 Work-related migration is a common livelihood strategy for many young people in Nepal. It is estimated that about 3.5 million Nepali work abroad, mainly in Malaysia, the Gulf countries, and India. The economic contribution of Nepali migrants to the country is highly significant as they send over US$6.1 billion in remittances which is 26 % of Nepal’s gross domestic product (GDP) [1].
Work-related migration is a common livelihood strategy for many young people in Nepal. It is estimated that about 3.5 million Nepali work abroad, mainly in Malaysia, the Gulf countries, and India. The economic contribution of Nepali migrants to the country is highly significant as they send over US$6.1 billion in remittances which is 26 % of Nepal’s gross domestic product (GDP) [1].
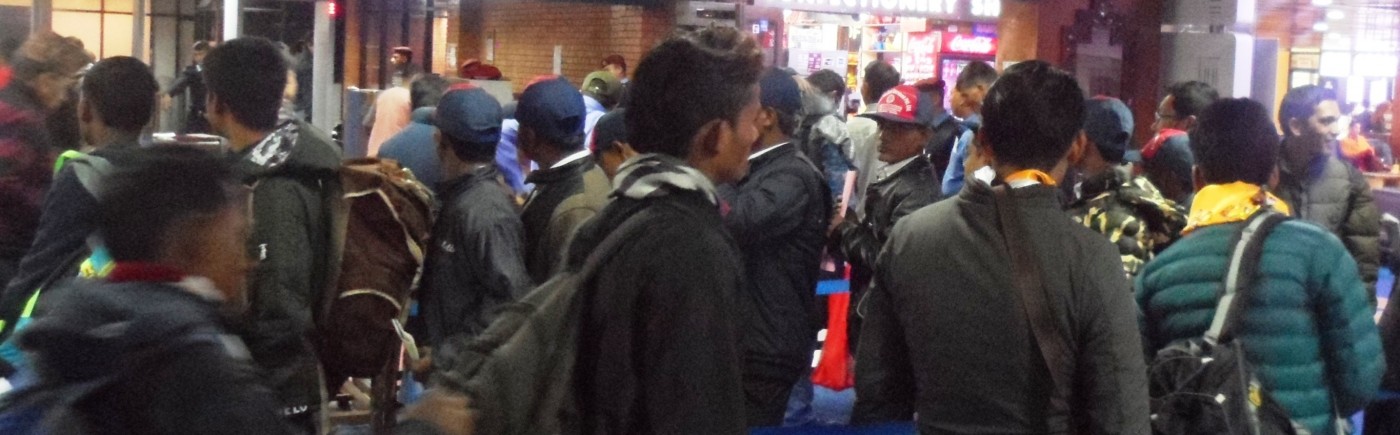 There is a growing global literature on migrant workers’ poor health and wellbeing and of those they leave behind. Over the past decade the media in Nepal have reported on the mortality and morbidity of Nepali migrants abroad. Every year at least one thousand dead bodies of Nepali migrants return back home via Tribhuvan International Airport (the only international airport in Nepal the country). The Government of Nepal estimated 5,982 deaths in migrant workers in the period 2008 to 2017, however there is likely to have been under-reporting [2].
There is a growing global literature on migrant workers’ poor health and wellbeing and of those they leave behind. Over the past decade the media in Nepal have reported on the mortality and morbidity of Nepali migrants abroad. Every year at least one thousand dead bodies of Nepali migrants return back home via Tribhuvan International Airport (the only international airport in Nepal the country). The Government of Nepal estimated 5,982 deaths in migrant workers in the period 2008 to 2017, however there is likely to have been under-reporting [2].
Although there have been studies on Nepali migrants’ health [3-9], these are largely around (a) sexual risk-taking behaviours of Nepali migrants in India; and, (b) occupational health and injuries issues among Nepali migrants in Gulf countries. These studies are carried out with the support from development partners and/or government organisations. However, most migration health research in Nepal has been small-scale for example to collect baseline information or as part of Masters or PhD projects. Currently, there is no research priority agenda on the topic of Nepali migrants’ health and wellbeing issues.
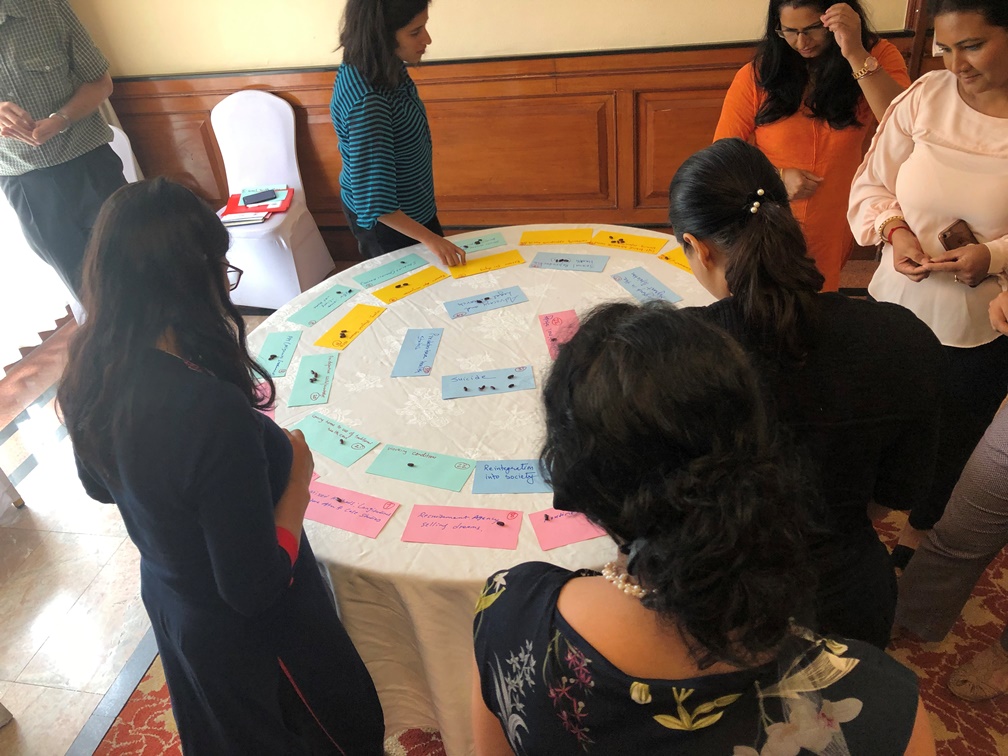
 To address this gap in the research agenda staff in BU’s Faculty of Health & Social Sciences and their collaborators organised a consultation workshop on August 2nd of this year in Kathmandu, Nepal. This workshop aimed to identify Nepali migrant workers’ health research prioritites and gaps. A total of 26 participants representing universities, ministries, non-governmental organisations working for migrants and research organisations attended the workshop.
To address this gap in the research agenda staff in BU’s Faculty of Health & Social Sciences and their collaborators organised a consultation workshop on August 2nd of this year in Kathmandu, Nepal. This workshop aimed to identify Nepali migrant workers’ health research prioritites and gaps. A total of 26 participants representing universities, ministries, non-governmental organisations working for migrants and research organisations attended the workshop.
The workshop was participatory in nature. To start with BU Professor Edwin van Teijlingen and Professor Padam Simkhada (BU Visiting Professor) shared global perspectives on migrant workers health. Whilst BU lecturer Dr Pramod Regmi highlighted key findings of BU’s migration research of Nepali migrants and their left-behinds. This contextual information helped focus the discussion on Nepali migrant health research priorities and gaps.
In order to identify the research agenda and prioritise issues and problems, participants were divided into four groups, each comprising 6-8 experts in the migration field. Groups were purposively formed to include participants from diverse backgrounds, e.g., migration related researchers, migration programme managers and policy-makers. Each member of the team was requested to identify two to five research needs around Nepali migrants’ health and share within their group for consensus. The group then prepared research priorities agreed in their team. Each team presented the research priorities to the wider group. A total of 46 research agenda items were identified which were subsequently prioritised through a voting process. Table 1 shows who participants ranked the top issues requiring further research.
Table 1 Top migration health research priorities in Nepal
- Causes of sudden cardiac deaths among Nepali migrant workers in the countries of Gulf and Malaysia
- Left-behind adolescents and social blaming/separation
- Methods/mixed/iterature searching/before and after study/case study
- Cross-border/national studies
- Research on undocumented migrants
- Culturally appropriate health care to migrants
- School education on migration
- Living condition of migrants abroad
- Pre-departure health status

The way forward
The consultation workshop was very productive in many ways. First, it identified wide ranging health research for Nepali migrants and prioritised these research issues. This information may help guide future research on migration studies. Secondly, the workshop offered a platform to build a network among researchers working for Nepali migrants.
Pramod R Regmi, Nirmal Aryal, and Edwin van Teijlingen
References:
- Ministry of Finance. (2018). Economic survey: Fiscal Year 2017/18. In. Kathmandu: Ministry of Finance: Government of Nepal.
- Ministry of Labour and Employment, Government of Nepal. (2018) Labour migration for employment: a status report for Nepal: 2015/2016 – 2016/2017. In. Kathmandu, Nepal: Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- Adhikary P, van Teijlingen E., Keen S. (2019) Workplace accidents among Nepali male workers in the Middle East and Malaysia: A qualitative study, Journal of Immigrant & Minority Health 21(5): 1115–1122. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10903-018-0801-y
- Adhikary P., Keen S., van Teijlingen E. (2011) Health Issues among Nepalese migrant workers in Middle East. Health Science Journal 5: 169-75. www.hsj.gr/volume5/issue3/532.pdf
- Adhikary, P, Sheppard, Z., Keen, S., van Teijlingen, E. (2017) Risky work: accidents among Nepalese migrant workers in Malaysia, Qatar & Saudi Arabia, Health Prospect 16(2): 3-10.
- Adhikary P, Sheppard, Z., Keen S., van Teijlingen E. (2018) Health and well-being of Nepalese migrant workers abroad, International Journal of Migration, Health & Social Care 14(1): 96-105. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJMHSC-12-2015-0052
- Regmi, P., van Teijlingen, E., Mahato, P., Aryal, N., Jadhav, N., Simkhada, P., Zahiruddin, Q.S., Gaidhane, A. (2019) The Health of Nepali Migrants in India: A Qualitative Study of Lifestyles and Risks. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16 (19). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193655
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., Faller, E.M., van Teijlingen, E., Khoon, C.C., Pereira, A., Simkhada, P. (2019) Sudden cardiac death and kidney health related problems among Nepali migrant workers in Malaysia. Nepal Journal of Epidemiology, 9 (3), 788-791. https://doi.org/10.3126/nje.v9i3.25805
- Simkhada, P.P., Regmi, P.R., van Teijlingen, E., Aryal, N. (2017) Identifying the gaps in Nepalese migrant workers’ health and well-being: A review of the literature. Journal of Travel Medicine, 24 (4). https://doi.org/10.3126/nje.v9i3.25805
 Yesterday Dr. Pramod Regmi, Dr. Shovita Dhakal Adhikari, Dr. Nirmal Aryal and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen, all based in the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences, presented at the tenth Annual Kathmandu Conference on Nepal & the Himalaya. Their paper ‘Moral panic and othering practices during Nepal’s COVID-19 Pandemic (A study with returnee migrants and Muslims in Nepal)’ was co-authored by Dr. Sharada Prasad Wasti from the University of Huddersfield and Shreeman Sharma (Department of Conflict, Peace & Development
Yesterday Dr. Pramod Regmi, Dr. Shovita Dhakal Adhikari, Dr. Nirmal Aryal and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen, all based in the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences, presented at the tenth Annual Kathmandu Conference on Nepal & the Himalaya. Their paper ‘Moral panic and othering practices during Nepal’s COVID-19 Pandemic (A study with returnee migrants and Muslims in Nepal)’ was co-authored by Dr. Sharada Prasad Wasti from the University of Huddersfield and Shreeman Sharma (Department of Conflict, Peace & Development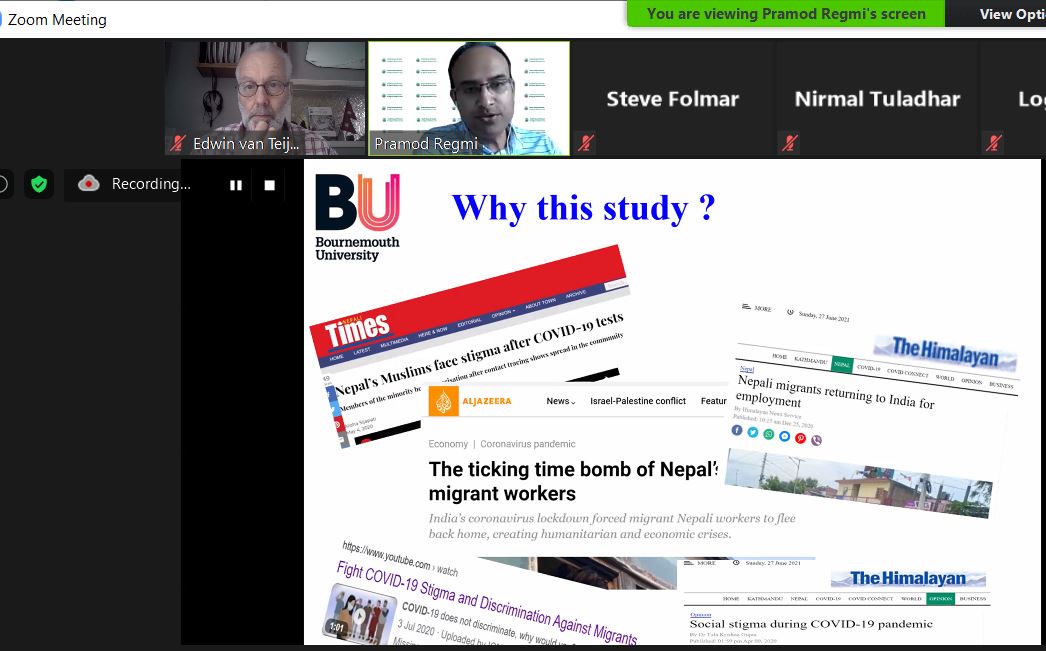


























































 Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU
Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU 3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Friday 20 March 1-2pm
3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Friday 20 March 1-2pm Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop
Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching
UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives
SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease