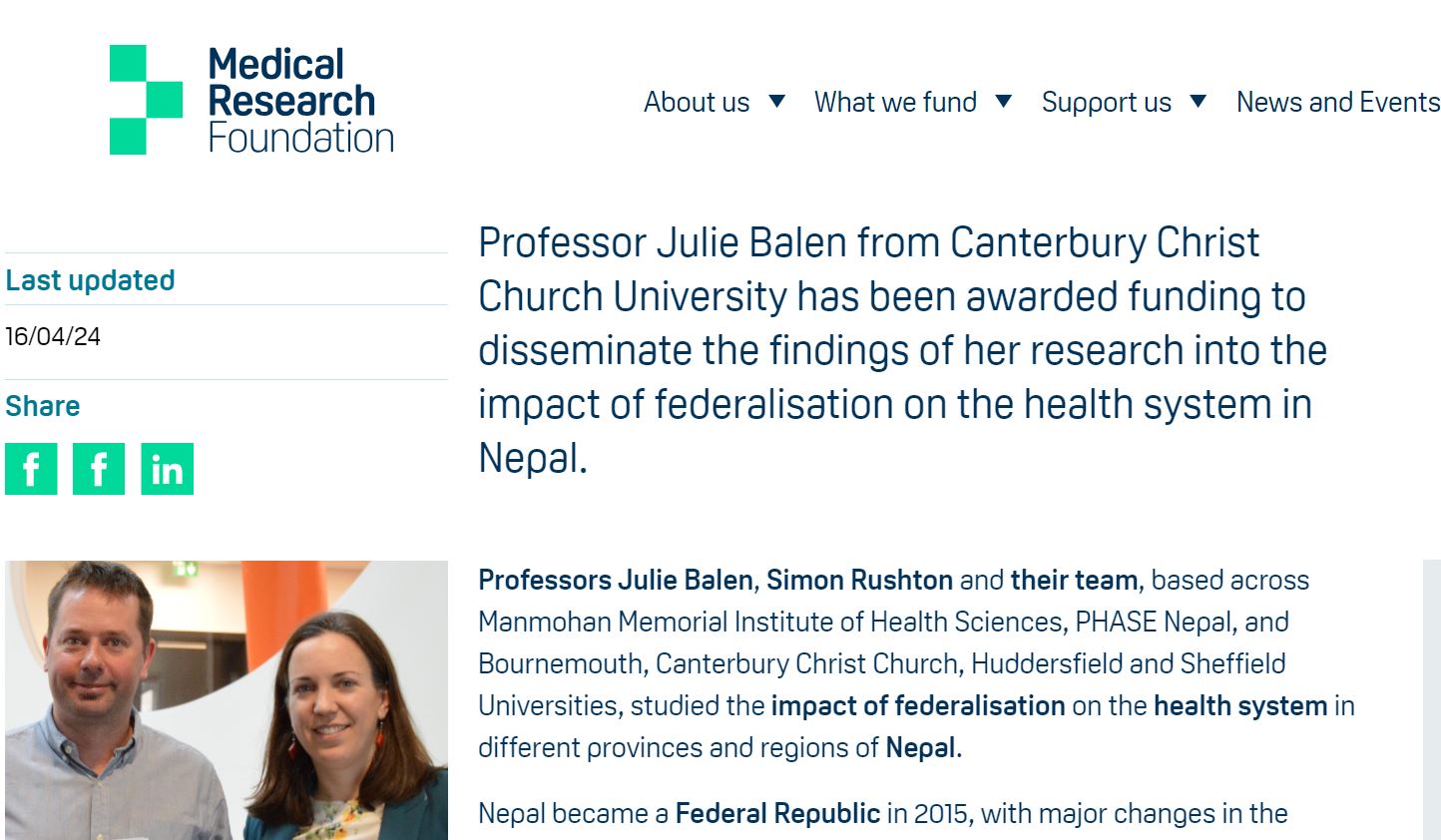
Yesterday our latest methodological paper ‘Methods or Methodology: Terms That Are Too Often Confused’ appeared online. [1] We recently published a methods paper outlining the difference between Methods and Methodology as so many postgraduate students manage to get it wrong or don’t understand the distinction between the two. There is a distinct difference between methodology and methods in research. However, too many students, researchers, and authors of academic papers do not seem to pay attention to the crucial difference. This is true not only in education research but also in many other academic disciplines. In simple terms, the term methods refers to the research tools and techniques; for example, in the qualitative field, interviews are a tool to collect data, and in the quantitative field, a questionnaire-based survey is an example of a data collection tool. Methodology is a broader concept as it refers to the overall approach to the research, includes a justification for this approach, and links to research philosophy, i.e., how we produce knowledge. This methodological note aims to explain the confusion, drawing on examples from the published literature in education research and beyond. It also considers the complexities and crossovers. The final section ends with key advice to researchers and authors on key mistakes to avoid regarding the difference between methods and methodology, including covering this in early supervision discussions.
 Our interdisciplinary team, based in the UK and Nepal, comprises Dr. Orlanda Harvey in BU’s Department of Sociology & Social Work, Dr. Pramod Regmi in BU’s Department of Nursing Science, Dr. Preeti Mahato from Royal Holloway, University of London, Dr. Shovita Dhakal Adhikari, London Metropolitan University, Dr. Rolina Dhital, based at Health Action & Research in Nepal and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen in BU’s Department of Midwifery & Health Sciences. In addition it is worth mentioning that both Preeti and Shovita are both former member of staff in the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences (FHSS) at BU. Finally, although the official publication date is Sept 2023, it only appeared online yesterday. This new methods paper is part of growing series of methods papers by members of this team of academics [2-12].
Our interdisciplinary team, based in the UK and Nepal, comprises Dr. Orlanda Harvey in BU’s Department of Sociology & Social Work, Dr. Pramod Regmi in BU’s Department of Nursing Science, Dr. Preeti Mahato from Royal Holloway, University of London, Dr. Shovita Dhakal Adhikari, London Metropolitan University, Dr. Rolina Dhital, based at Health Action & Research in Nepal and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen in BU’s Department of Midwifery & Health Sciences. In addition it is worth mentioning that both Preeti and Shovita are both former member of staff in the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences (FHSS) at BU. Finally, although the official publication date is Sept 2023, it only appeared online yesterday. This new methods paper is part of growing series of methods papers by members of this team of academics [2-12].
References:
- Harvey, O., Regmi, P. R., Mahato, P., Dhakal Adhikari, S., Dhital, R., van Teijlingen E. (2023) Methods or Methodology: Terms That Are Too Often Confused. Journal of Education & Research, 13(2): 94-105.
- Regmi, P.R., Waithaka, E., Paudyal, A., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2016) Guide to the design and application of online questionnaire surveys. Nepal Journal of Epidemiology 6(4): 640-644. http://www.nepjol.info/index.php/NJE/article/view/17258
- Regmi, PR., Aryal, N., Kurmi, O., Pant, PR., van Teijlingen, E, Wasti, PP. (2017) Informed consent in health research: challenges and barriers in low-and middle-income countries with specific reference to Nepal, Developing World Bioethics 17(2):84-89.
- Mahato, P., Angell, C., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P.P. (2018) Using Mixed-methods Research in Health & Education in Nepal, Journal of Health Promotion Official Publication of Health Education Association of Nepal (HEAN), 6: 45-48.
- van Teijlingen, E., Regmi, P., Adhikary, P., Aryal, N., Simkhada, P. (2019). Interdisciplinary Research in Public Health: Not quite straightforward. Health Prospect, 18(1), 4-7. https://doi.org/10.3126/hprospect.v18i1.19337
- Dhakal Adhikari, S., van Teijlingen, E., Regmi,P., Mahato, P., Simkhada, B., Simkhada, P. (2020) The presentation of academic self in the digital age: the role of electronic databases, International Journal of Social Sciences & Management 7(1):38-41.
- Shanker, S., Wasti, S.P., Ireland, J., Regmi, P., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2021) The Interdisciplinary Team Not the Interdisciplinarist: Reflections on Interdisciplinary Research, Europasian Journal of Medical Sciences 3(2): 1-5. https://doi.org/10.46405/ejms.v3i2.317
- Arnold, R., Gordon, C., Way, S., Mahato, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2022) Why use Appreciative Inquiry? Lessons learned during COVID-19 in a UK maternity service, European Journal of Midwifery 6 (May): 1-7. https://doi.org/10.18332/ejm/147444
- Mahato, P., Tamang, P., Simkhada, B., Wasti, S. P., Devkota, B., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E.R. (2022) Reflections on health promotion fieldwork in Nepal: Trials and tribulations. Journal of Health Promotion 10(1): 5–12. https://doi.org/10.3126/jhp.v10i1.50978
- Khatiwada, S., Gautam, P., Koju, A., Niraula, B., Khanal, G., Sitaula, A., Lamichhane, J., Regmi, P., van Teijlingen, E (2023). Patient and Public Engagement in Health Research: Learning from UK Ideas. Journal of Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences, 8(1): 28–35. https://doi.org/10.3126/jmmihs.v8i1.57268
- Thapa, R., Regmi, P., van Teijlingen, E., Heaslip, V. (2023) Researching Dalits and health care: Considering positionality, Health Prospect 21(1): 6-8.
- Harvey, O., van Teijlingen, E., Parrish, M. (2024) Using a range of communication tools to interview a hard-to-reach population, Sociological Research Online 29(1): 221–232 https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/13607804221142212


 Since the introduction of workstreams in October 2022, the Transformation team and the Research Development and Support (RDS) team have been working collaboratively on three workstreams to improve BU’s Research & Knowledge Exchange (RKE) service provision. Feedback from the academic community at BU suggested there is a need to reduce bureaucracy and to streamline processes. As part of these efforts, and with the support of IT Services, we have reviewed and improved the Intention to Bid (ItB) form. The form has been developed and tested with input from the academic community and the Business and Knowledge Exchange Managers.
Since the introduction of workstreams in October 2022, the Transformation team and the Research Development and Support (RDS) team have been working collaboratively on three workstreams to improve BU’s Research & Knowledge Exchange (RKE) service provision. Feedback from the academic community at BU suggested there is a need to reduce bureaucracy and to streamline processes. As part of these efforts, and with the support of IT Services, we have reviewed and improved the Intention to Bid (ItB) form. The form has been developed and tested with input from the academic community and the Business and Knowledge Exchange Managers.  We have developed some
We have developed some 






 We’ll be joined by four postgraduate researchers from Bournemouth University on Tuesday 7 May 6:30 – 8:00pm.
We’ll be joined by four postgraduate researchers from Bournemouth University on Tuesday 7 May 6:30 – 8:00pm.
 We are looking for 3-4 post-graduate researchers to take part in a special edition of our Café Scientifique public event series to
We are looking for 3-4 post-graduate researchers to take part in a special edition of our Café Scientifique public event series to
 Two workshops coming up in March under the Post Award pathway
Two workshops coming up in March under the Post Award pathway
 We’ll be joined by Peter Phillips
We’ll be joined by Peter Phillips 















 Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian
Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian NIHR-funded research launches website
NIHR-funded research launches website Academics write for newspaper in Nepal
Academics write for newspaper in Nepal New paper published on disability in women & girls
New paper published on disability in women & girls Global Consortium for Public Health Research 2025
Global Consortium for Public Health Research 2025 MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease