After several little hiccups in our Sonamoni research project we can now show some of the work. Sonamoni is a four-year research study led by the University of Bournemouth and the Centre for Injury Prevention Research Bangladesh (CIPRB) with the University of Southampton, the University of the West of England (UWE), the Royal National Lifeboat Institution (RNLI) and Design Without Borders (DWB) to develop a number of interventions to prevent drowning in children under the age of 2 years in rural Bangladesh. After several stages of well-planned research we worked with local communities and stakeholders to propose six interventions with the prospect of been taken further to a full community-based feasibility study.
These six interventions are being piloted in Bangladesh as I am writing this. This pilot phase is made more difficult at the moment as the country is in the ban of the forthcoming national elections. These elections are particularly challenging for the people in Bangladesh and CIPRB as the local research partner. The previous national election resulted in violent changes, and the lead up to this election has been, and still is, a difficult period.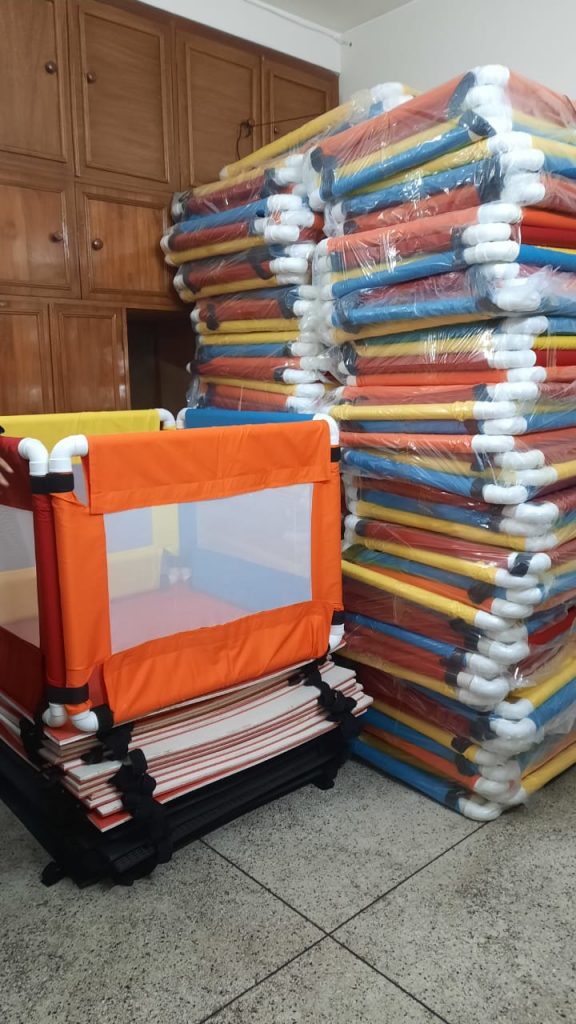
We would like to highlight one of the six interventions in a little more detail, as the Human-Centred Design approach, resulted in a neat, simple and low-cost playpen. The colourful pictures shows the first batch of flatpack playpens in the CIPRB office and some being delivered to rural villages. However, getting the first sixty developed in Bangladesh turned out more difficult than expected.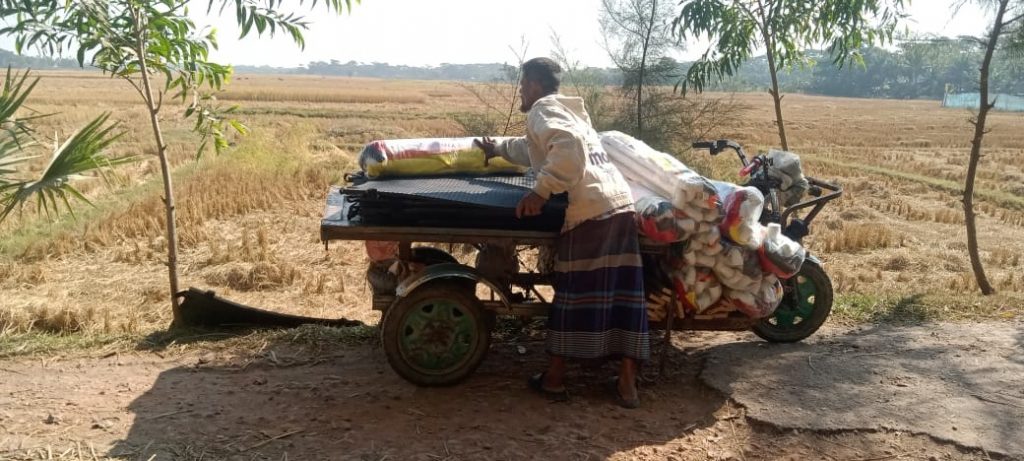  Our collagues in Bangladesh approached several small to medium-sized companies in the country with the production capabilities to produce a large number of playpens. In the end only one way interested to try and this company took much longer than agreed to produce enough for our pilot stage. The good news is that the first stage of the pilot is underway, although now we have the difficulty of forthcoming national election slowing down our research.
Our collagues in Bangladesh approached several small to medium-sized companies in the country with the production capabilities to produce a large number of playpens. In the end only one way interested to try and this company took much longer than agreed to produce enough for our pilot stage. The good news is that the first stage of the pilot is underway, although now we have the difficulty of forthcoming national election slowing down our research.
This interdisciplinary study is funded through the NIHR Research on Interventions for Global Health Transformation programme (Ref: NIHR203216). The Bournemouth University team comprises staff from across the university covering all three faculties: Dr. Mavis Bengtsson, Dr. Kyungjoo Cha, Dr. Mehdi Chowdhury, Dr. Yong Hun Lim, Mr. John Powell, and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen, and Ph.D. student Mr. Md. Shafkat Hossain. For more information about our ongoing research in Bangladesh, please visit the NIHR website.




































 Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop
Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching
UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives
SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives BRIAN upgrade and new look
BRIAN upgrade and new look Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh
Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
Explore our work, meet our partners, and find out how you can collaborate with us by clicking here! MIHERC is led by Sheffield Hallam University, with Bournemouth University as a key partner and the important funding coming from NIHR (National Institute for Health and Care Research) Maternity Challenge Initiative. The BU key academics are: Huseyin Dogan, Vanora Hundley, Edwin van Teijlingen, and Deniz Çetinkaya. Please share with all who may be interested.