 On Christmas Day (25 December 2025) the Journal of Mixed Methods Studies published Dr. Orlanda Harvey’s latest paper ‘Using A Range Of Recruitment Strategies To Recruit Those Who Use Anabolic Androgenic Steroids‘ [1].
On Christmas Day (25 December 2025) the Journal of Mixed Methods Studies published Dr. Orlanda Harvey’s latest paper ‘Using A Range Of Recruitment Strategies To Recruit Those Who Use Anabolic Androgenic Steroids‘ [1].  The Journal of Mixed Methods Studies is an Open Access journal, hence this paper is freely available to anybody with internet access.
The Journal of Mixed Methods Studies is an Open Access journal, hence this paper is freely available to anybody with internet access.
Dr. Harvey is a Senior Lecturer in Social Work in the Faculty of Health, Environment & Medical Sciences. This is the latest in a series of publications based on Orlanda’s Ph.D. work at Bournemouth University. She has published a steady stream of papers over the past six years [2-7].
Congratulations!
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
References:
- Harvey, O., van Teijlingen, E., Parrish, M. (2025). Using A Range Of Recruitment Strategies To Recruit Those Who Use Anabolic Androgenic Steroids. Journal of Mixed Methods Studies, 11: 43–60. https://doi.org/10.59455/jomes.42
- Harvey, O., van Teijlingen, E., Parrish, M. (2024) Using a range of communication tools to interview a hard-to-reach population, Sociological Research Online 29(1): 221–232 https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/13607804221142212
- Harvey, O., Keen, S., Parrish, M., van Teijlingen, E. (2019) Support for people who use Anabolic Androgenic Steroids: A Systematic Literature Review into what they want and what they access. BMC Public Health 19: 1024
- Harvey, O., Parrish, M., van Teijlingen, E., Trenoweth, S. (2020) Support for non-prescribed Anabolic Androgenic Steroids users: A qualitative exploration of their needs Drugs: Education, Prevention & Policy 27:5, 377-386. doi 10.1080/09687637.2019.1705763
- Harvey, O., Parrish, M., van Teijlingen, E, Trenoweth, S. (2022) Libido as a reason to use non-prescribed Anabolic Androgenic Steroids, Drugs: Education, Prevention & Policy 29(3):276-288.
- Harvey, O., van Teijlingen, E., Parrish, M. (2022) Mixed-methods research on androgen abuse – a review, Current Opinion in Endocrinology & Diabetes 29(6):586-593.
- Harvey, O., van Teijlingen, E. (2022) The case for ‘anabolics’ coaches: selflessness versus self-interest? Performance Enhancement & Health 10(3) August, 100230



















 This first week of March has been a good week for FHSS publications. On March 1st CMMPH Prof. Vanora Hundley published her collaborative paper ‘Do Cochrane summaries help student midwives understand the findings of Cochrane systematic reviews: the BRIEF randomised trial’.[1] With colleagues based across the UK and Ireland she surveyed over 800 midwifery students at nine universities. This results of the study can be found in the journal
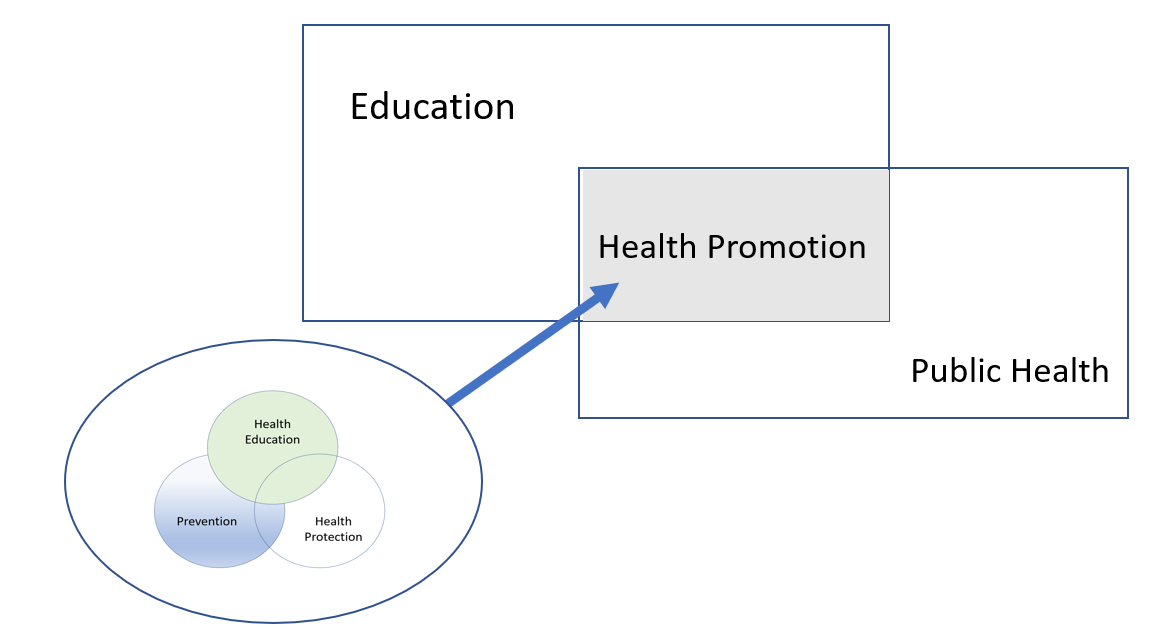
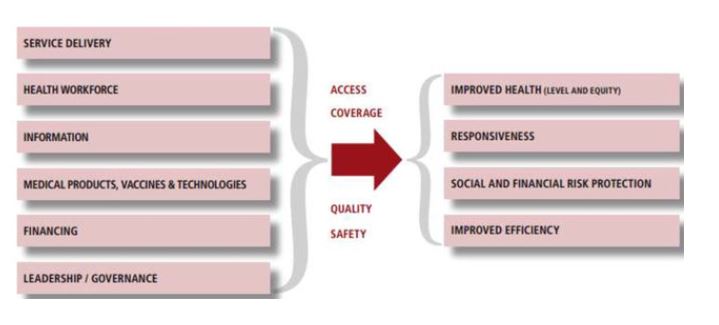
This first week of March has been a good week for FHSS publications. On March 1st CMMPH Prof. Vanora Hundley published her collaborative paper ‘Do Cochrane summaries help student midwives understand the findings of Cochrane systematic reviews: the BRIEF randomised trial’.[1] With colleagues based across the UK and Ireland she surveyed over 800 midwifery students at nine universities. This results of the study can be found in the journal  The second FHSS publication is a chapter in a Kindle book on the Importance of public health in low- and middle- income countries, written by Dr. Puspa Raj Pant,CMMPH’s Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen, and BU Visiting Faculty Prof. Padam Simkhada.[2] Padam Simkhada is Professor of International Public Health and Associate Dean (Global Engagement) for the Faculty of Education, Health and Community at Liverpool John Moores University. The chapter is part of the Kindle book with the long title: Public Health for the Curious: Why Study Public Health? (A Decision-Making Guide to College Major, Research & Scholarships, and Career Success for the College Students and Their Parents) edited by Richard Lee Skolnik from Yale University, USA.
The second FHSS publication is a chapter in a Kindle book on the Importance of public health in low- and middle- income countries, written by Dr. Puspa Raj Pant,CMMPH’s Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen, and BU Visiting Faculty Prof. Padam Simkhada.[2] Padam Simkhada is Professor of International Public Health and Associate Dean (Global Engagement) for the Faculty of Education, Health and Community at Liverpool John Moores University. The chapter is part of the Kindle book with the long title: Public Health for the Curious: Why Study Public Health? (A Decision-Making Guide to College Major, Research & Scholarships, and Career Success for the College Students and Their Parents) edited by Richard Lee Skolnik from Yale University, USA.















 Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU
Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU 3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching
UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease