletic skills as a child. I chose to follow this up with a degree in sport and exercise science, where the lecturers and my desire to adventure inspired me to dig deeper into what happens to our bodies in different stressful environments, whether that was exercise, disease or different extreme environments. Now, research from sports science and environmental physiology, like that of my PhD research on heat and hypoxia, is being used to explore therapeutic treatments to aid clinical populations.”
What sparked your interest in male-dominated sports and extreme environmental physiology?
“Growing up, my drive to be involved with sports stemmed from wanting to explore, learn new skills, and compete. When you’re competitive, you want to achieve, no matter what sport it is, so I would train with anyone who thought the same – often men. The same was true for exploring science throughout school and my degree, and these experiences led to me completing a PhD in Environmental Physiology, working with a team of like-minded people.
What do you consider to be your biggest achievements so far in your career?
“So far, I’m particularly proud of the series of publications that came out of my PhD, as the experiments were demanding, involving about 40 different types of whole-body and molecular physiological measurements, with human participants visiting the laboratory over 30 times across several months. More recently, I led the successful launch of a new degree programme at BU, during a pandemic, which we are excited to see develop now our new students are back on campus and in the Human Performance Laboratory.”
Have you faced any challenges in your chosen field because you’re a woman?
“Exercise physiology is a STEM area that combines topics that have historically been led by men: science and sport/exercise. We have progressed in many ways, but in both areas, there is much work to do for equal opportunities. Support exists for women researchers and educators in exercise physiology, however there is not equal representation yet at international conferences, and the focus of this research is often on male physiological responses. Still, the ability of women to lead complex studies is often underestimated. There is a drive in current research, which our research at BU is a part of, to include and focus studies on female physiology both during exercise and at different stages of their life – to better serve more people and further our knowledge.”

Dr Amanda Wilding
Dr Amanda Wilding, Senior Lecturer in Sport and Psychology. Amanda has supported athletes, coaches and parents in hockey, rugby, fencing and athletics, from county to international level, including athletes at their relevant world championships. She is also visiting lecturer at the Azerbaijan Sport and Physical Education University
Her colleague, Susan Dewhurst, Head of Department and Principal Academic in Exercise Physiology, says: “In addition to teaching, Amanda works as a sports psychologist in professional male football and army rugby. Her involvement in male-dominated sports led to her being invited to lead a workshop on Women in Sport to women at the Princess Nourah Bint Abdulrahman University in Saudi Arabia.”
What does Ada Lovelace mean to you?
“As a child I was always told I was no good at maths. I’m the fanciful Ada that wanted to fly, not the logical one. I never imagined I would end up in a STEM subject.”
What or who inspired you to pursue your career in a STEM subject?
“As a child, I was a runner. My father pointed out a woman once and told me: ‘She’s the lady who went to the Olympics’. ‘Wow!’, I thought. How do you do that? I’m never going to be a professional athlete but how do I ensure others are?’ At the end of my undergraduate degree I still hadn’t found my passion, but I knew the woman still worked in athletics so I contacted her. She told me that on her way home from the Olympics, she asked a man what event he did. He told her he was a sports psychologist, and helped ‘people to be at their best under pressure’. She told him: ‘I wish I’d met you three days ago, I could have been sat here with a medal. I underestimated myself and just ran my slowest time of the season.’ That was when I knew I was destined to be a sport psychologist.”
What sparked your interest in male-dominated sports?
“I fell into it. When the Premier League started the Elite Player Performance Plan, football clubs were required to hire a registered sport psychologist. Southampton FC contacted me and 11 years later I’m still there. It’s been an accident rather than design, but I love it.
Have you faced any challenges in your chosen field because you’re a woman?
“I’m working on a project called ‘Women in elite football: have you got the balls for it?’, investigating female experiences of operating in a male-dominated environment. I’ve previously been told not to stand on the side-lines as it’s ‘not your place, go to the grandstand’, I’ve been to places with no changing facilities as there are ‘no women in football’. The challenge is to be taken seriously without compromising my own identity and philosophy.”
Tell us about your area of work/research
“It is all about getting the best out of people, whether that’s an elite athlete striving for the Olympics, a stroke patient trying to walk again, or a student getting a first in their degree. My work is about people, helping them to understand themselves and the environment around them. It about educating the next generation, and also working directly with those in the sports arena: athletes, coaches, parents etc. I research the real world to drive up professional standards. I currently work with Southampton FC Ladies first team, the Royal Signals Rugby team and England Athletics coaches to support integrating sport psychology into their high-performance teams.”
What would you like to change as a result of your research?
“I’d like to see more women working in the elite context as scientists. The perception that women wear suits, not tracksuits, is something I’d like to see change. My goal is to help males feel more comfortable with women entering their domain, so women don’t feel the need to mould themselves into something they’re not. I don’t want a female to feel like she can’t enter the field because of her gender. ”
What do you consider to be your biggest achievements so far in your career?
“Getting my PhD was amazing. I had two children during this period and thought it was never going to happen. I remember being on stage and as I went to walk across, I got so overwhelmed I cried. It suddenly hit me how much I had given to it.”
What was it like leading a workshop on Women in Sport to women at the Princess Nourah Bint Abdulrahman University in Saudi Arabia?
“The trip was petrifying and amazing. Getting into the country was so intimidating as I was travelling alone but the country, the people, and the whole experience was fantastic. The ladies were so engaged – I learnt just as much from them as they did from me. We compared and contrasted our different cultures, our approaches to sport and where women fit into this picture. This trip sparked my interest in examining female experiences in elite sport and male-dominated environments.”
What would your advice be to girls looking at STEM subjects as a possible career?
“There is much more to STEM subjects than what we are taught at school. You can go down avenues you never knew existed. Keep going until you find the right path for you. Ask questions, seek experiences, and go for it – you never know where it will take you.”
 BU is launching a brand new funding stream for public engagement with research (PER) in early November. Researchers at all stages of their careers will be eligible to apply, whether they are new to PER or have already undertaken some public engagement activity.
BU is launching a brand new funding stream for public engagement with research (PER) in early November. Researchers at all stages of their careers will be eligible to apply, whether they are new to PER or have already undertaken some public engagement activity. This year’s RKEDF programme of training for public engagement with research begins next week with an introduction for anyone new to PER.
This year’s RKEDF programme of training for public engagement with research begins next week with an introduction for anyone new to PER. Join the PER network at BU
Join the PER network at BU





 Research Development and Support (RDS) would like to understand more about BU academics’ expertise in reviewing external grant applications and funding panel experience. As part of this we are collecting information about the external funding panels that BU academics are members of.
Research Development and Support (RDS) would like to understand more about BU academics’ expertise in reviewing external grant applications and funding panel experience. As part of this we are collecting information about the external funding panels that BU academics are members of. The next round of the Research Impact Fund will be launched in early November
The next round of the Research Impact Fund will be launched in early November
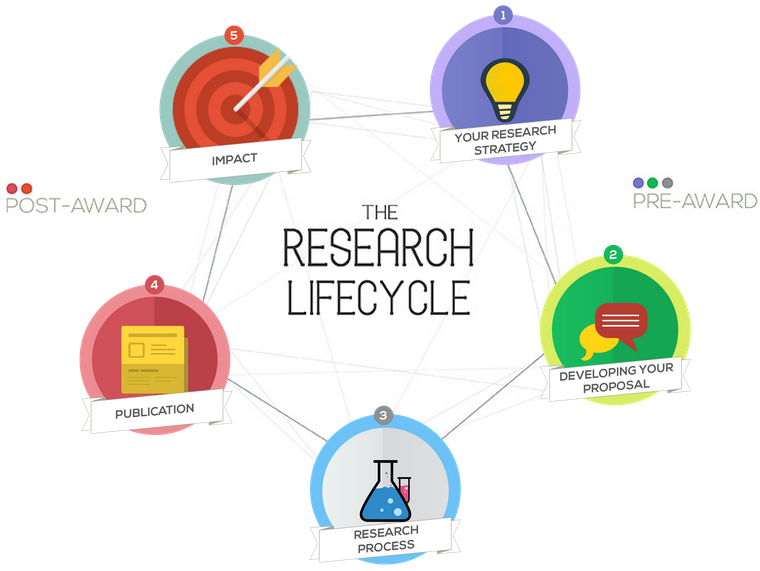















 This week on the BU Research Blog we are considering bid quality and how to make a bid as good as it can possibly be. I set off on a quest to speak to members of the BU Clinical Research Unit to understand how they contribute to improving bid quality.
This week on the BU Research Blog we are considering bid quality and how to make a bid as good as it can possibly be. I set off on a quest to speak to members of the BU Clinical Research Unit to understand how they contribute to improving bid quality.












 Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration
Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration 3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March
Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward?
Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward? ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease